Complex Reports
Complex reports integrate various native Excel editing capabilities and formula configuration capabilities, supporting multi-data source access. Through visual drag-and-drop and configuration, users can quickly implement complex Chinese-style reports with intricate layouts and calculations within the Excel interface. Additionally, complex reports are deeply integrated with the platform's original analytical capabilities, supporting data update synchronization, data filtering linkage, data row and column permission control, and embedded scenario analysis.
Complex reports have the following advantages over ordinary tables:
- Multi-data source: Complex reports can analyze and display data from multiple data sources, which can come from one database or multiple databases.
- Diverse styles: The headers of complex reports support dynamic expansion, diagonal headers, and other styles. Fields can be grouped and expanded by rows and columns, enabling various forms of reports such as grouped reports and detailed reports.
- Complex calculations: Both row and column fields in reports can use advanced calculations provided by HENGSHI SENSE, as well as Excel formula functions for calculations.
Create a Complex Report
In the dashboard, click on New Chart -> Complex Report, select the data source and dataset, and click OK to create a new blank complex report. 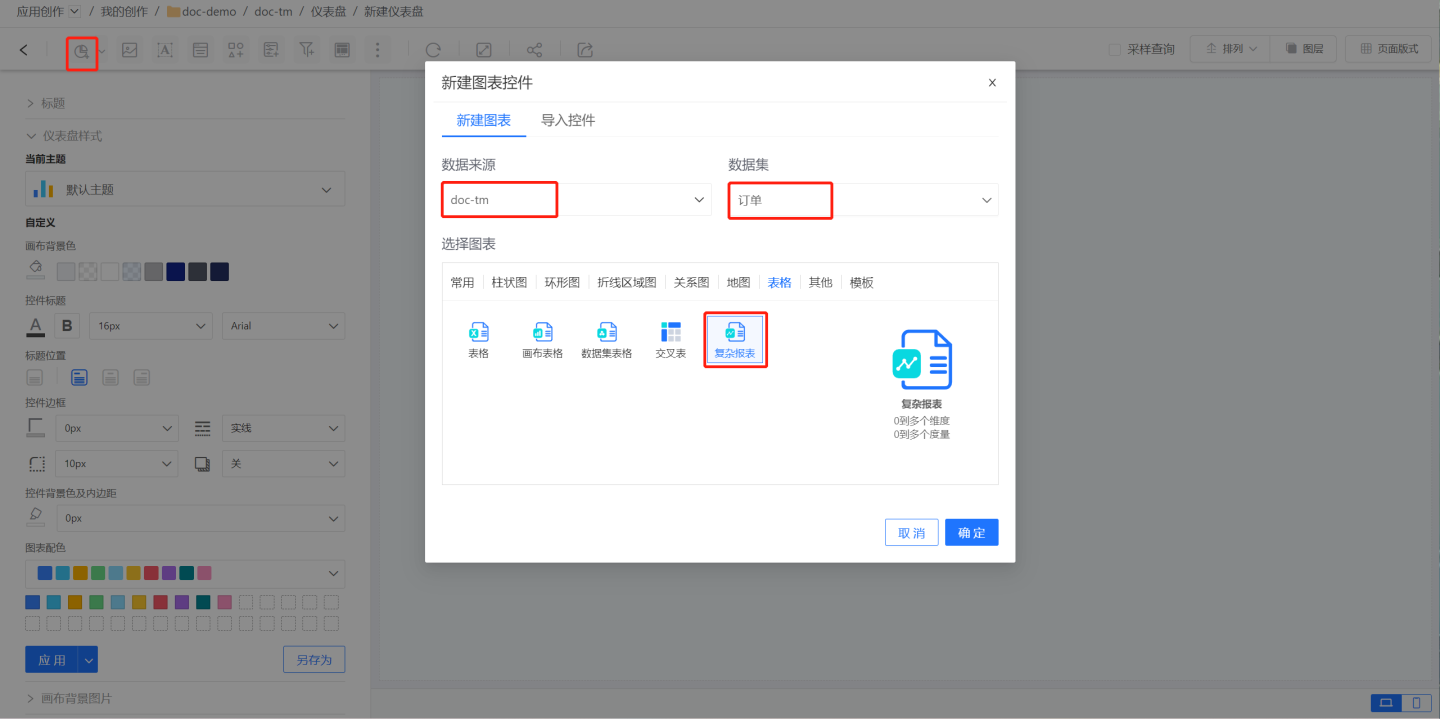
The newly created complex report contains no data. Unlike other reports, a complex report needs to be opened for editing. Click on the three-dot menu in the upper right corner to open the complex report and enter the editing page. 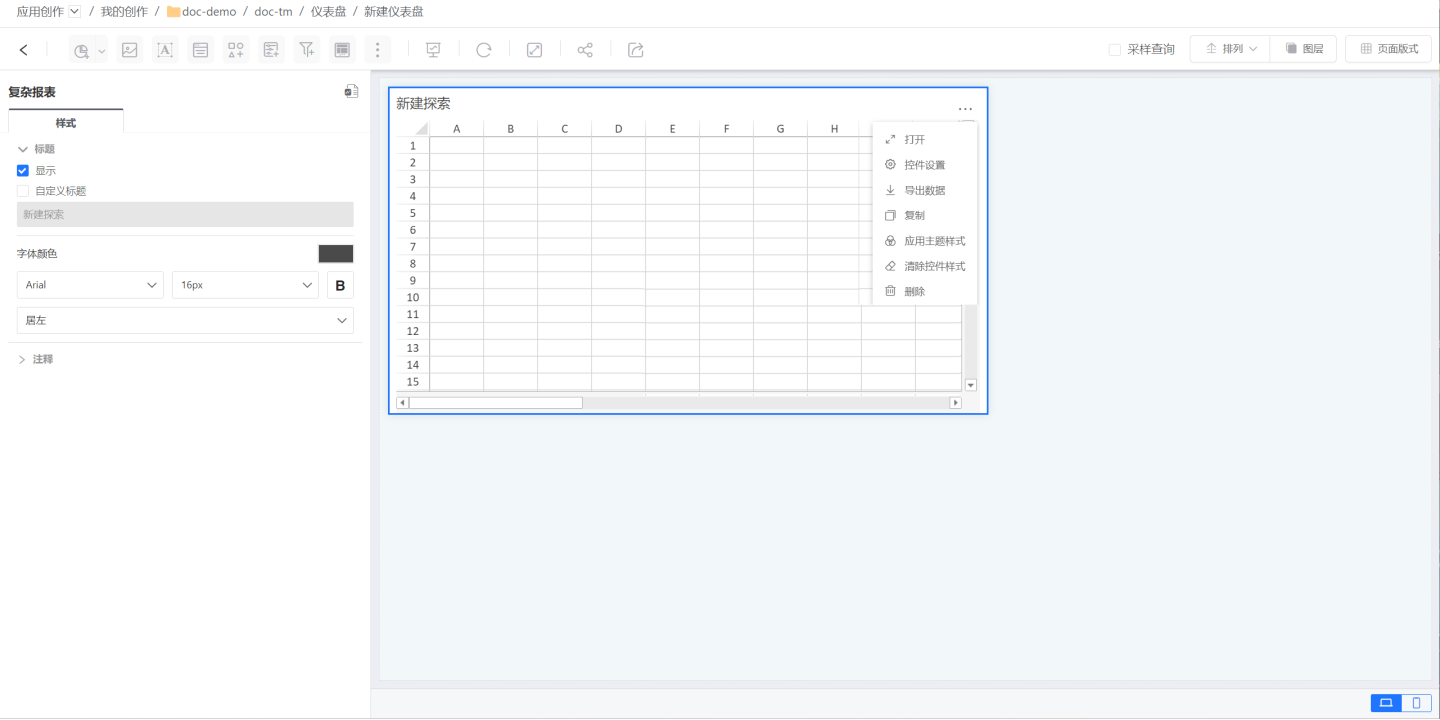
Editing Complex Reports
The complex report editing page is divided into three sections. The leftmost section (red box) is the data area, displaying the data used in the complex report. The middle section (blue box) is the configuration area, primarily for configuring report-related data and data display formats. The right section is the cell area, where you can set cell properties and cell styles. After completing the complex report editing, click the preview button in the upper right corner to view the report display style. 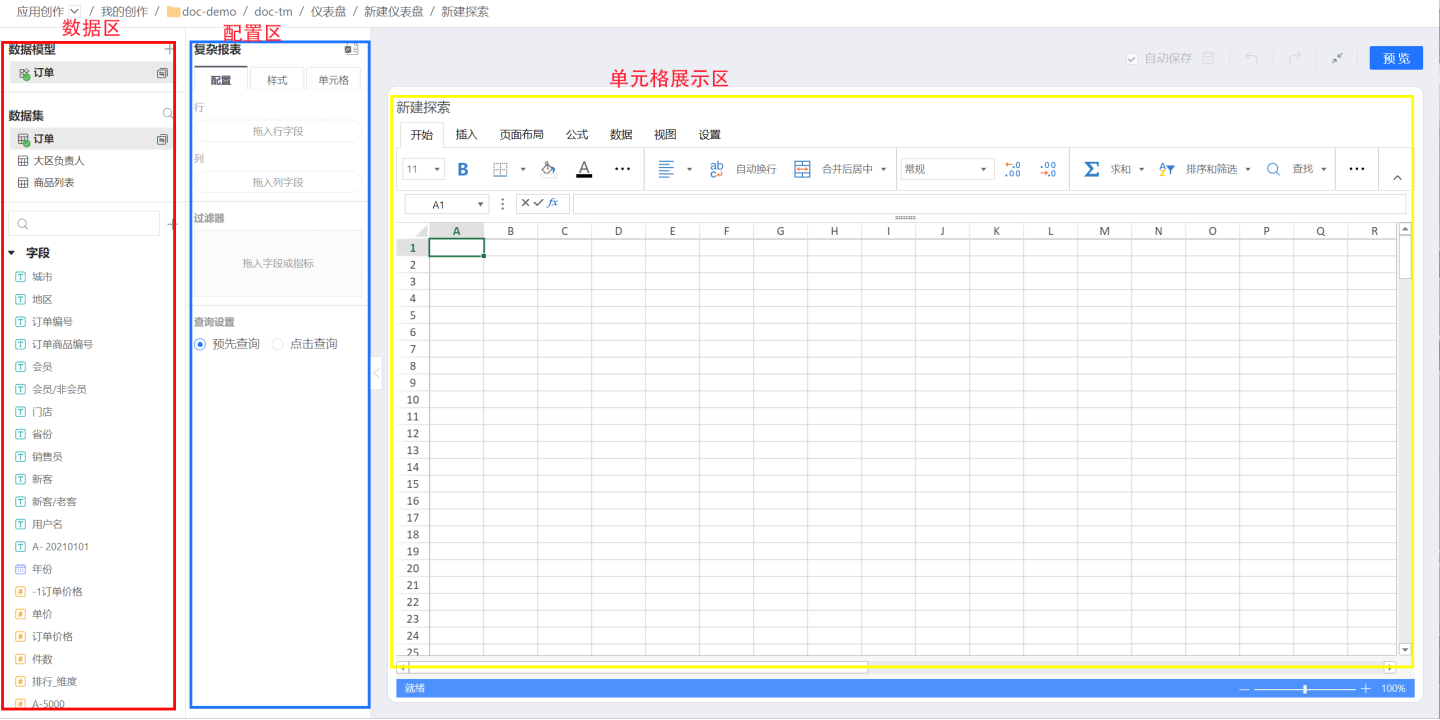
Row and Column Data Display
When displaying data in cells, it is divided into two steps. First, select the display position of the data in the table, such as selecting a specific cell, and then drag the fields that need to be displayed to the row or column display area.
In the example, first select cell A3, and then drag the City field as a row field. The field will be displayed in rows. 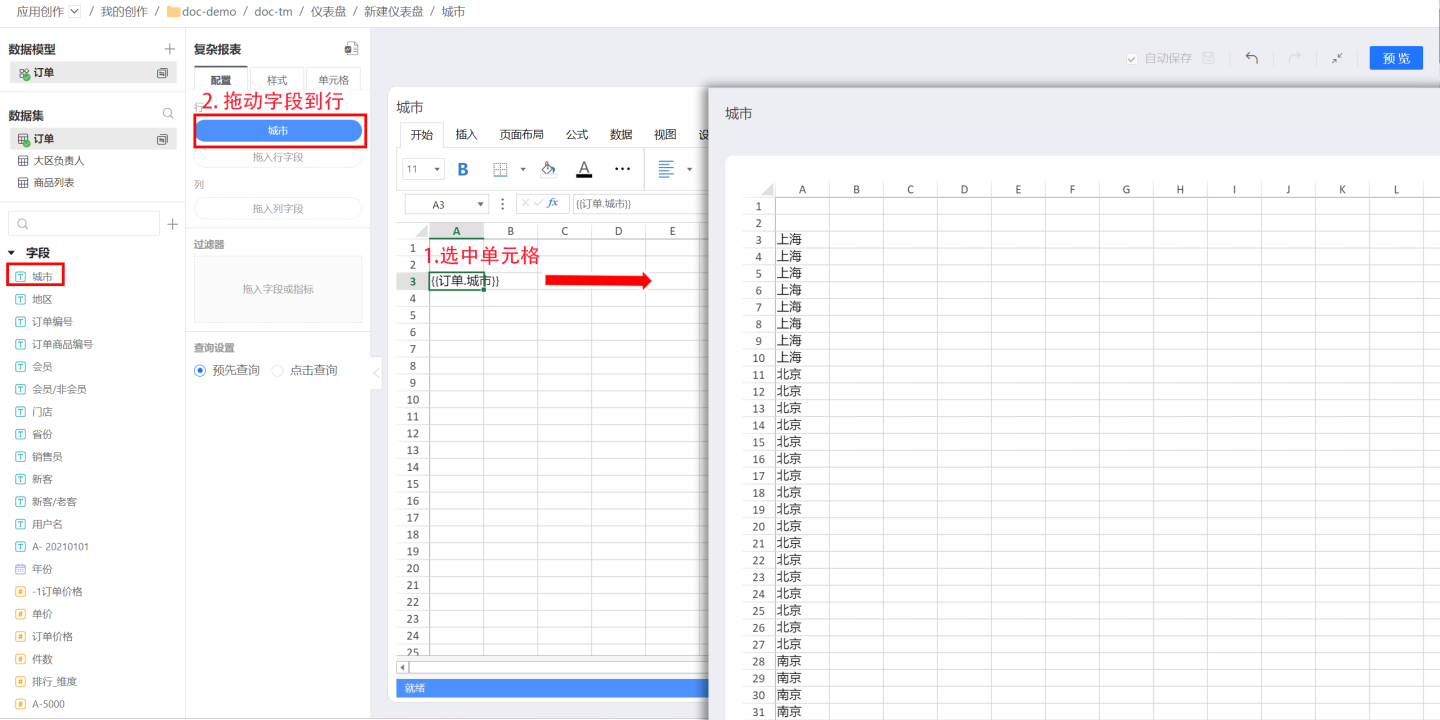 When dragging the
When dragging the City field as a column field, the field will be displayed in columns. 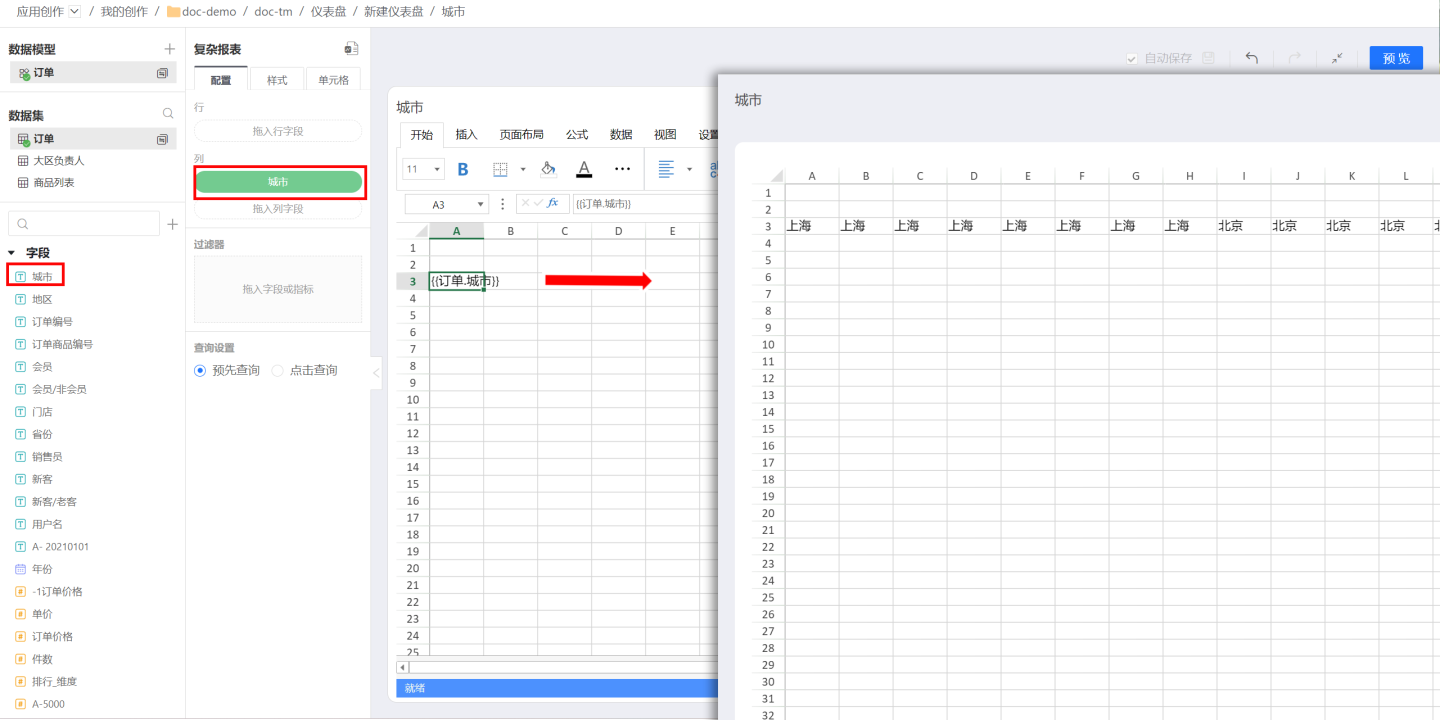
Detailed Data When dragging a field directly into a row or column, detailed data information is displayed. Detailed data is the specific data in the dataset. If you want to display aggregated data information, you can set up grouping for the field.
Aggregated Data After dragging a field into a row or column, select grouping in the calculation to achieve aggregated data display. For example, setting up grouping for cities will display the results as follows.
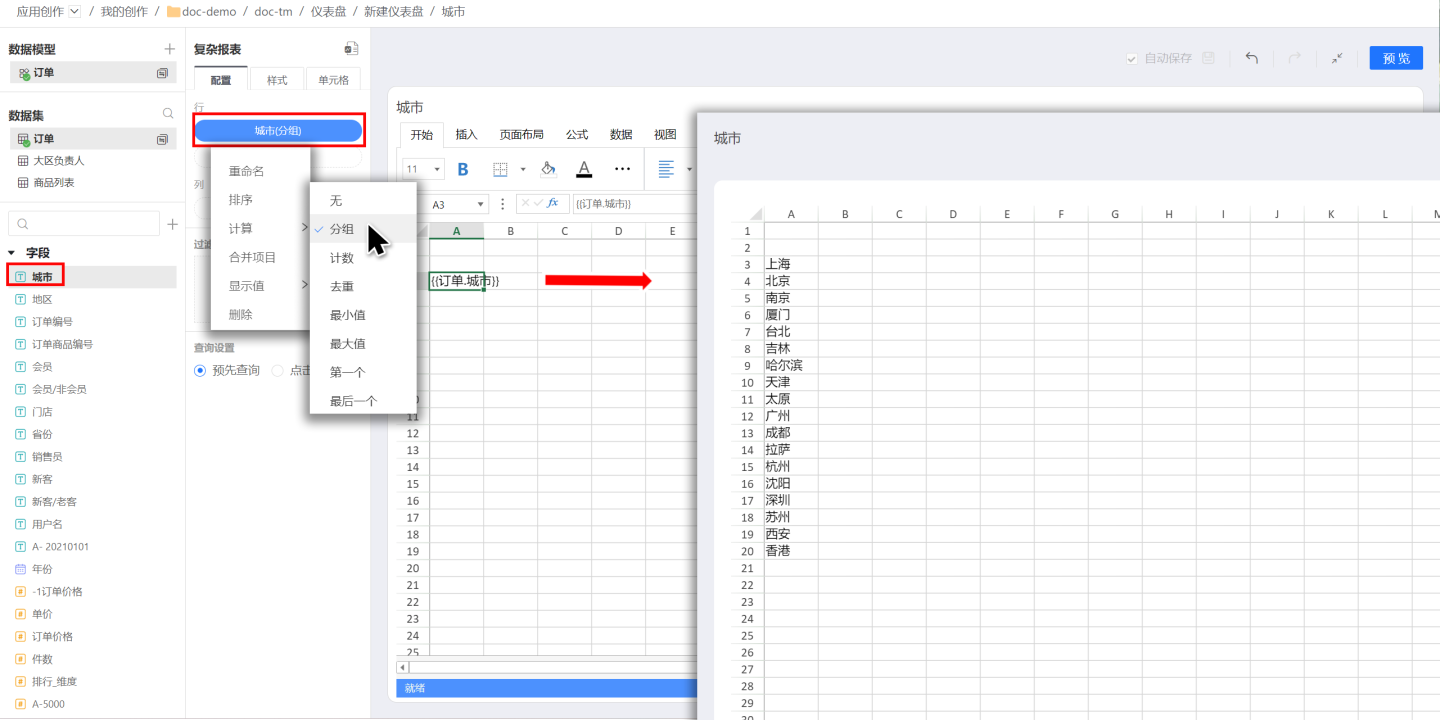
Tips
- When "cutting-copying" a cell with configured data in the cell area, the configured data and its dependencies can be carried over. As shown in the figure, cutting cell A3 and then copying it to cell A8 will also display the corresponding configured data in cell A8.
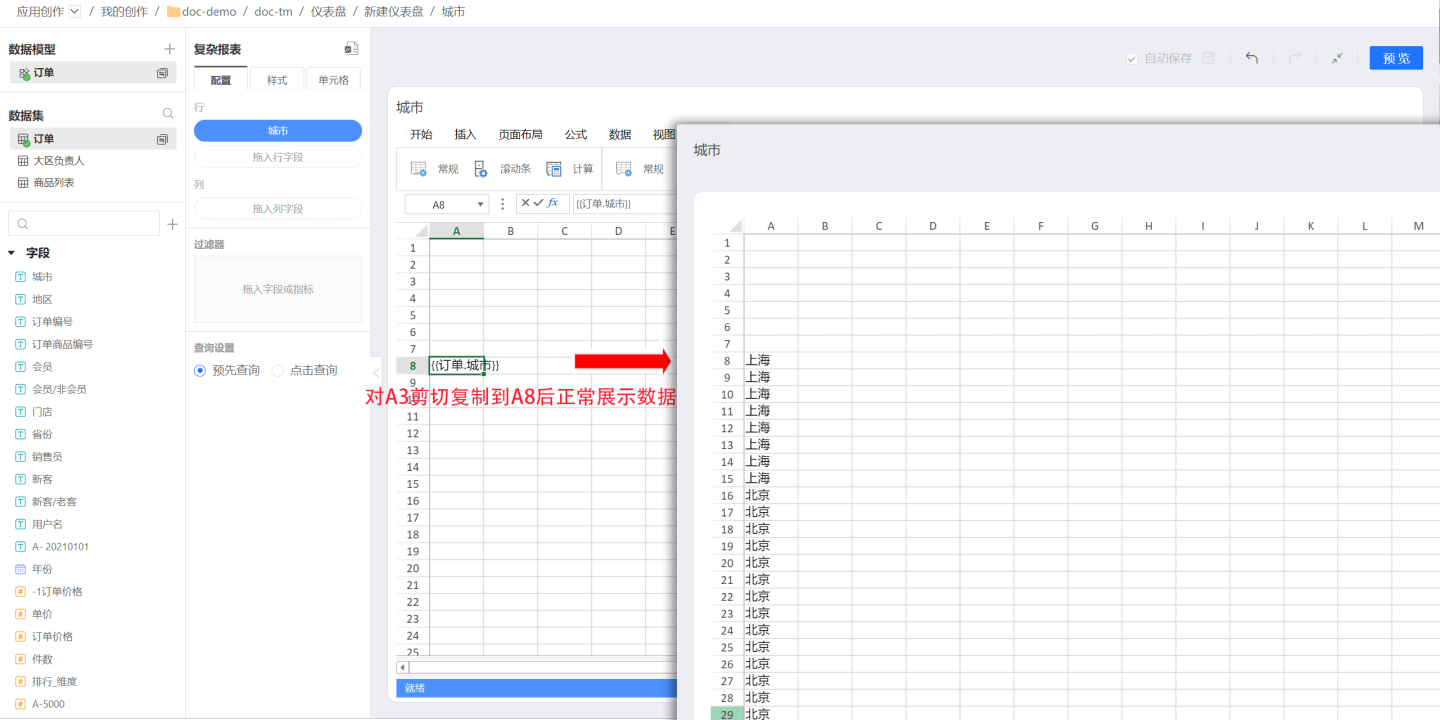
- There is a one-to-one mapping relationship between fields and their bound cells, allowing for quick association between the two. When clicking on a field, the bound cell is highlighted, and vice versa.
Group By
Field Grouping Basis
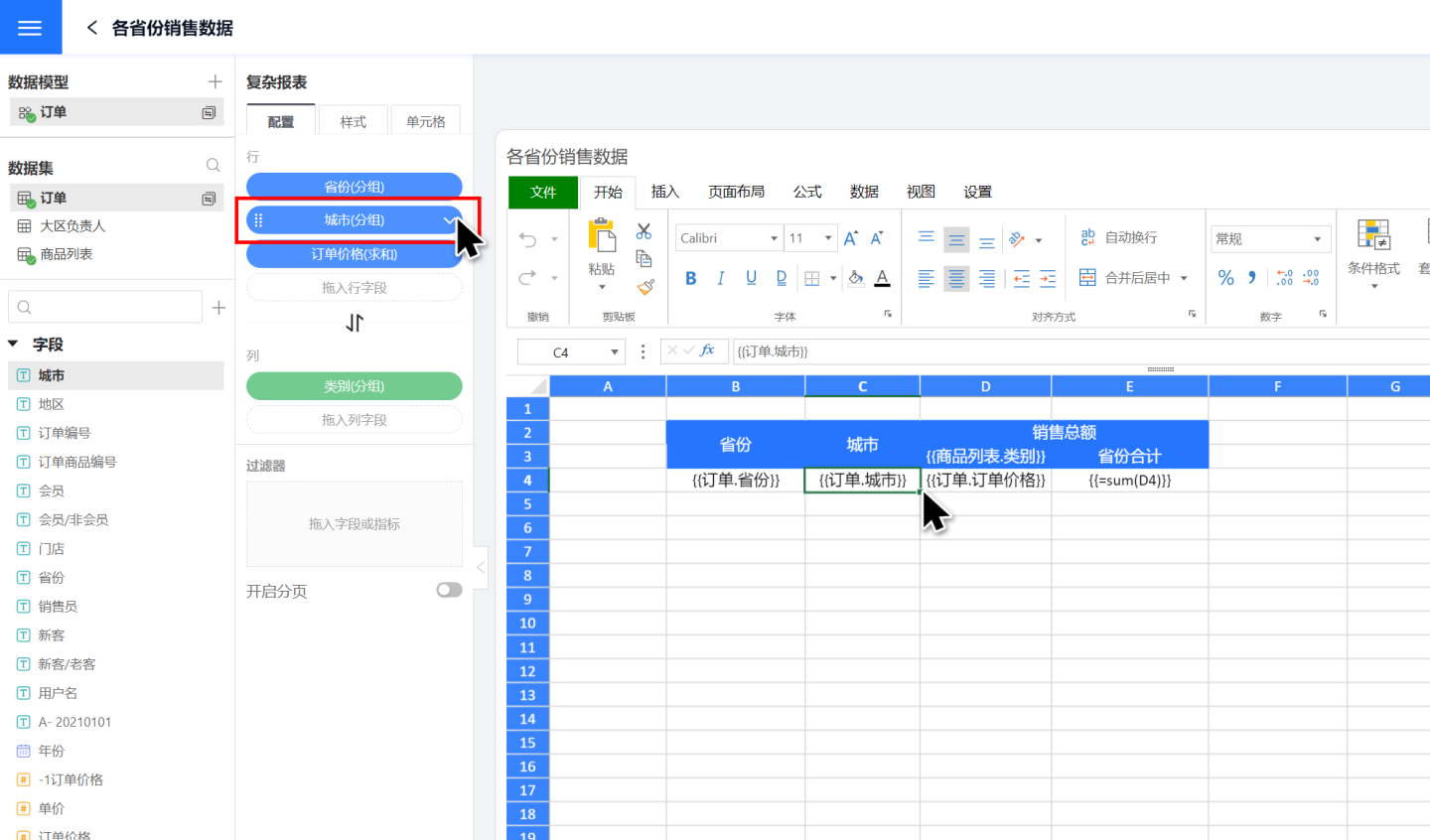
When fields are dragged into complex reports for row and column data display, they are not associated with other fields. Multiple fields from the same dataset or data model are displayed independently without bringing in the corresponding relationships from the dataset. As shown in the figure, dragging in the fields for province and city, they are not related and are displayed randomly. In fact, cities and provinces have corresponding relationships, such as Hangzhou belonging to Zhejiang Province and Guangzhou belonging to Guangdong Province. They need to be displayed accordingly.
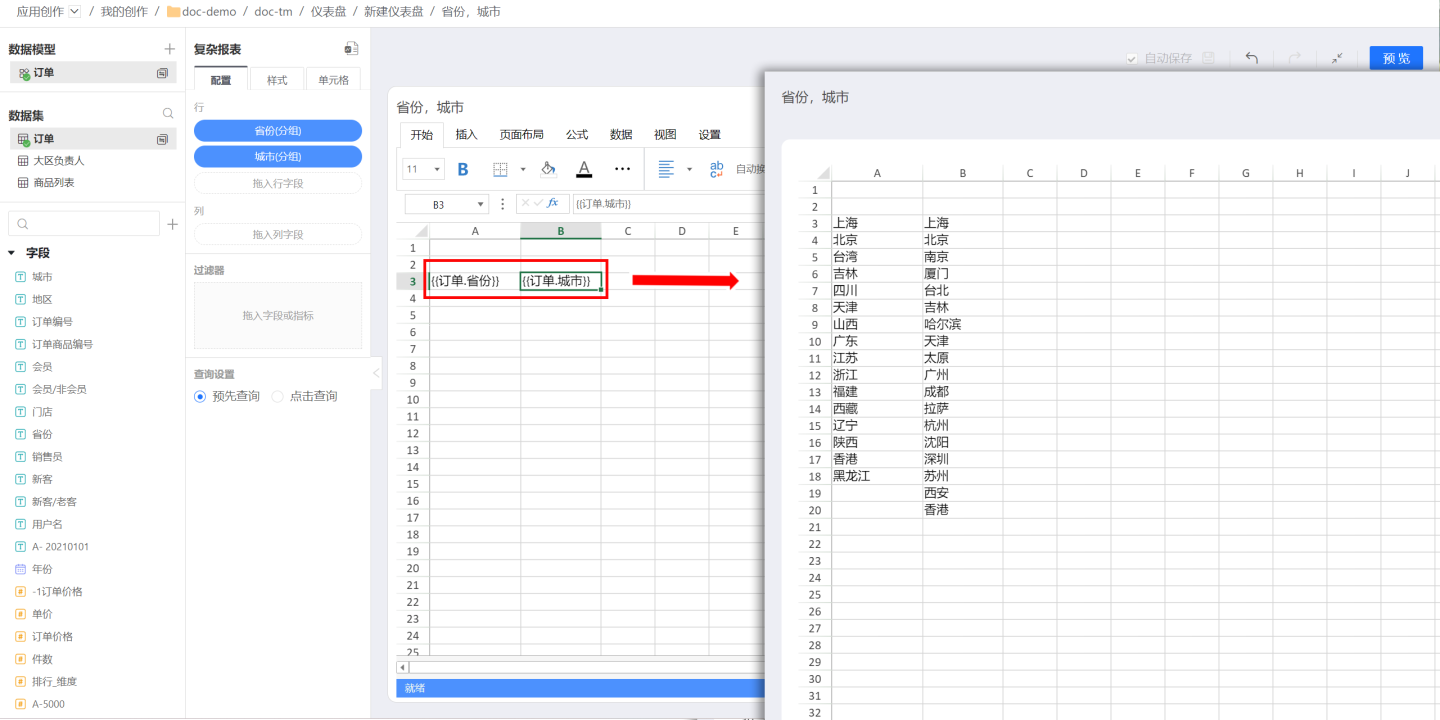
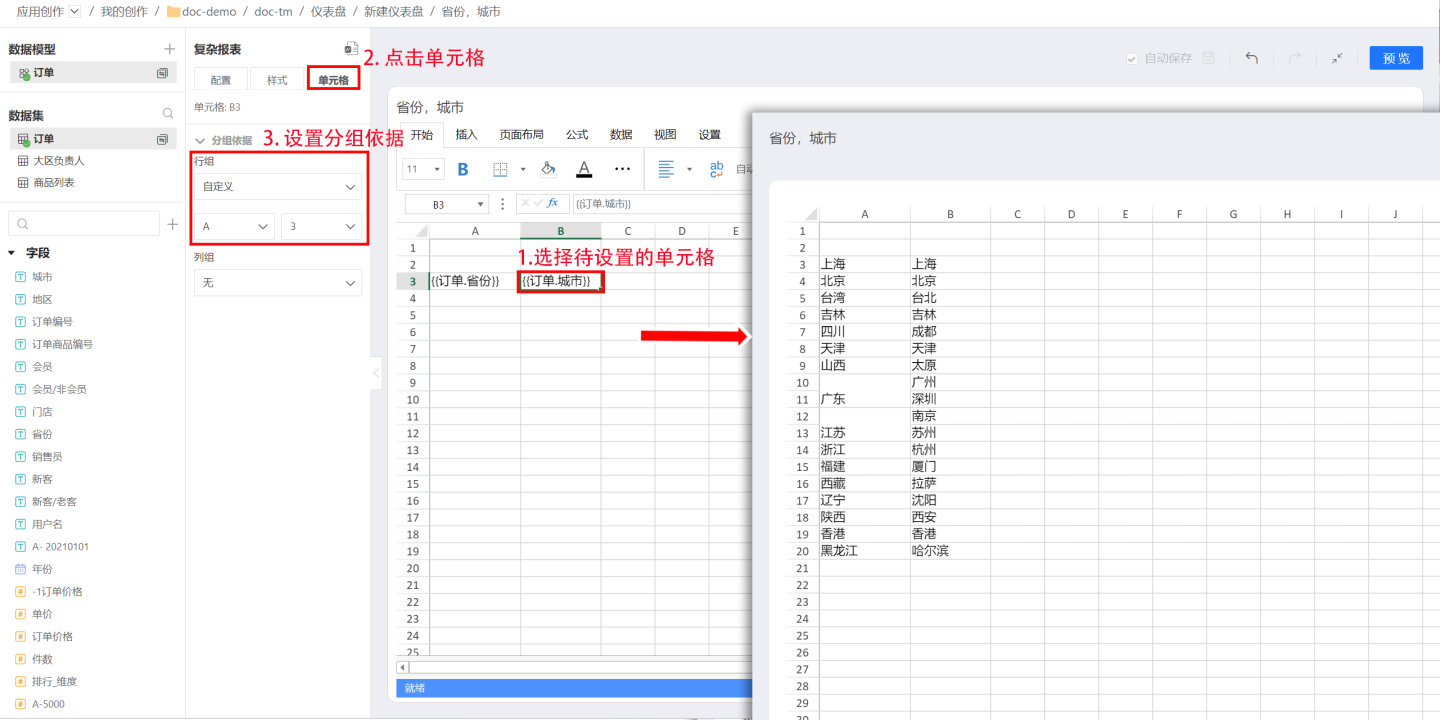
In complex reports, grouping basis is used to establish a relationship between two fields. First, select the cell to be set, then set the grouping field for the field in the configuration area on the left. After successful setup, the field in the cell will be displayed based on the grouping field. For example, to display cities by province, first click the cell where the city field is located, then click the cell in the configuration area on the left, and select to group by row group A3 (A3 is the cell where the province field is located) in the grouping basis. When displaying data, the city field will be grouped and displayed by province.
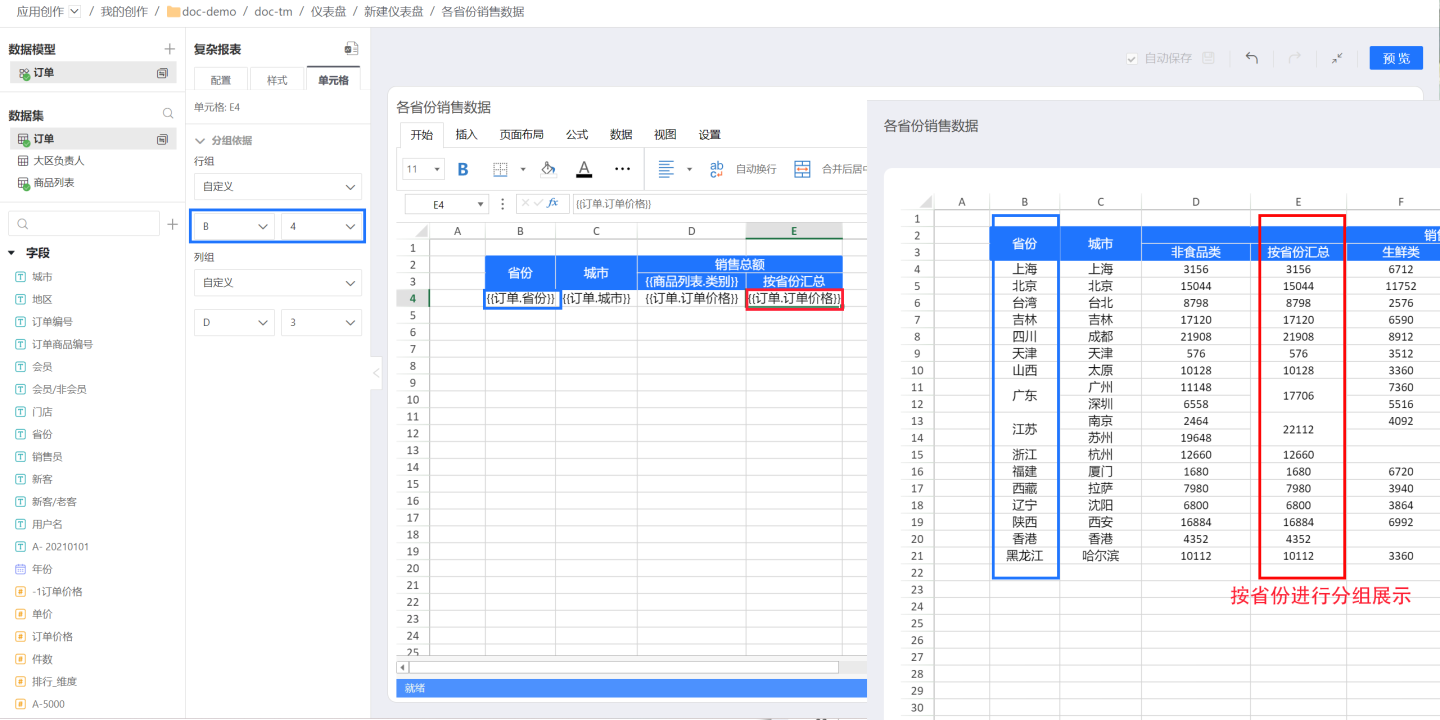
In the above example, grouping is displayed by row group. Complex reports also support grouping display by column group. In some complex cases, it may be necessary to group by both row group and column group. For example, in a sales report of a large supermarket's stores in various cities, the sales amount is displayed by product category. Therefore, to calculate the order price, i.e., the sales amount (yellow box), group by C4 (blue box) in the row group direction, i.e., display by each city, and group by D3 (red box) in the column group direction, display by product category. The final data display result is as shown in the yellow box on the right. 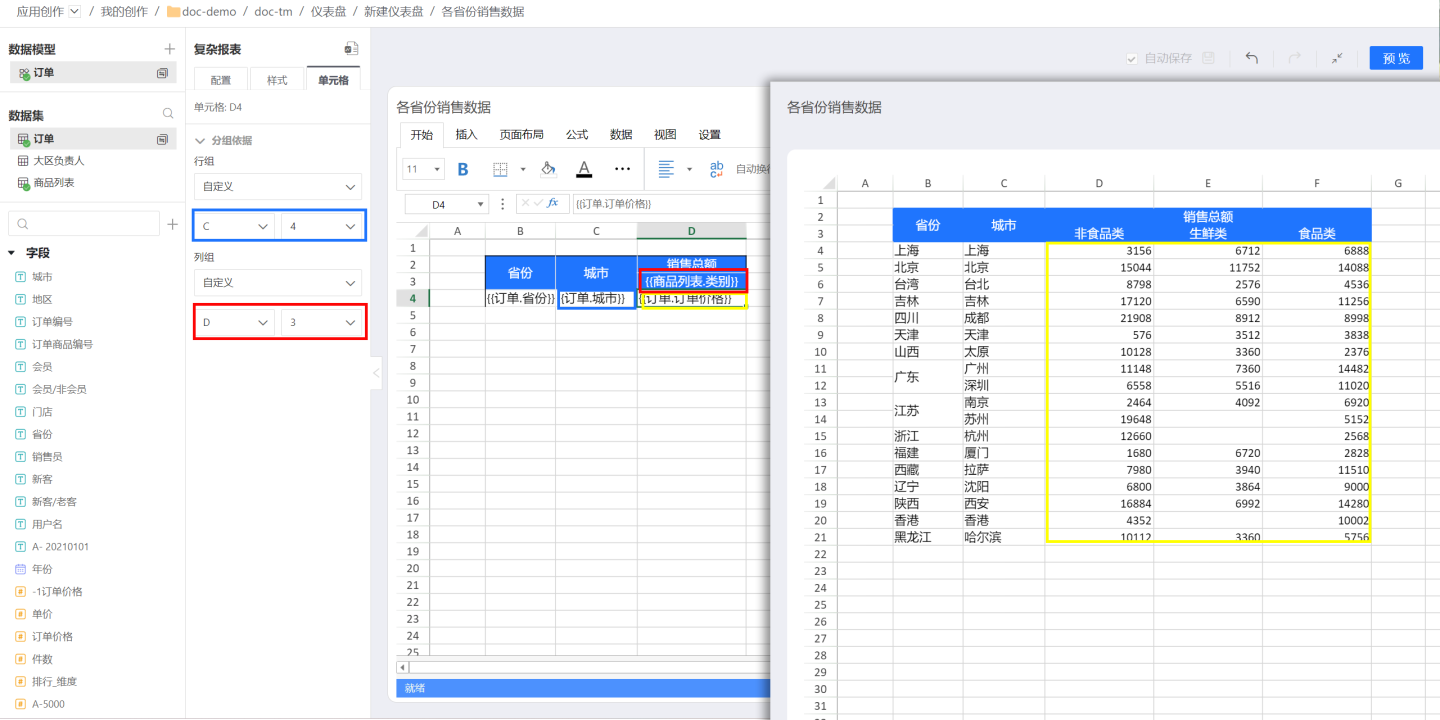
Tip
- The selection of grouping basis does not necessarily have to be adjacent cells, any cell in the current complex table can be used as a grouping basis.
- Complex reports support selecting cells to the left and above as grouping basis. For example, the cell E4 can only set A(1-4), B(1-4), C(1-4), D(1-4), E(1-3) as grouping basis, cannot select columns after F as grouping basis, cannot select rows below 5 as grouping basis, and cannot select itself as grouping basis.
Text Grouping Basis
In some cases, text content in complex tables also needs to be grouped based on settings and associated with other fields, expanding as other fields expand.
As shown in the figure, in the sales data of various provinces, 'Total Sales' and 'Province Total' are text information, but D3{{Product List.Category}} in the header is a field that will expand based on the field content, so 'Total Sales' and 'Province Total' will also change as {{Product List.Category}} expands.
First, let's look at 'Total Sales', which will expand horizontally as {{Product List.Category}} expands, so in the expansion direction, it is set to horizontal expansion.
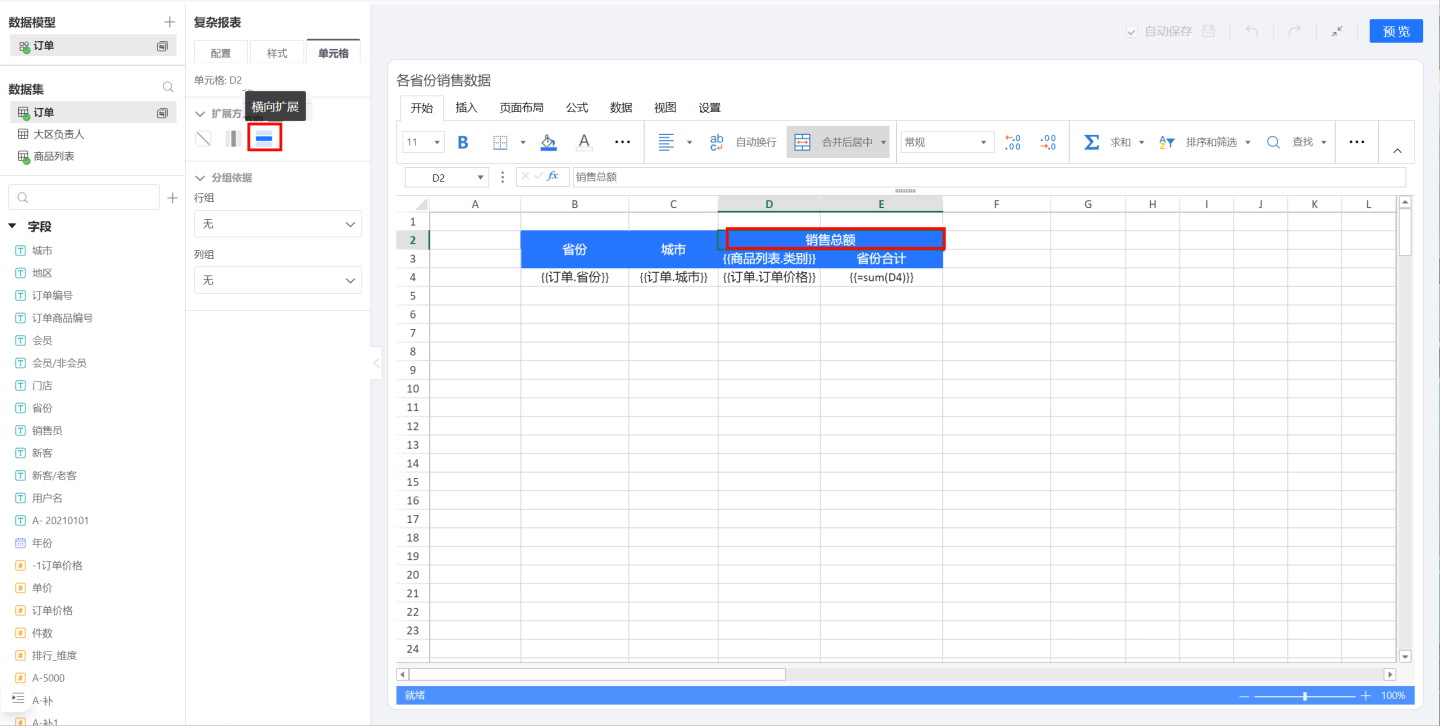
Next, let's look at 'Province Total', which will expand with {{Product List.Category}}, such as having a province total for fresh produce, a province total for food, etc. Therefore, 'Province Total' should be grouped by {{Product List.Category}}.
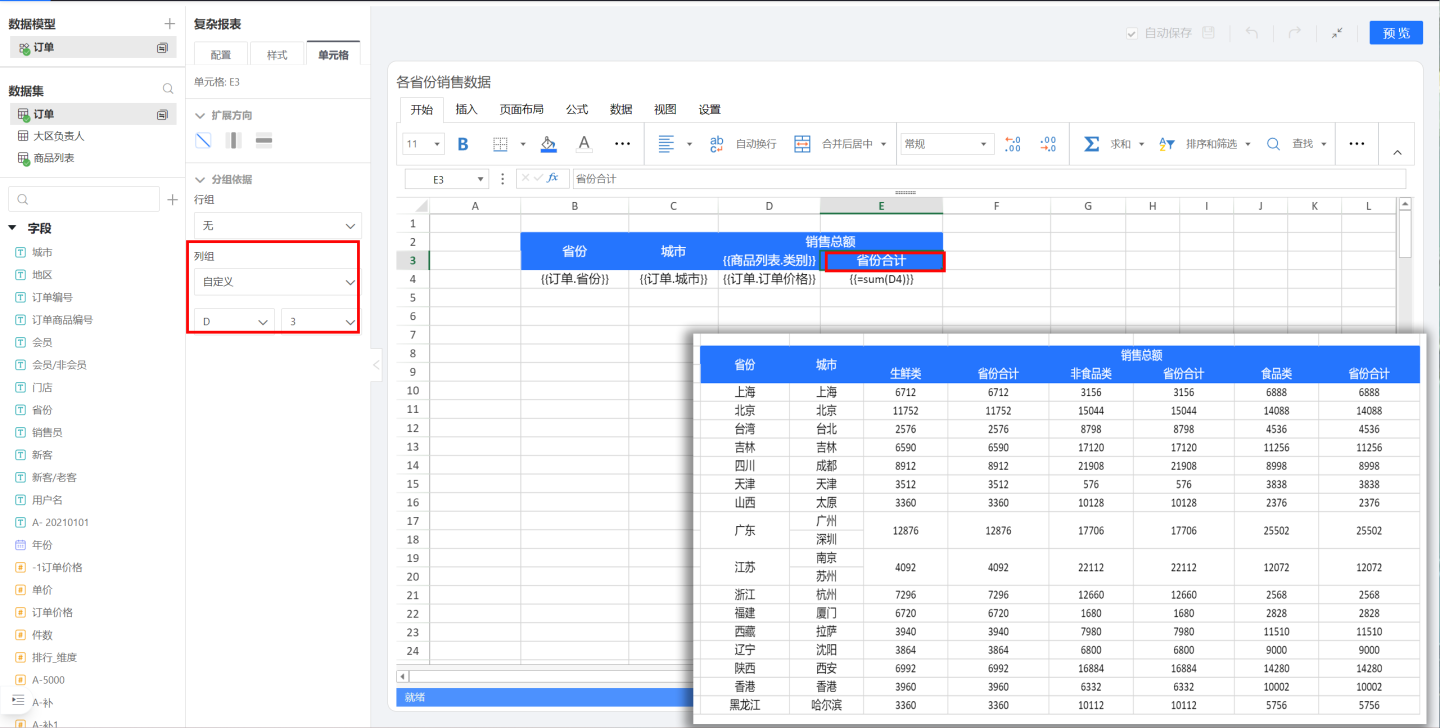
The dynamically expanding field {{Product List.Category}} should be displayed within the range of the 'Total Sales' cell, so the grouping basis of {{Product List.Category}} should be set to D2, establishing a connection with 'Total Sales'.
Data Calculation
The fields in complex reports inherit HENGSHI's original calculation capabilities, supporting various advanced calculations, and also allow the use of Excel formula functions for calculations.
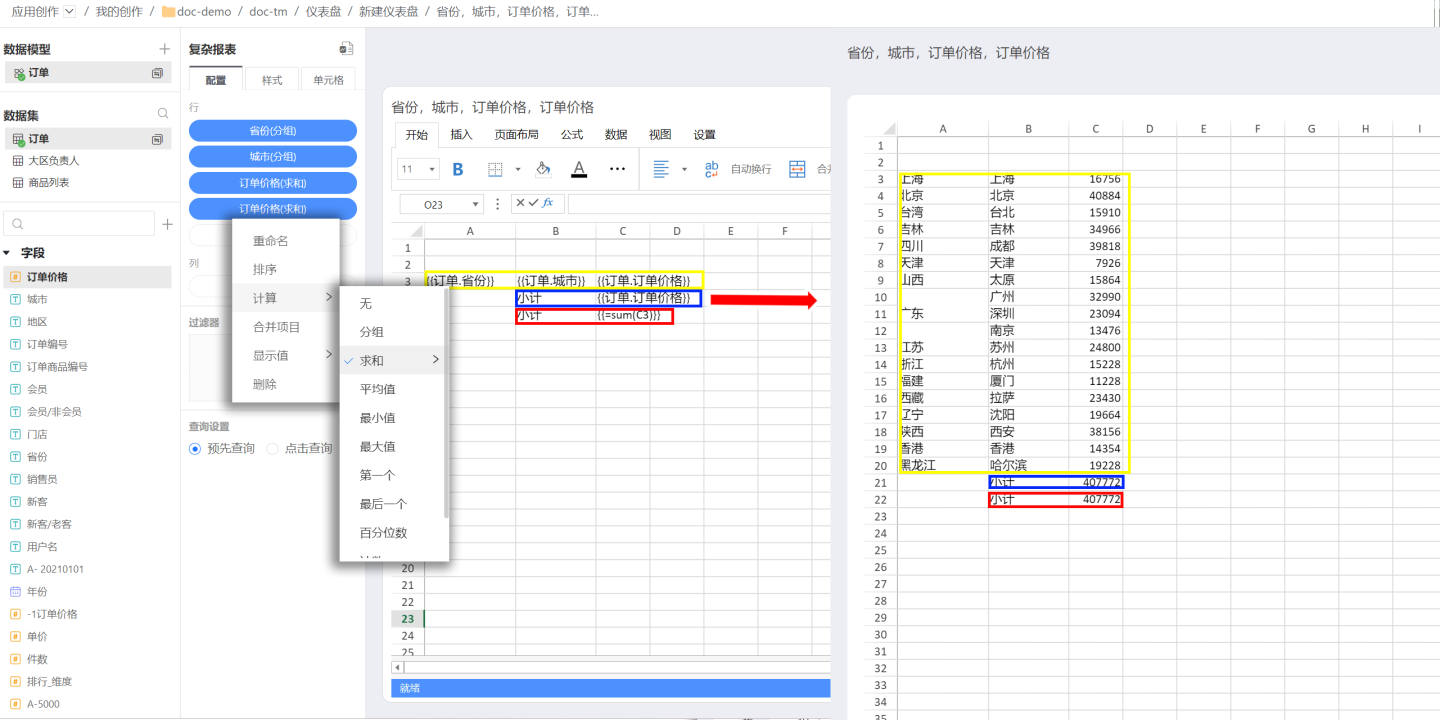
As shown in the complex report displaying sales data for various cities (highlighted in yellow in the image), it is necessary to calculate the total sales data for each city. At this point, you can use HENGSHI's built-in calculation capabilities (highlighted in blue) or use Excel's sum function for calculation (highlighted in red).
Tips
- When using Excel functions, if you are calculating fields configured in a cell, the function formula needs to include
{{}}, and the formula will apply to all data expanded from the cell fields. If you are only calculating a single cell value, there is no need to include{{}}. - The standard Excel functions supported by complex report fields are Sum, Count, Average, Max, Min, Product, StdDev, StdDevp, Var, and Varp. Other functions are not currently supported.
Multi-source Complex Reports
Unlike other charts, complex reports support the simultaneous display and analysis of multiple data sources, which can come from the same database or from multiple different databases.
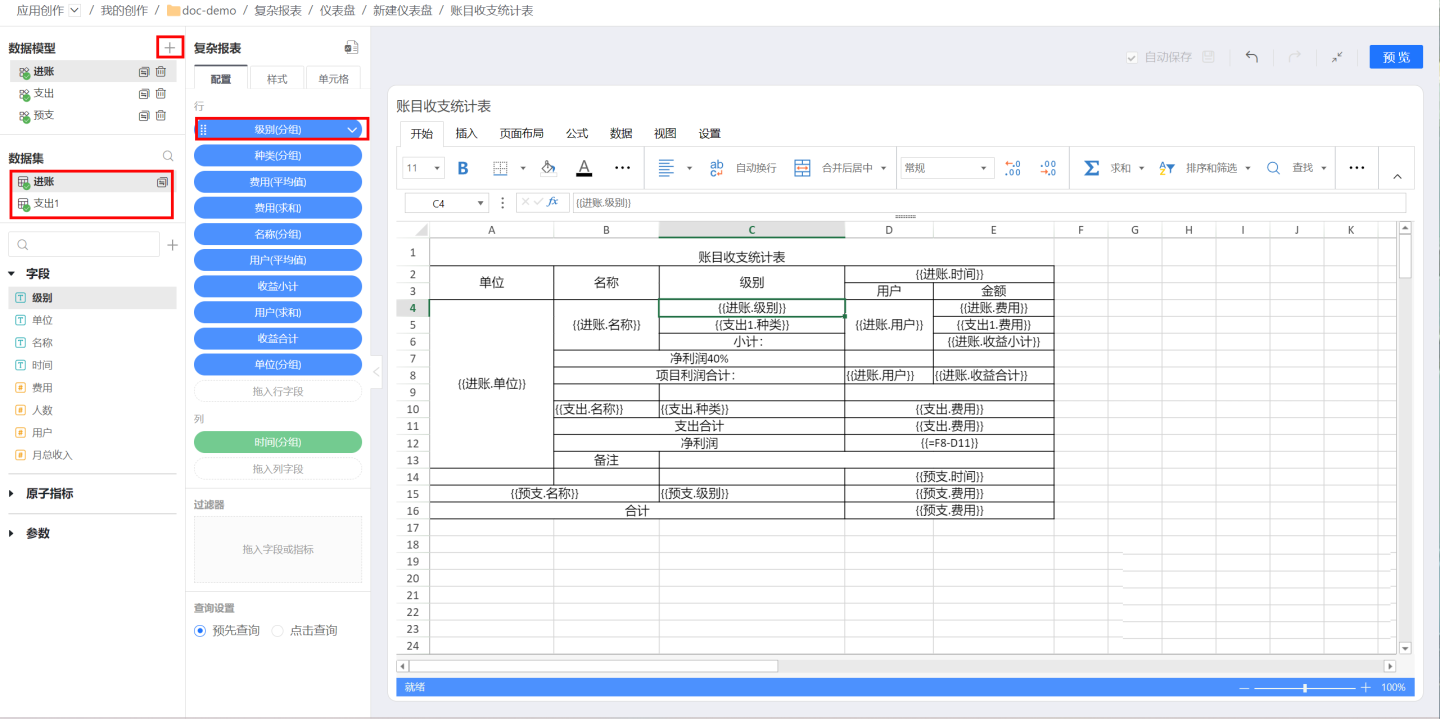
As shown in the figure, click the + sign on the right side of the data model to add new data. The configuration table on the left only displays the field configuration information related to the selected data model. For example, if the Income model is currently selected, it shows the fields used in the Income model. To configure or view the fields used in the Expense model, you need to click the Expense model and switch to the expense model to select field configurations.
Header Display
The headers of complex reports can be divided into static headers and dynamic headers from the perspective of change. Static headers do not contain field information of configured data and will not change once set. Dynamic headers contain data field information and will change as the fields expand. Below are examples of both types of headers.
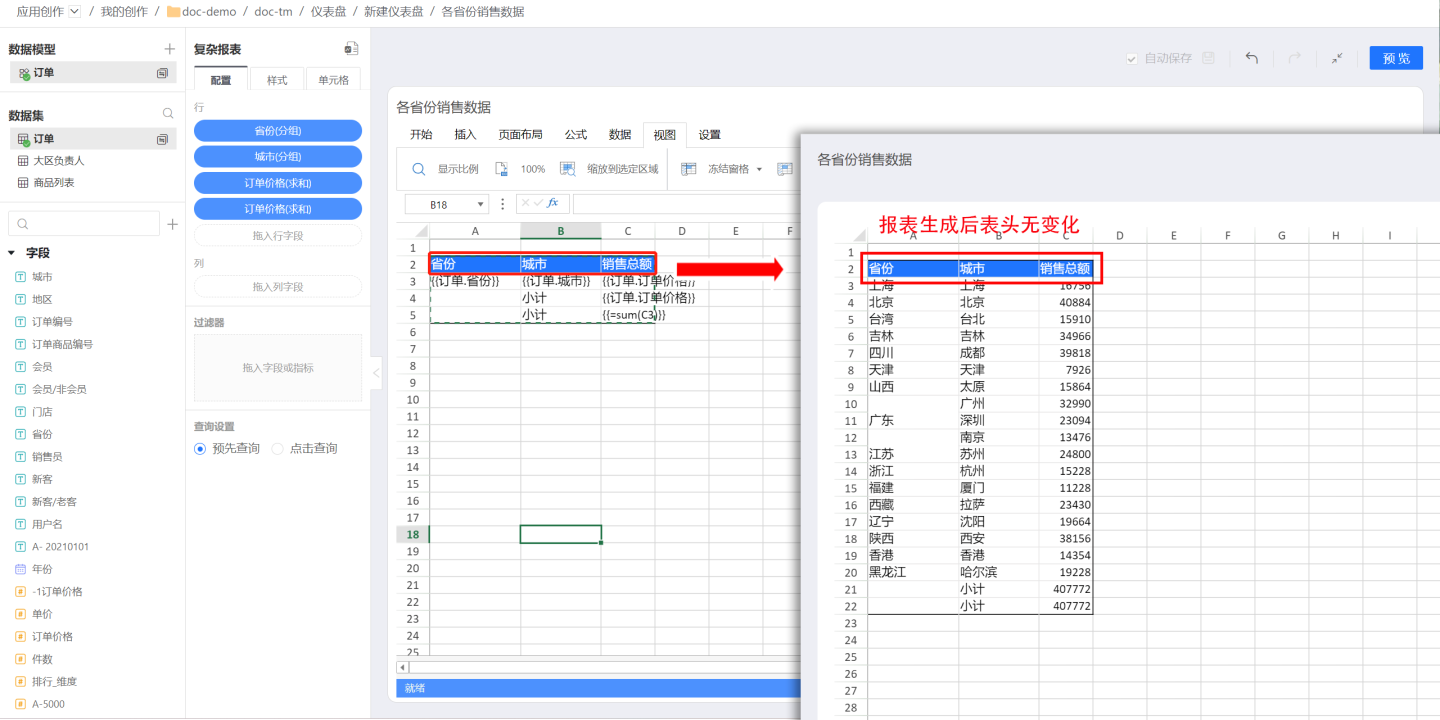
Static Header
The static header consists of plain text information and does not contain field information, so it will not dynamically expand. The number of cells in the header is fixed. As shown in the figure, the header of the sales data report for various cities is composed of three columns: Province/City, City, and Total Sales during editing, and only these three columns are present when the report is generated.
Dynamic Headers
Dynamic headers refer to headers that contain field information, and the headers will change as the fields expand. For example, in a sales data report for various cities, it is necessary to display sales data for different types of products. Therefore, the product category field is dragged into the header cell. This field will dynamically expand according to the product category when generating the report, and the corresponding upper-level title "Total Sales" will also dynamically expand with the product category. This type of header is called a dynamic header. 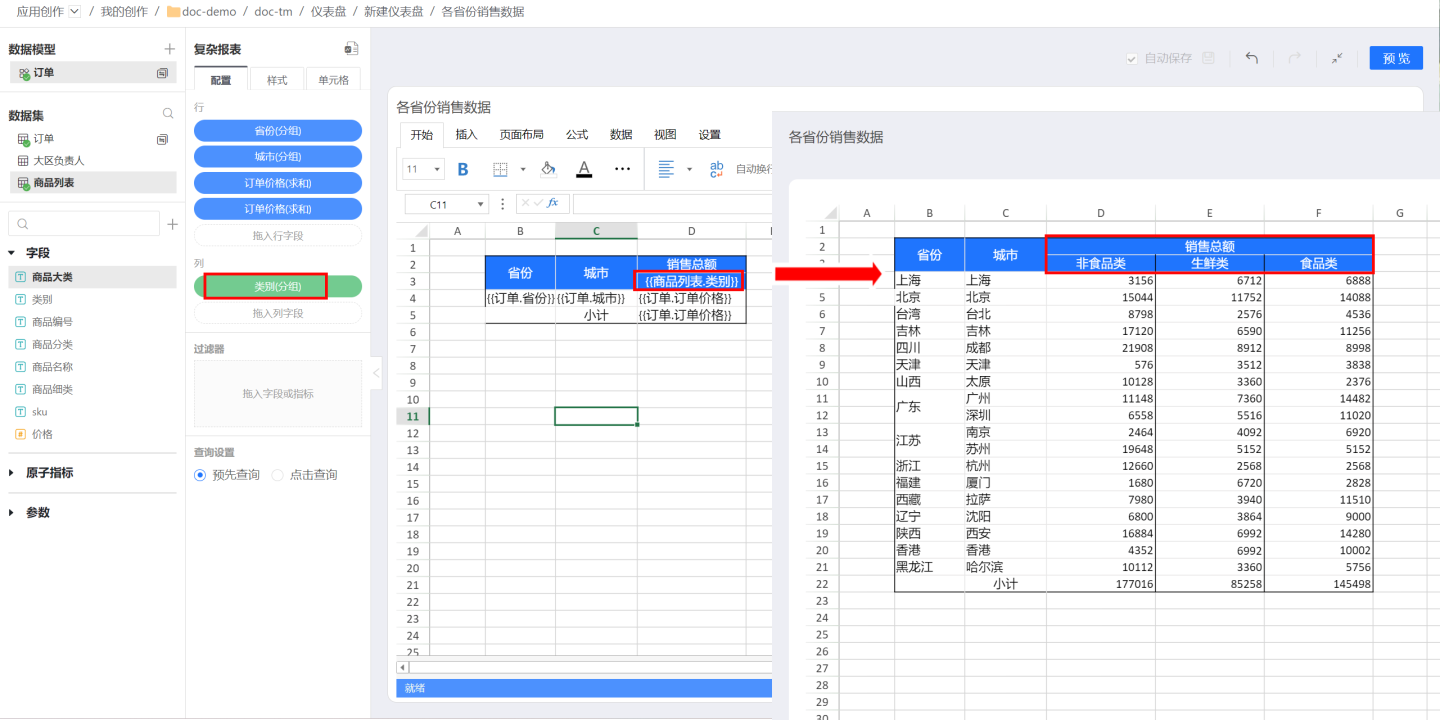
In dynamic headers, attention should be paid to the grouping basis of the fields. If the field is at the top level, it will not be restricted by other cells when expanding. If there is other text information above it, as in the example, the dynamically expanding field {{Product List.Category}} must be within the scope of the 'Total Sales' cell. Therefore, the grouping basis of {{Product List.Category}} should be set to D2 to establish a connection with 'Total Sales'.
Complex Report Interaction
Image Settings
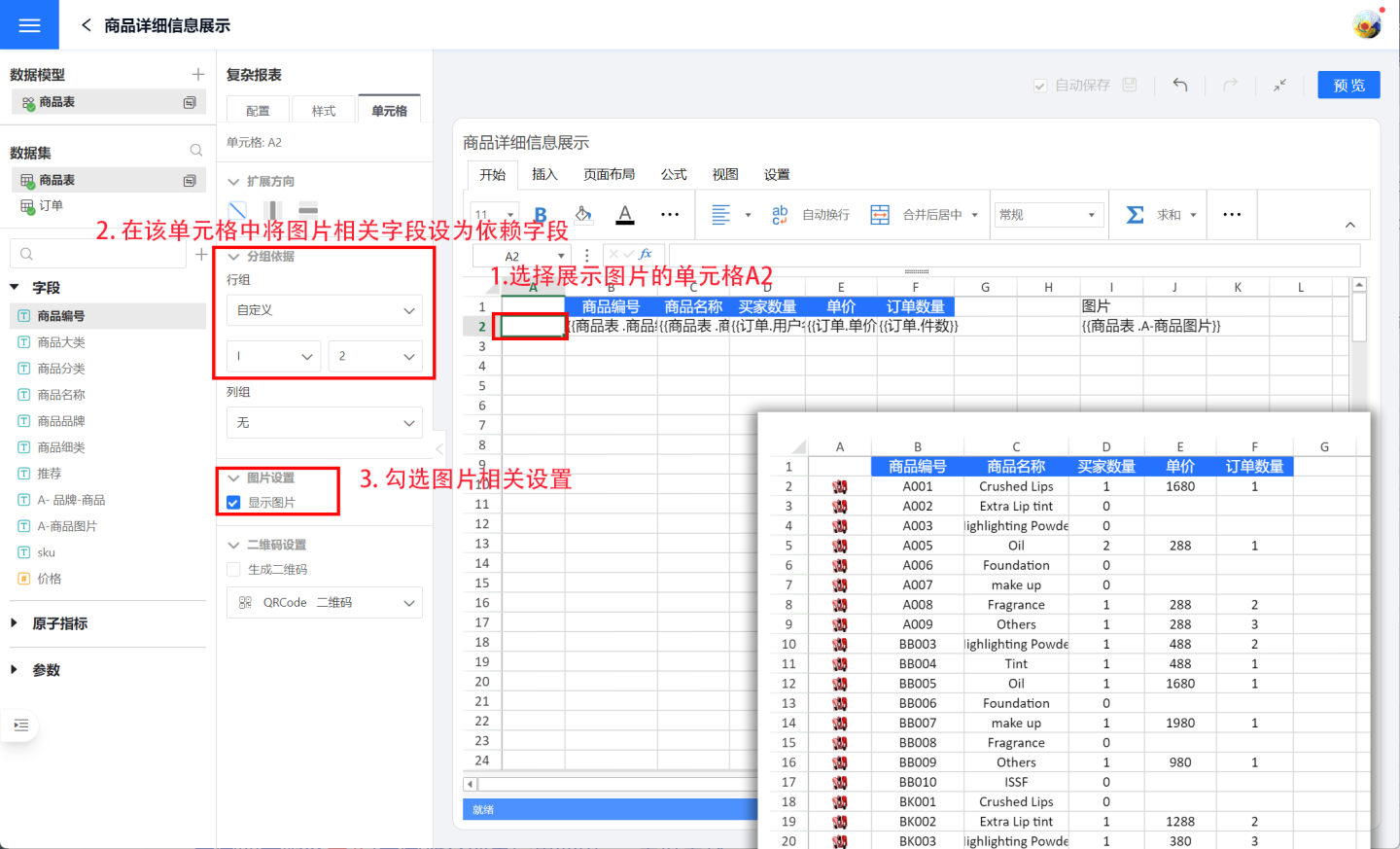
Complex reports support image recognition and display of data. You can follow the steps below to set up images.
- Set the cell to display the image. In the example, the image is displayed in cell A2.
- Drag the image information field from the dataset into the cell where the image will be displayed, and set this field as the basis field in the image display cell. In the example, the image-related field is dragged into cell I2 (this column will not be displayed in the chart and will be hidden later), and the grouping basis in cell A2 is set to I2.
- Check the "Display Image" option in the image settings.
- Complete the image settings and click preview to see the effect.
QR Code Settings
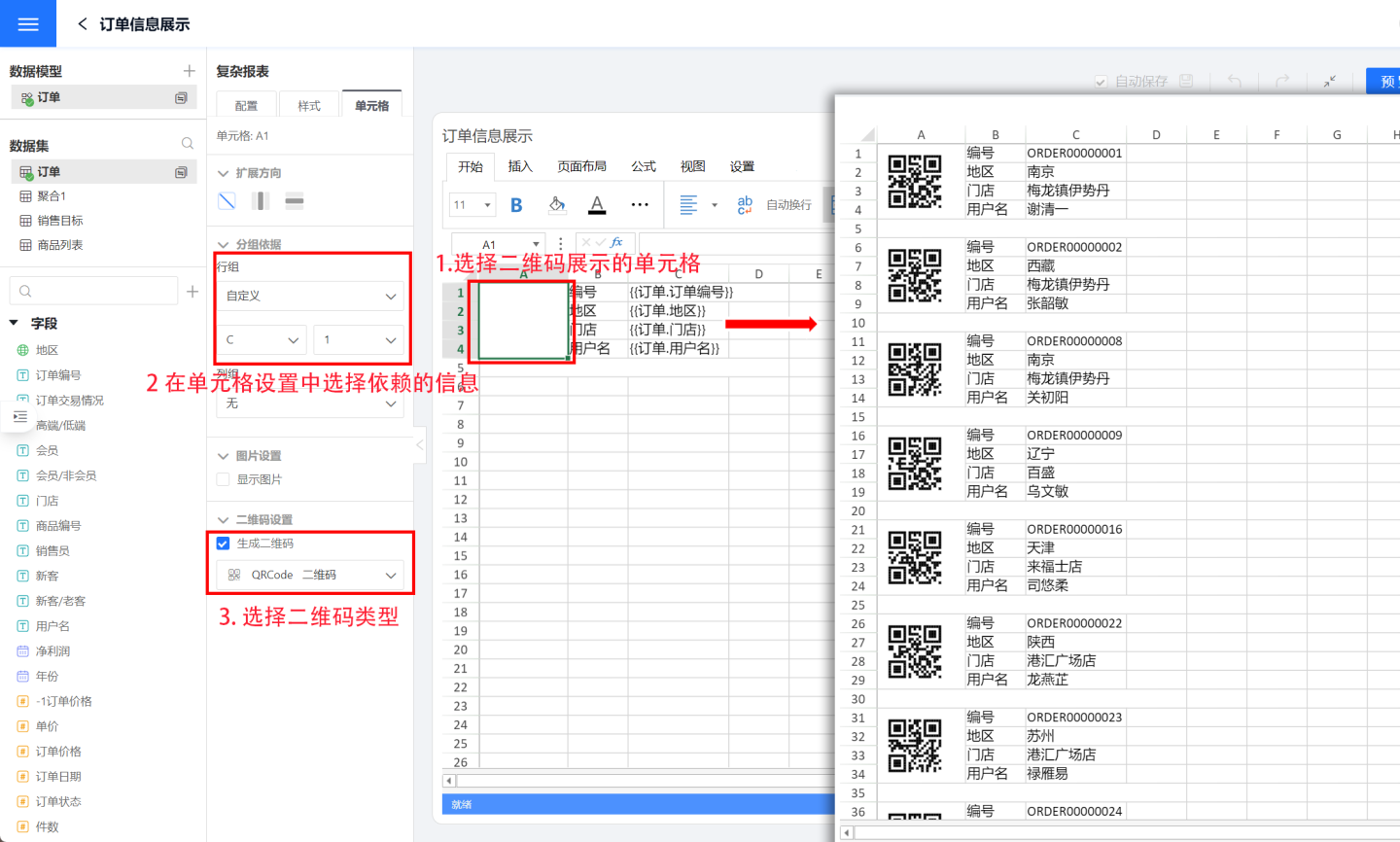
Complex reports can generate QR codes or barcodes for the report content. Currently supported types include QRCode, PDF417, GS1_128 barcode, EAN8 barcode, EAN13 barcode, Code93 barcode, and Codabar barcode. Below, using QRCode as an example, we will introduce how to use the QR code setting function.
Setting up a QR code requires three steps.
- Select the cell where the QR code will be displayed. In the example, cell A1 is chosen to display the QR code.
- Drag the field to be displayed as a QR code into the cell, and set the content to be displayed as the grouping basis in the QR code display cell. In the example, the order code in C1 is displayed as a QR code, so the grouping basis in cell A1 is set to C1.
- Choose the type of QR code to display. In the example, QRCode is selected.
- Once the QR code settings are complete, click preview to view the setup effect.
Pagination
When a complex report contains a large amount of data, you can set up pagination to display the content. Each page shows a fixed amount of data, and any content that exceeds the page size is displayed on the next page. Users can navigate through the pages using a page turner. To use the pagination feature, you need to turn on the pagination switch.
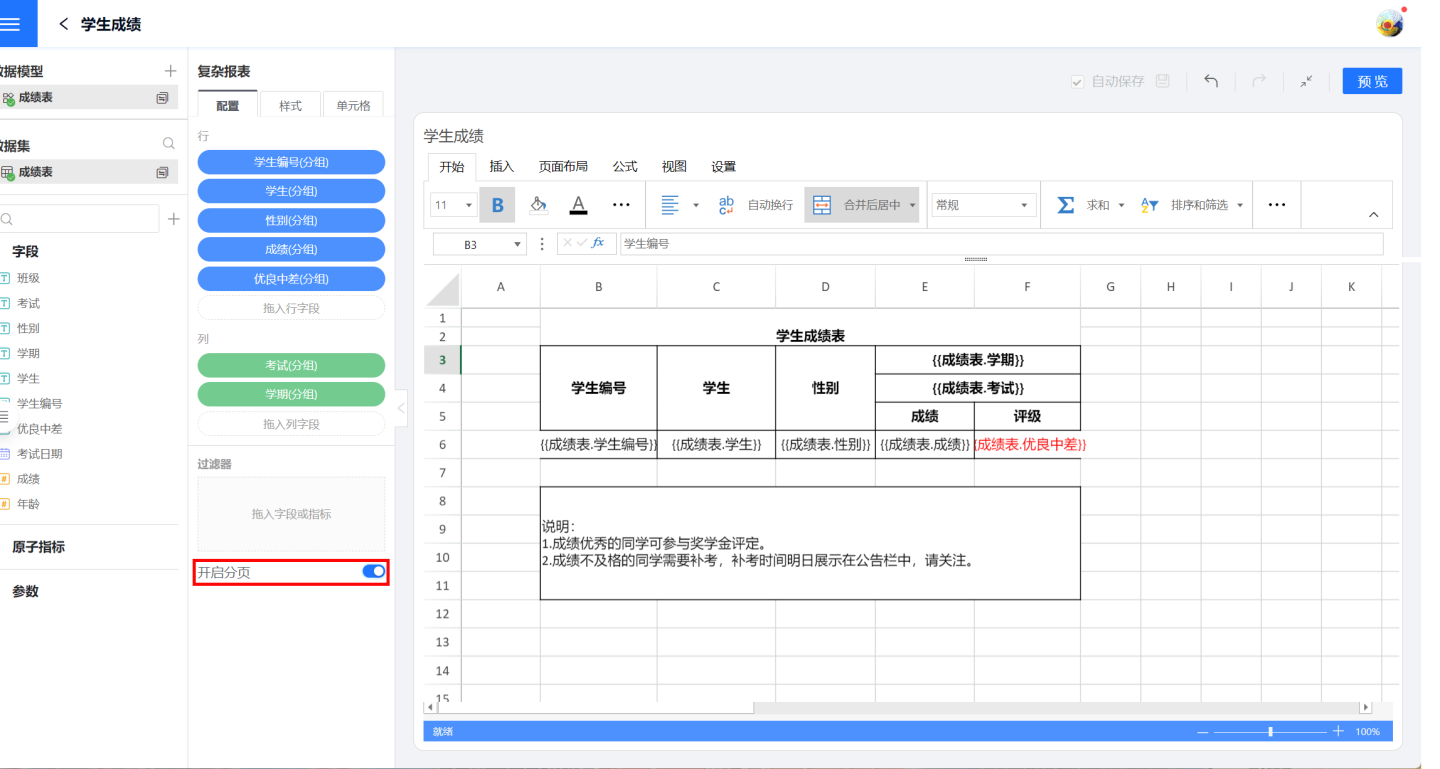
To ensure that the data is displayed more beautifully, smoothly, and completely during pagination, the following settings are supported:
- Merge cells across pages
- Specify cells to repeat display
- Specify cells to display together
- Do not break pages
Merged Cells Display Across Pages
When merged cells are split across two pages, typically only the first page's cell displays content, while the second page's cell remains blank. As shown in the figure, the red box on the second page contains no data, which may lead to confusion when viewing the data due to missing content, requiring a flip back to the previous page to retrieve the merged cell's content.
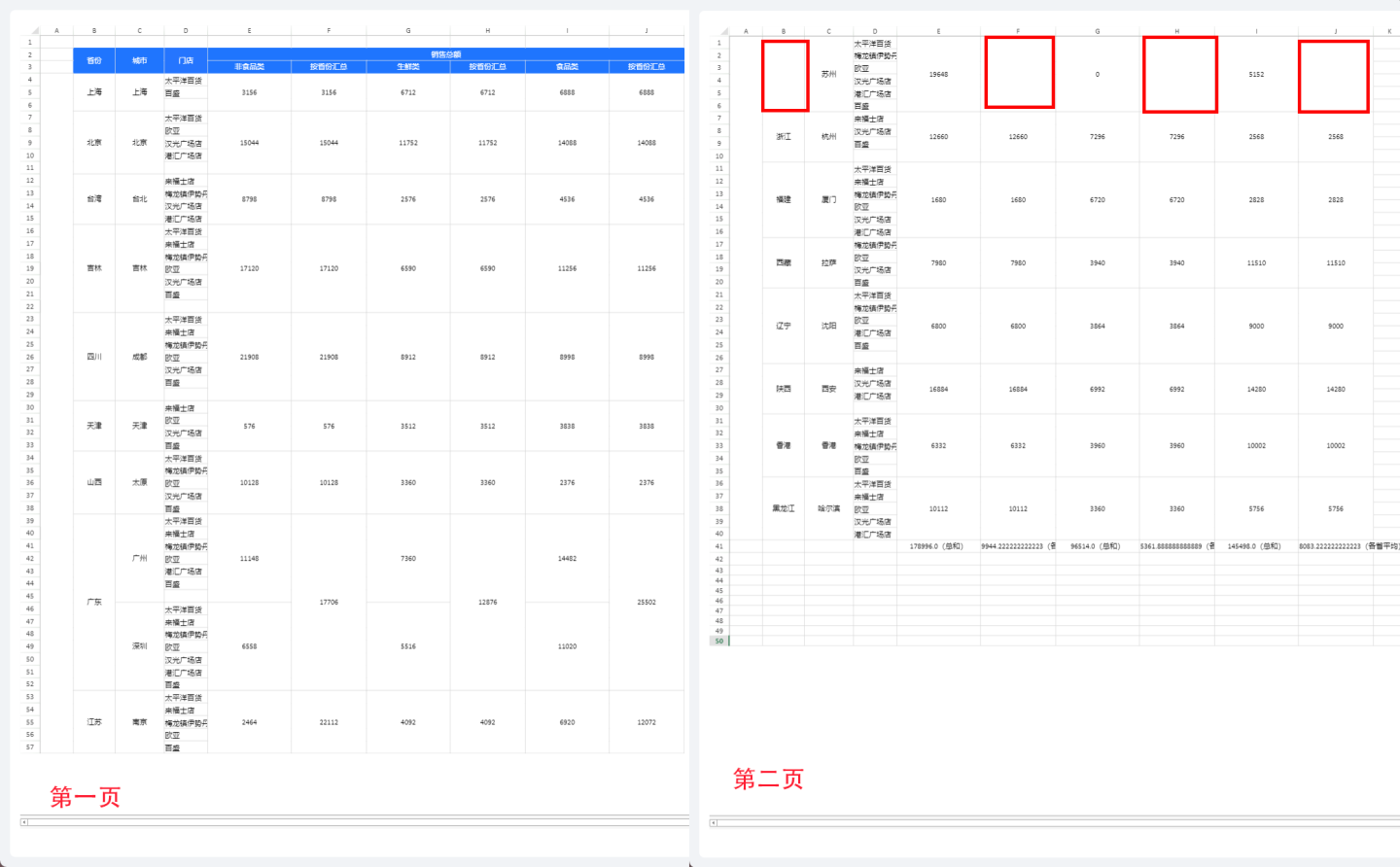
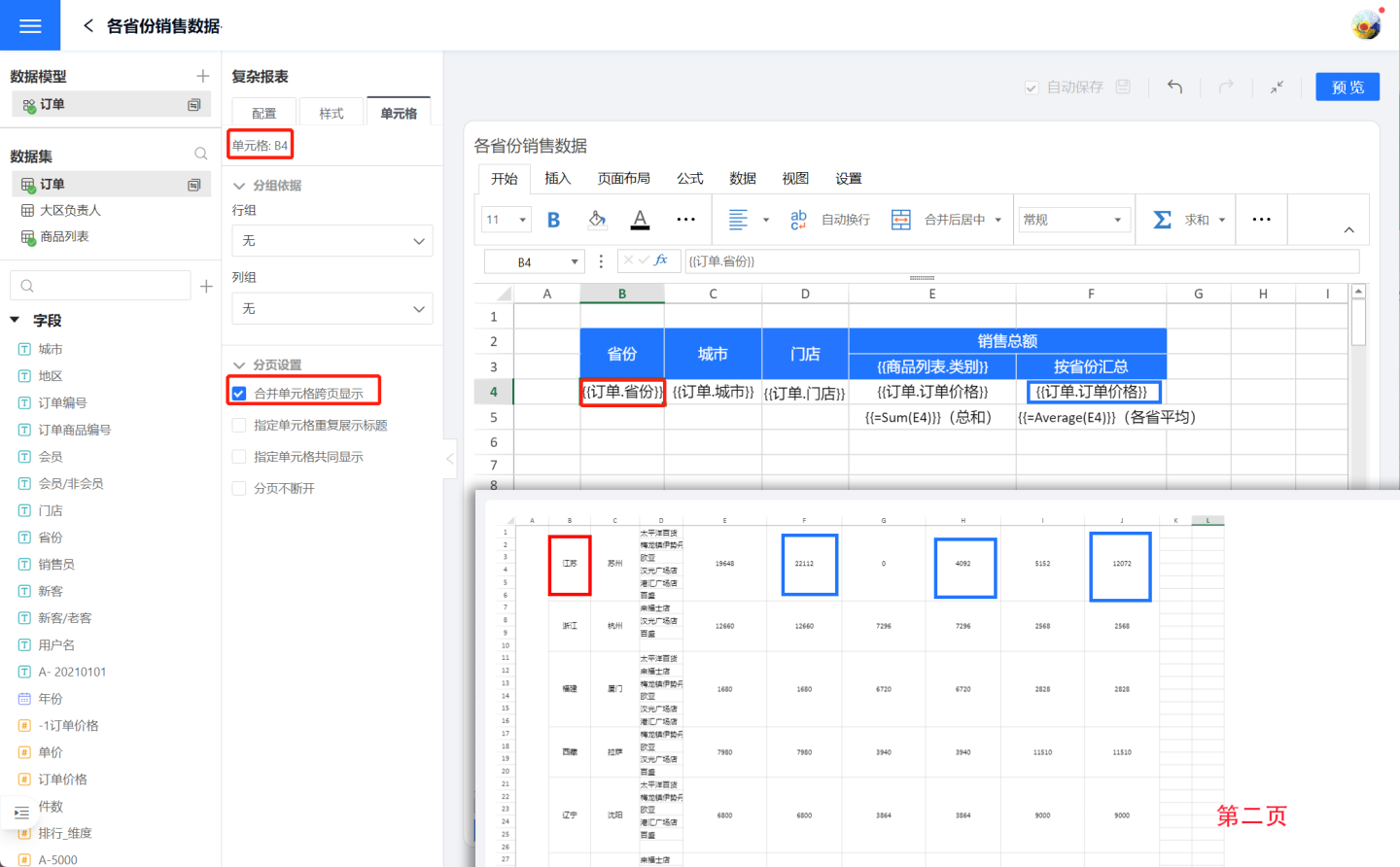
Complex reports support the display of merged cells across pages, meaning that when merged cells span across pages, content is displayed on each page. In the example above, after setting "Jiangsu Province" and the corresponding "Province Summary" to display merged cells across pages, data is shown on each page. First, select cell B4{{Order.Province}} (red box), then check the option for merged cells to display across pages in the pagination settings. Apply the same settings to the order prices summarized by province (blue box). The preview effect is as shown in the figure, where the cells "Jiangsu Province" and the corresponding "Province Summary" display data on each page.
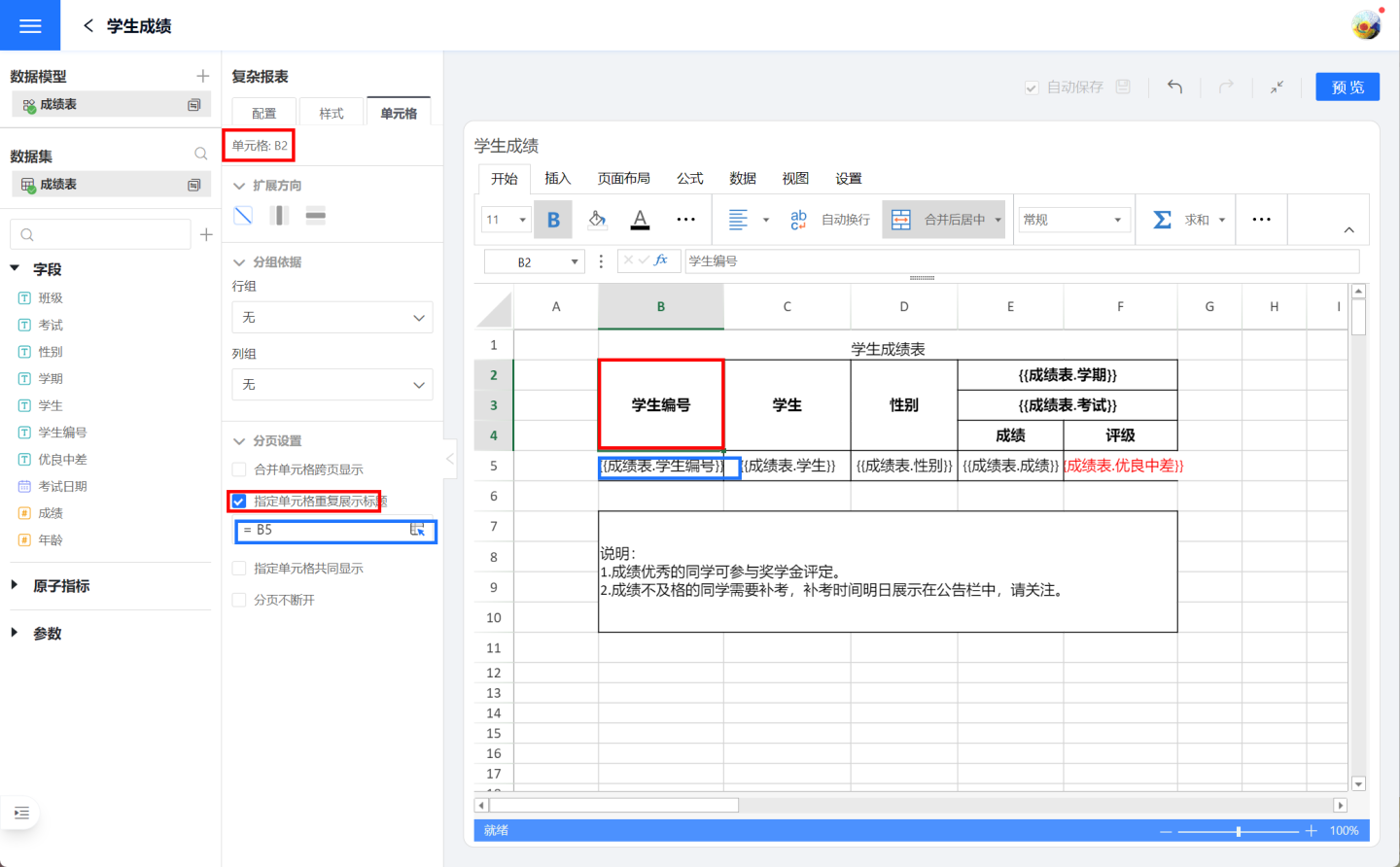
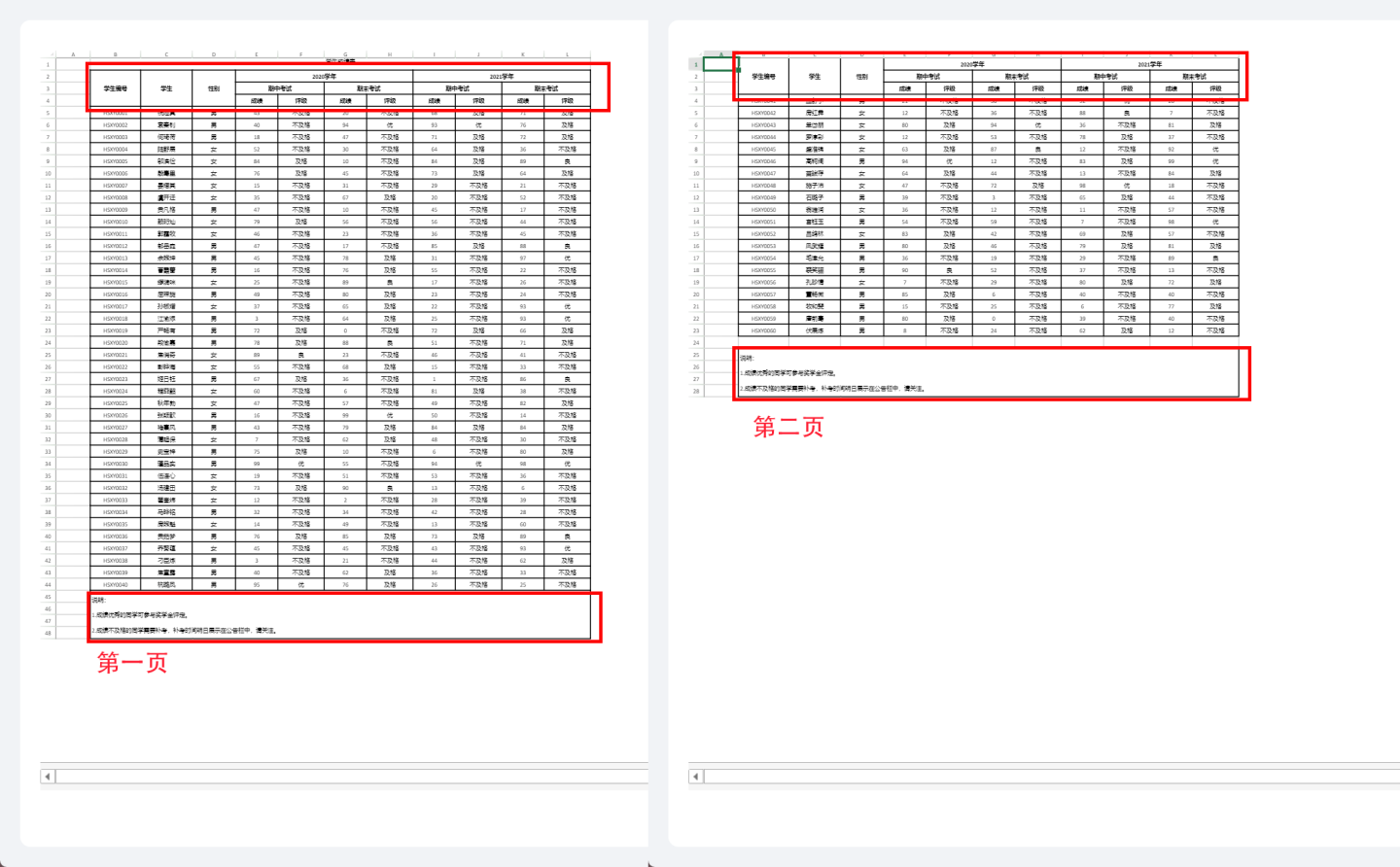
Specifying Cell Repetition Display
Specifying cell repetition display refers to certain cells being repeatedly displayed on the page, commonly used for header or footer explanatory information. As shown in the figure, when the student grade table is displayed in pages, it is desired to display the header and explanatory information on each page. Therefore, the header cell B2 (red box) is set for page display, making it follow cell B5 (blue box) for display, meaning that the header is displayed on each page when student grades are shown. Similarly, the explanatory information cell B7 is also set for page display, making it follow cell B5 for display, meaning that the explanatory information is displayed on each page when grades are shown.
The paging effect after setting is shown in the figure, with the header and explanatory information displayed on each page.
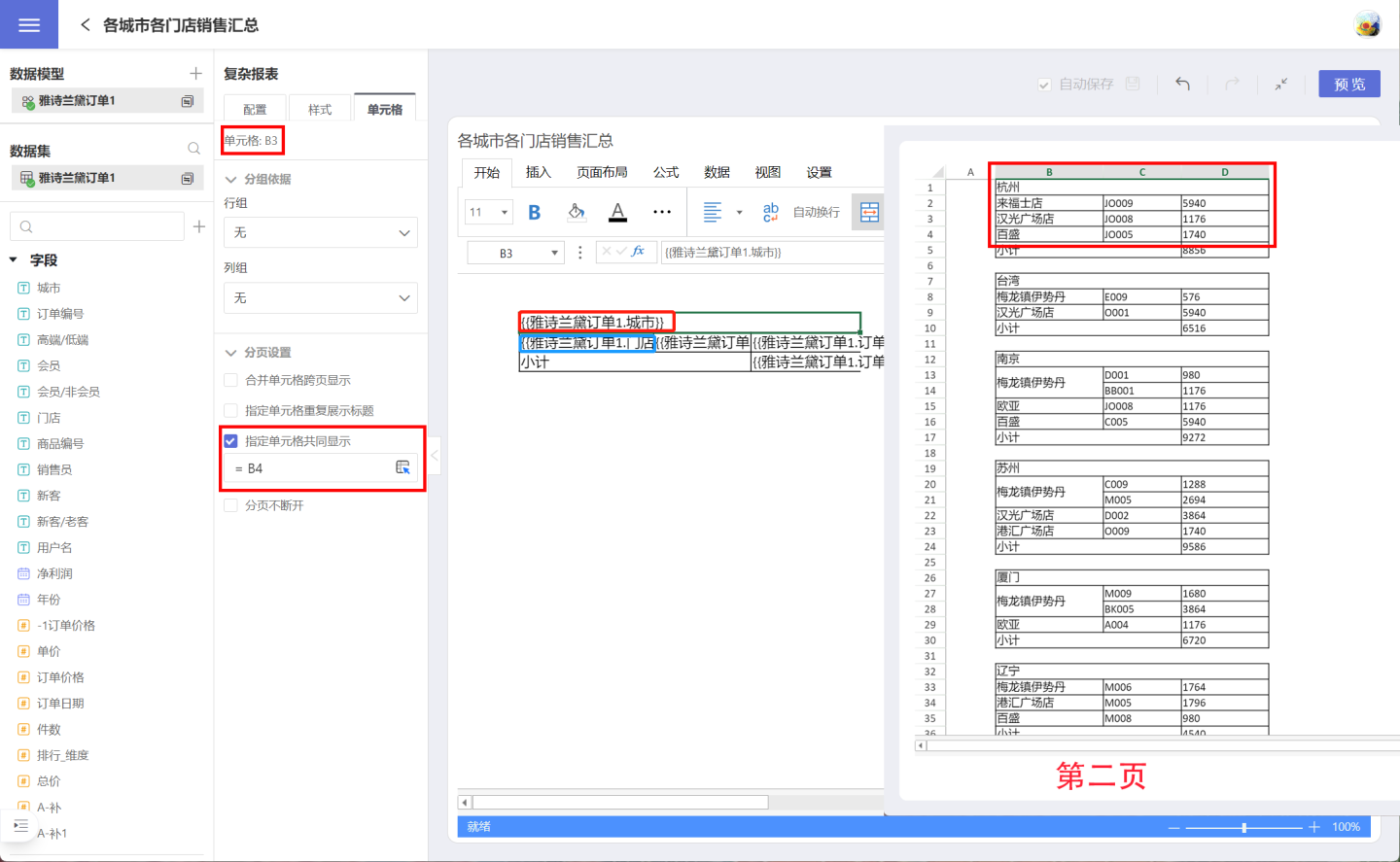
Specifying Cells to Display Together
When a report is paginated, data exceeding the system-specified page size will be split, and some related data may be displayed across two pages, potentially resulting in orphaned rows on one page, thus breaking the continuity of data information. As shown in the figure, the report displays the sales of products by city stores. During the report display, the city "Hangzhou" and its stores are split across two pages.

To ensure that the city and its associated stores are displayed together, pagination settings are applied to cell B3 (the city), configuring it to display together with cell B4 (the store). After this setting, the city "Hangzhou" is no longer displayed as a single row but is shown together with its associated stores.
Page Break Continuation
During the pagination of reports, some complete information may be split into two parts. In such cases, the page break continuation setting can be used to display the complete information together. For example, in the display of a certain unit's payroll, it is desired that each employee's information be fully displayed on one page without being split by pagination. The pagination setting is made in the header C6 (red box), setting the range from header C6 to the end of the salary details display row F13 (blue box) to not break. 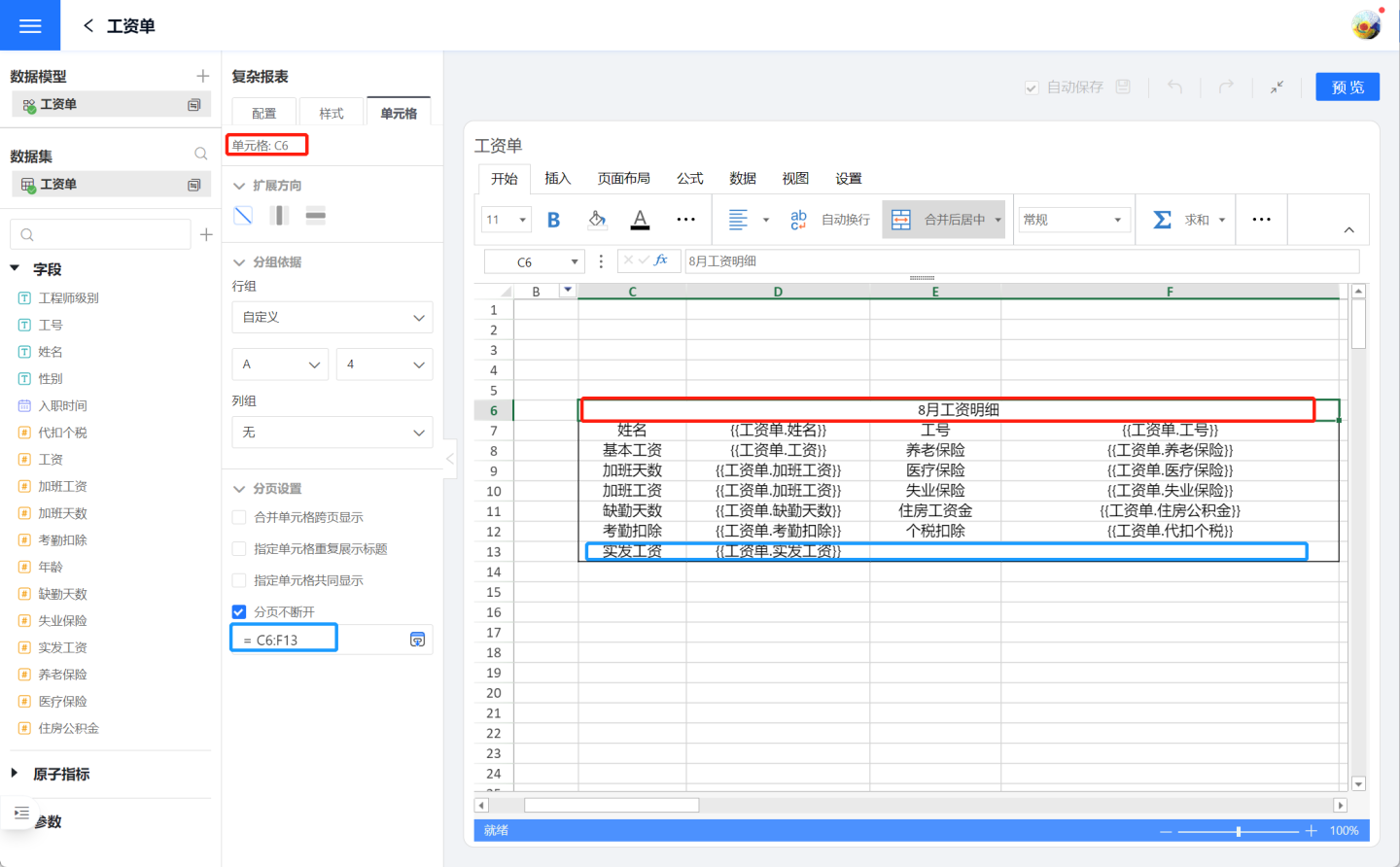
When the page break continuation is not set, the information of the employee "Yan Yiqi" is displayed across two pages. After setting, the information of the employee "Yan Yiqi" is completely displayed on the second page.
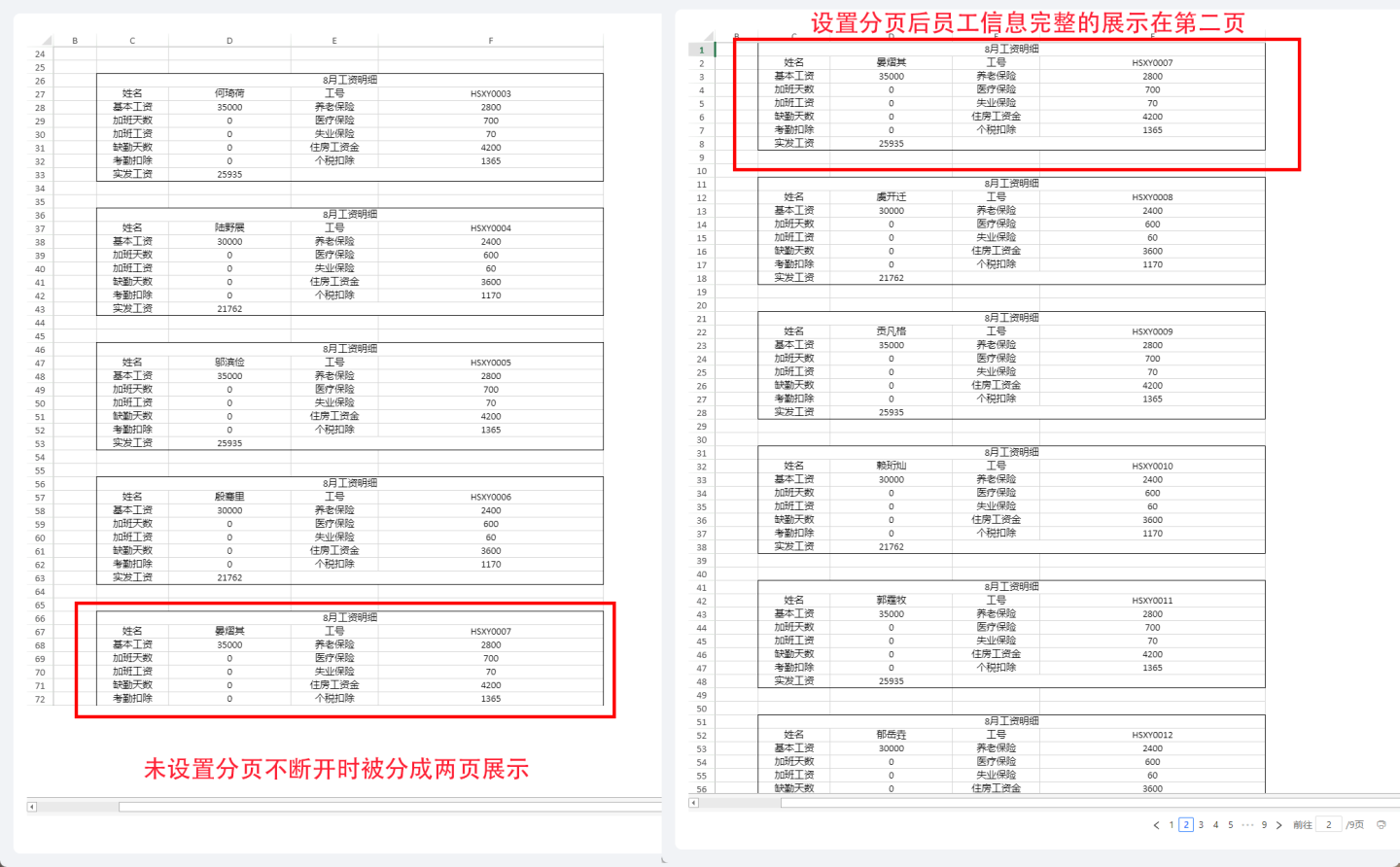
Tip
Page break continuation requires selecting all the cell data that should not be broken, setting the range value of the display cells. In the above example, the unbroken range is set from C6:F13. If there is only one row of data, set the entire row.
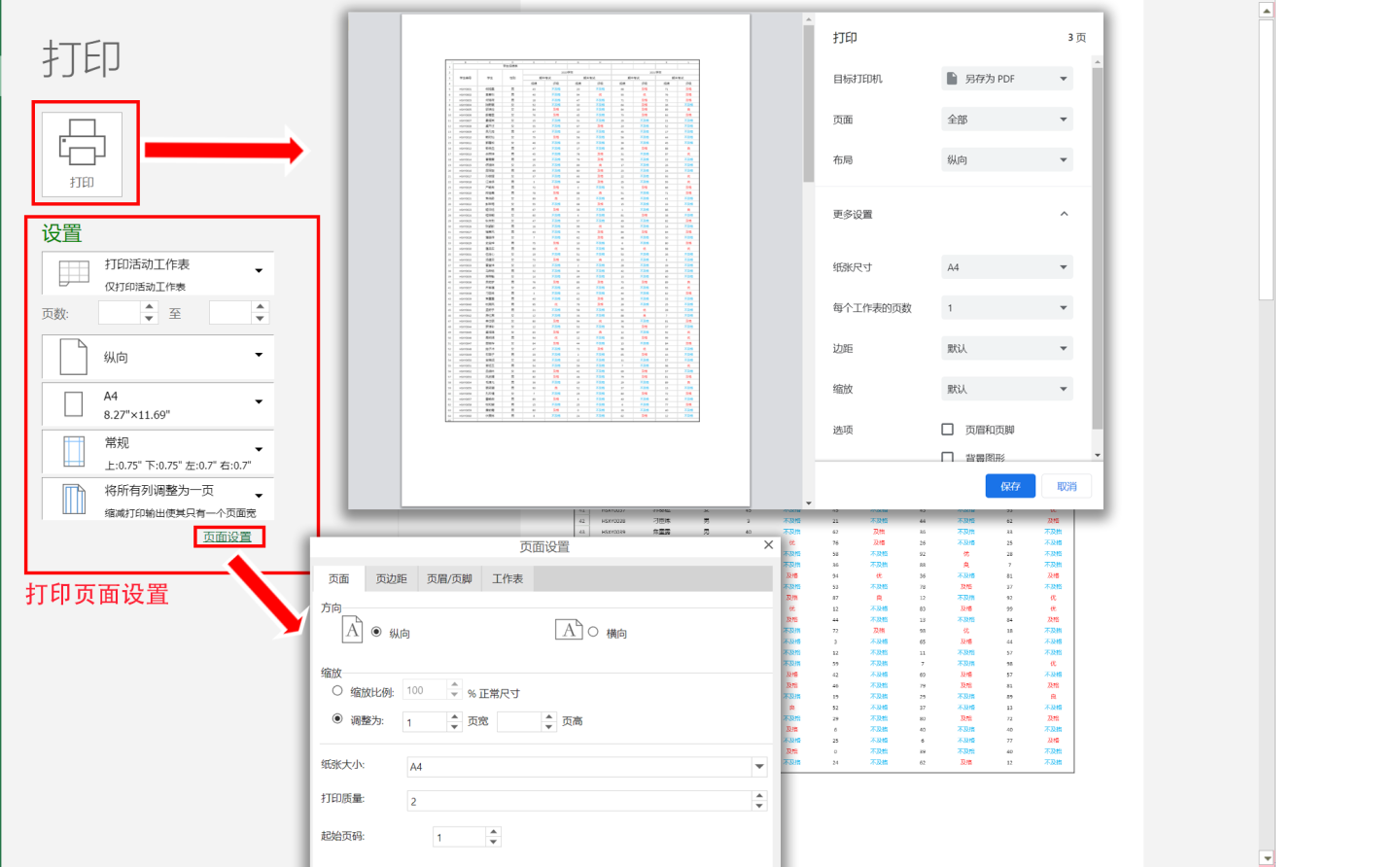
Printing
Complex reports support printing. In the App Marketplace, open the report and you will find a print button in the lower right corner. Click the button to print.
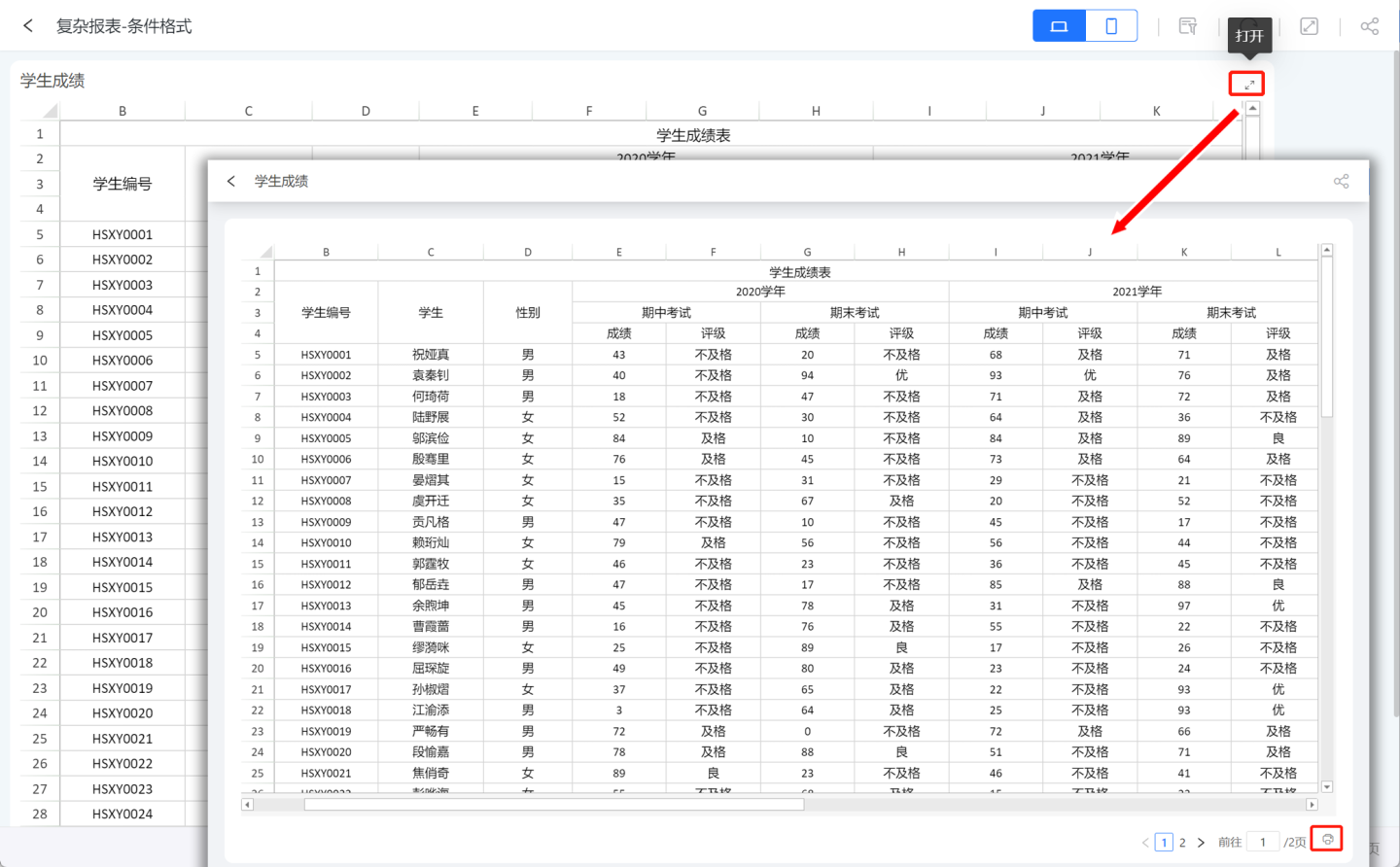
On the print page, you can set the number of pages, page margins, headers/footers, and worksheets. Clicking print will bring up a print dialog where you can set up the printer for printing. The functionality of each print item will not be described in detail here.
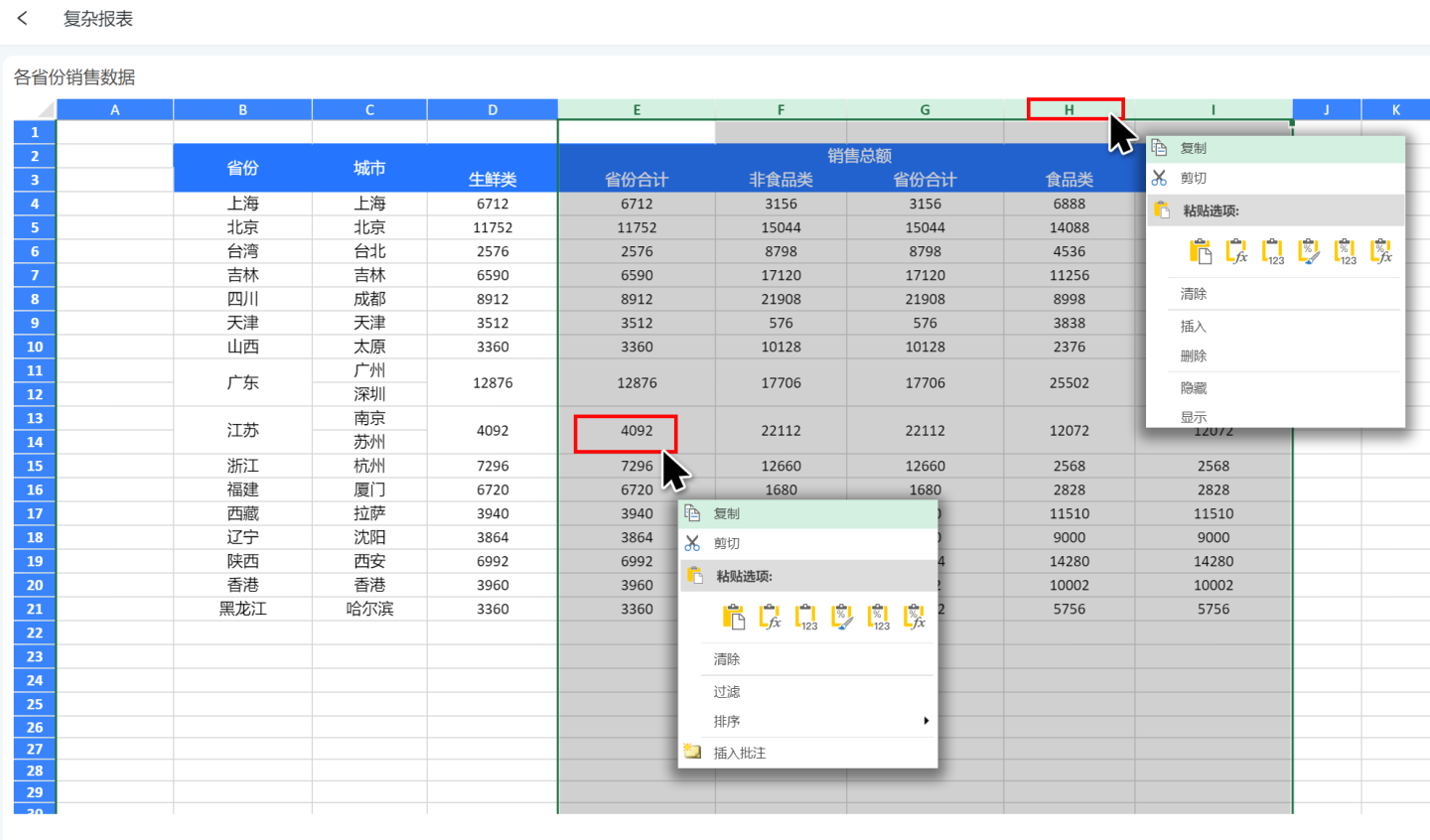
Complex Report Publishing
Complex reports support operations such as data filtering, sorting, column hiding, editing, inserting, and copying in the published state.
Interaction with Other Controls
Complex reports currently do not support interaction with other controls.
Usage Limitations and Considerations for Complex Tables (Complex Reports):
- Row Limit Not Effective: The system setting that limits the number of rows for table data export does not apply to complex tables. Since complex tables support rendering results from multiple data tables through templates, the row limit for a single table is not meaningful here and is currently not supported for complex tables.
- Data Source Row Limit: The process of rendering templates with data in complex tables involves calculations, which are memory-intensive. Therefore, we have imposed a row limit on the data used for rendering templates, defaulting to 500,000 rows. This can be modified via the configuration item COMPLEX_TABLE_DB_QUERY_LIMIT. Considering memory usage, it is recommended not to set this too high.
- Display Format Settings: Display formats are set within the cells, which is different from setting them in the axes of other charts.
- Chinese Character Encoding Issues in Export: If Chinese characters appear garbled when exporting to PDF or Excel, the corresponding Chinese fonts need to be installed on the server, and the GRAPECITY_GCEXCEL_FONTS_PATH configuration item should be set to point to the parent path of the font location.
- No Support for Cross-Source Template Calculations: Cross-data source calculations via template formulas are not supported. For such needs, it is recommended to first synthesize a single data source at the dataset level before using it in complex tables.
- Printing Overall Borders: Printing complex tables will include an overall border. If not needed, it is recommended to download the data before printing.
- Null Value Display Issues: Null values in templates may turn into strange numbers and sometimes cause the browser to freeze. It is recommended to replace null values before data rendering, such as replacing null values in the dataset.
- Conditional Formatting Fails with Pagination: Conditional formatting will fail when pagination is enabled. It is recommended not to enable pagination in this scenario.
- QR Code Recognition Fails with Pagination: QR code recognition will fail when pagination is enabled. It is recommended not to enable pagination in this scenario.
- Image Recognition Fails with Pagination: Image recognition will fail when pagination is enabled. It is recommended not to enable pagination in this scenario.
- Double Equal Sign Formula Template Fails with Pagination: Double equal sign formula templates (e.g.,
{{==round(B8-C8,2)}}) will fail when pagination is enabled. It is recommended not to enable pagination in this scenario. - No Support for Non-Group Aggregation of Text and Date: Text and date types in the axes of complex tables can only be used for group calculations, not for aggregations like max. This configuration can cause display anomalies. It is recommended to perform aggregations in the dataset and then render the complex table with detailed data.
- Only One Sheet Supported: Currently, only one sheet is supported in the template; multiple sheets are not supported.
- Detailed and Aggregated Data are Calculated Separately: In the axes of complex tables, if one is detailed and the other is an aggregated calculation, one should not be set as the grouping basis for the other, as it will not take effect.
- Exporting to Excel Causes QR Codes and Images to Fail: QR code generation and image URL recognition are features of complex tables, not Excel.