Guide to Embedding Data Filters in Published Pages
When accessing or embedding HENGSHI SENSE dashboards/charts, you can add parameters to the URL to achieve similar functionality to filters within the dashboard/chart. Below are examples and detailed explanations.
Example
We use a simple dashboard to demonstrate filtering data via the URL parameter where.
First, as shown below, we created a Dashboard, using data from the movie table to create a Table chart, with the prime_genre field as a dimension and the votes field as a measure.

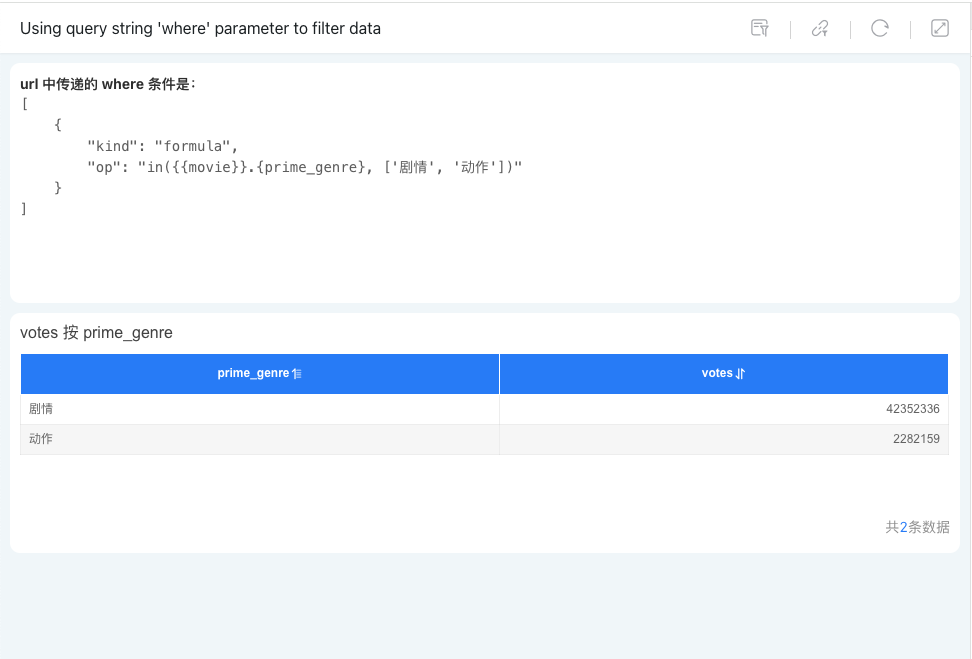
Suppose we want to filter the movie dataset to include only data where the prime_genre field value is 剧情 or 动作 in the URL of the published app or public link. We can set it as follows:
https://preview.hengshi.com/share/app/S23C1AA81F984C9822B354838730D3AF2/dashboard/1?where=%5B%7B%22kind%22%3A%22formula%22%2C%22op%22%3A%22in(%7B%7Bmovie%7D%7D.%7Bprime_genre%7D%2C%20%5B'%E5%89%A7%E6%83%85'%2C%20'%E5%8A%A8%E4%BD%9C'%5D)%22%7D%5D
The value of the where parameter is an HQL statement, decoded as follows:
[
{
"kind": "formula",
"op": "in({{movie}}.{prime_genre}, ['剧情', '动作'])"
}
]2
3
4
5
6
Opening the above link, as shown below, we can dynamically filter data by passing filter conditions in the URL.
Note
The format is {url}?where={where}. Note that the value of the where parameter needs to be JSON.stringify and URL-encoded before being passed, but the where= characters themselves do not need to be encoded. You can use the tool below to conveniently generate the URL-encoded where parameter value and complete the URL.
Using Data from Data Packs
If the chart uses data from a data pack, you need to include the data pack ID in the where condition, as shown in the example below:
[
{
"kind": "formula",
"op": "in({{movie}}.{prime_genre}, ['剧情', '动作'])"
"appId": 123
}
]2
3
4
5
6
7
URL Encoding
Result(Click to Copy)
https://preview.hengshi.com/share/app/S23C1AA81F984C9822B354838730D3AF2/dashboard/1?where=%5B%7B%22kind%22%3A%22formula%22%2C%22op%22%3A%22in(%7B%7Bmovie%7D%7D.%7Bprime_genre%7D%2C%20%5B'%E5%89%A7%E6%83%85'%2C%20'%E5%8A%A8%E4%BD%9C'%5D)%22%7D%5D
Introduction to HQL
HQL is a language for querying business data through structured data. It is HENGSHI SENSE Query Language (HQL), a proprietary computational process description language, primarily aimed at solving important problems in the field of data analysis. It provides a unified, cross-database data query language. For more details, please refer to the API Documentation.
HQL supports various data types such as Boolean, integers/floats, and strings. It also provides conditional functions like if and casewhen, as well as various operators including arithmetic, comparison, and logical operations. It supports most native SQL functions and some custom functions. Additionally, it includes built-in advanced functions for complex calculations, such as continuous activity rates, (activity/retention) rates, and year-over-year/month-over-month rates.
Data Types
HQL's data types are defined as follows:
- Boolean, with 2 values:
trueandfalse. null, a special keyword indicating a null value. Like SQL and other database languages, it is case-insensitive, sonullis the same asNull,NULL, or variants.- Numbers (Integer/Number), either integers or floats, e.g.,
42or3.14159. - Strings, a sequence of characters representing text values, e.g.,
"Howdy".
Conditional Judgment
Conditional judgment refers to executing specific statements based on the result (true or false or predefined) of a specified condition. HQL supports two conditional judgment functions: if and casewhen.
if
The if function returns a value based on a condition, with the following syntax:
if(condition, trueValue, falseValue)The if function has an alias with the same usage: ifelse().
casewhen
The casewhen function returns a value based on a condition, with the following syntax:
casewhen(value1, condition1, value2, condition2, ..., valueOfElse)Operators
HQL includes the following types of operators:
- Parentheses:
(), also known as grouping operators. - Not in:
not in - Exponentiation, Modulus:
^,% - Multiplication, Division:
*,/ - Addition, Subtraction:
+,- - Comparison Operators:
>=,<=,=,!=,<> - Logical Operators:
or,and
Expressions
Expressions are a collection of code used to compute and return a value. HQL supports the following types of expressions:
- Variables: Supports 4 types: Dataset, Field, Parameter, User Attribute, e.g.,
{{datasetNameOrId}},{fieldName},{{%parameterName}},{{$userAttributeName}}. - Strings: Results in a string, e.g.,
"Fred"or"234". Typically uses string-related functions likeconcat('Fr', 'ed'),concat('2', '34'). - Arithmetic: Results in a number, e.g.,
42,3.14159. Typically uses arithmetic operations like{number_field_a} + {number_field_b}. - Logical Values: Results in
trueorfalse, e.g.,if(42 > 3, true, false). - Basic Expressions.
Writing HQL Filter Conditions
Suppose there is a price numeric field in the dataset, and you want to filter data where the value is greater than 20. You can write the following HQL filter condition:
where = [
{
"kind": "function",
"op": ">",
"args": [
{
"kind":"field",
"op": "price",
},
{
"kind": "constant",
"op": 20
}
]
}
]2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Alternatively, it can be abbreviated as:
where = [
{
"kind": "formula",
"op": "{price} > 20"
}
]2
3
4
5
6
Suppose there is a time date field in the dataset, and you want to filter data where the time is greater than 2018-12-31. You can write the following HQL filter condition:
where = [
{
"kind": "function",
"op": ">",
"args": [
"time",
{
"kind":"constant",
"op":"2018-12-31",
"type": "date"
}
]
}
]2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Or you can use the formula shorthand as:
where = [
{
"kind": "formula",
"op": "{time} > '2018-12-31'"
}
]2
3
4
5
6
HQL's functions and operators are very rich, capable of meeting various complex filtering conditions. For specific functions, please refer to the HQL Function List.