Combination Chart
Combination Chart is a new chart type introduced in HENGSHI SENSE 3.2. In a combination chart, you can:
- Add any number of coordinate axes
- Set the position and direction of the axes
- Freely add elements in the Cartesian coordinate system
- Lines, columns, and areas support custom stacking
- Use measures outside the elements to control chart labels and tooltips
- Use any dimension/measure to control chart colors
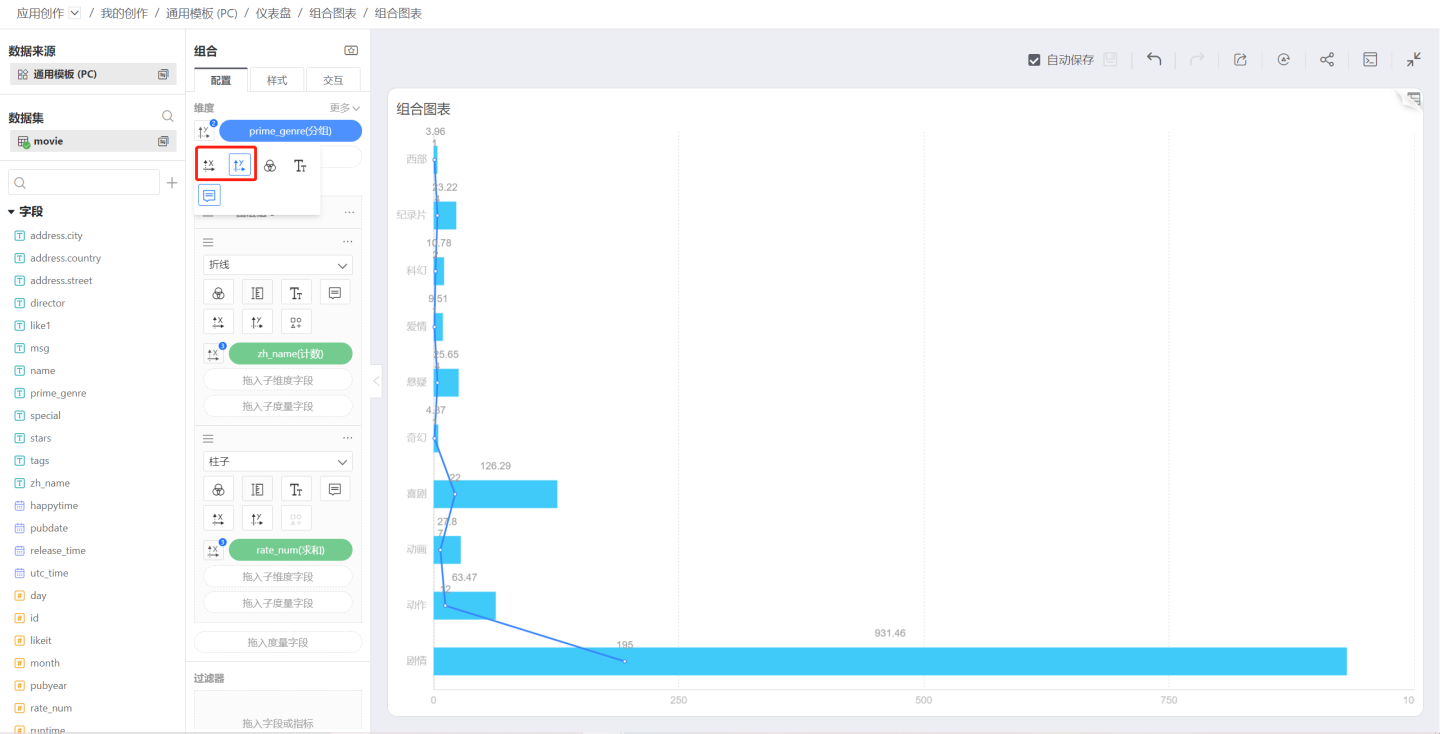
X Axis/Y Axis
In a combination chart, you can set which indicators control the X axis and Y axis, allowing you to create horizontal or vertical charts as needed.
Graphics
In a combination chart, you can select the shape of each measure above the measure area. Currently, the following shapes are supported:
- Column
- Line
- Area
- Circle
- Ring
- Shape
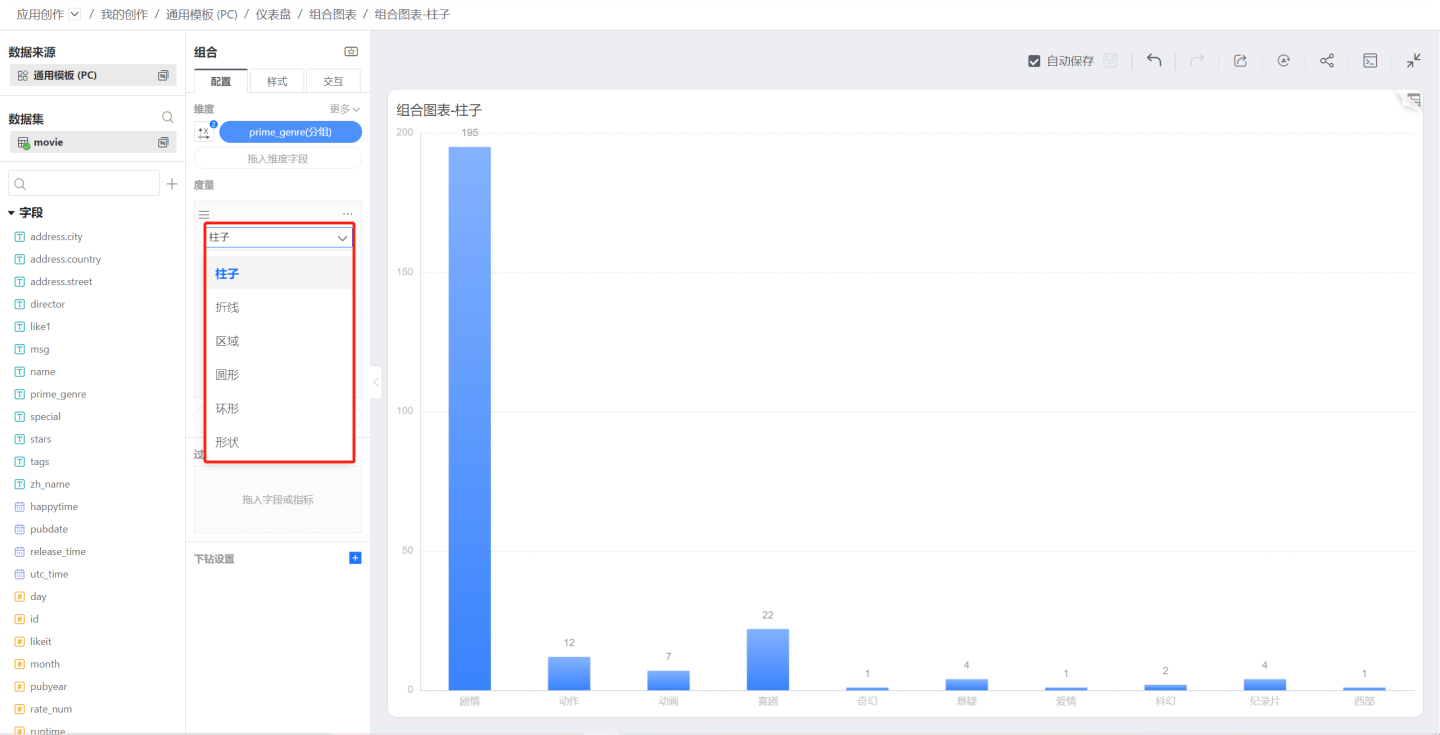
In a combination chart, each measure can specify a different shape, allowing multiple shapes to appear in one chart. The reason why shape settings are displayed in the measure area is that the elements are plotted based on the measure values.

Column
Column is the default plotting shape.
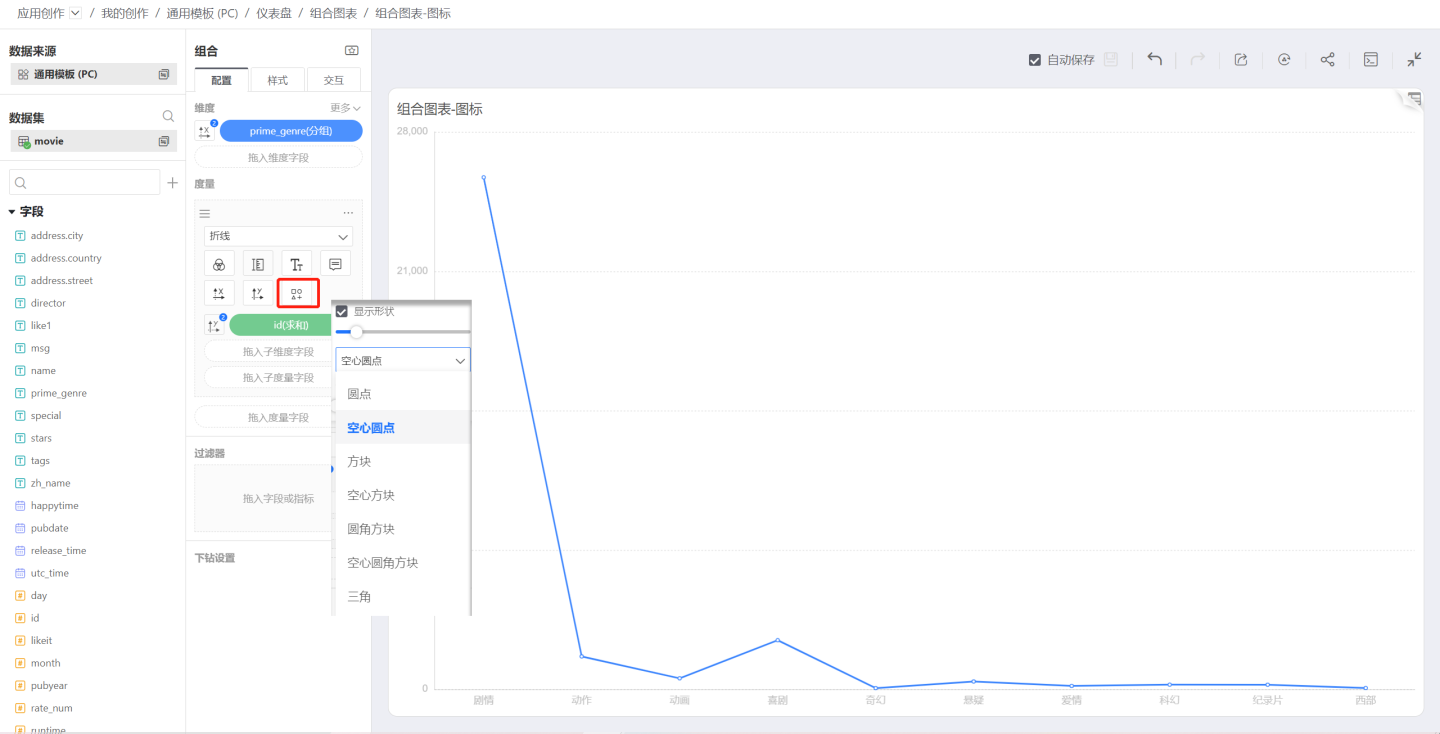
Line
When the shape is selected as Line, the symbol control will be enabled. Click the symbol icon to select the shape and size of each data point.
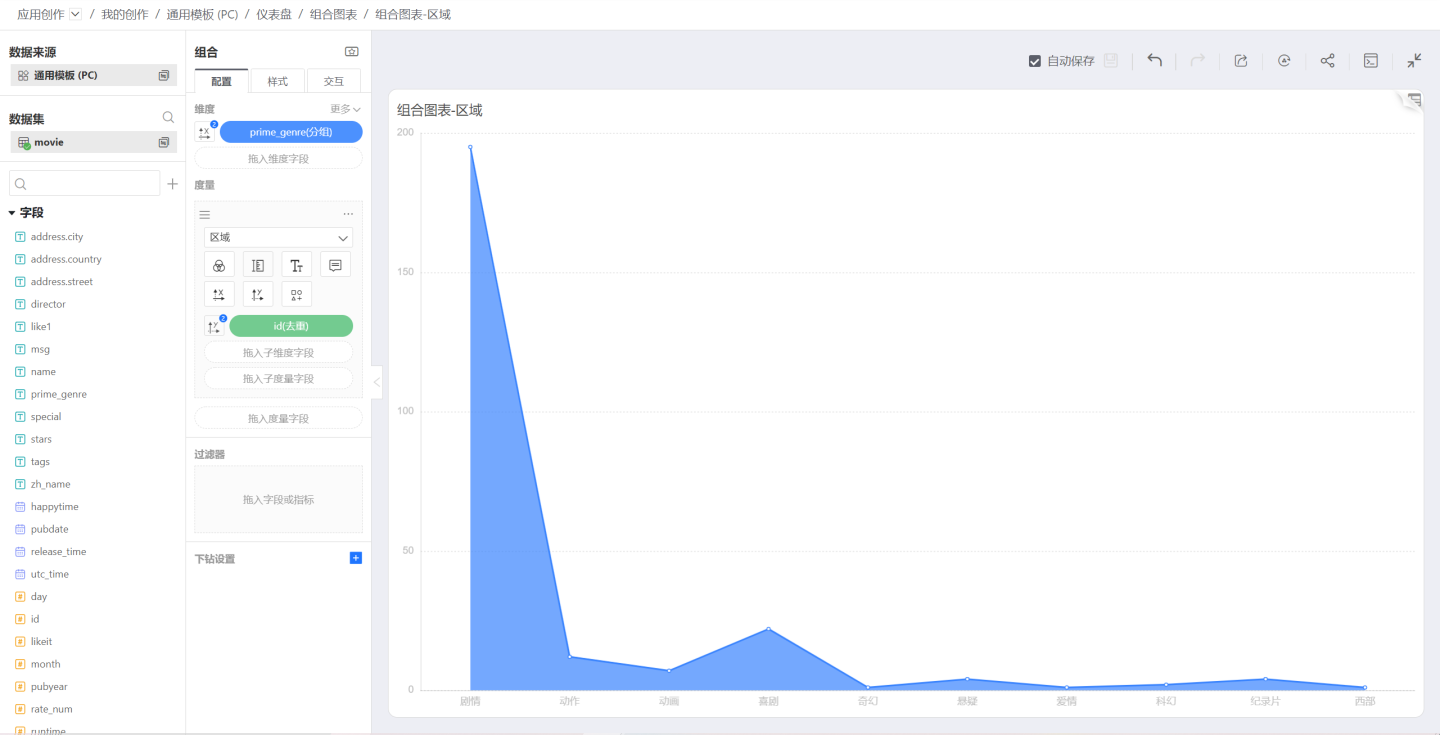
Area
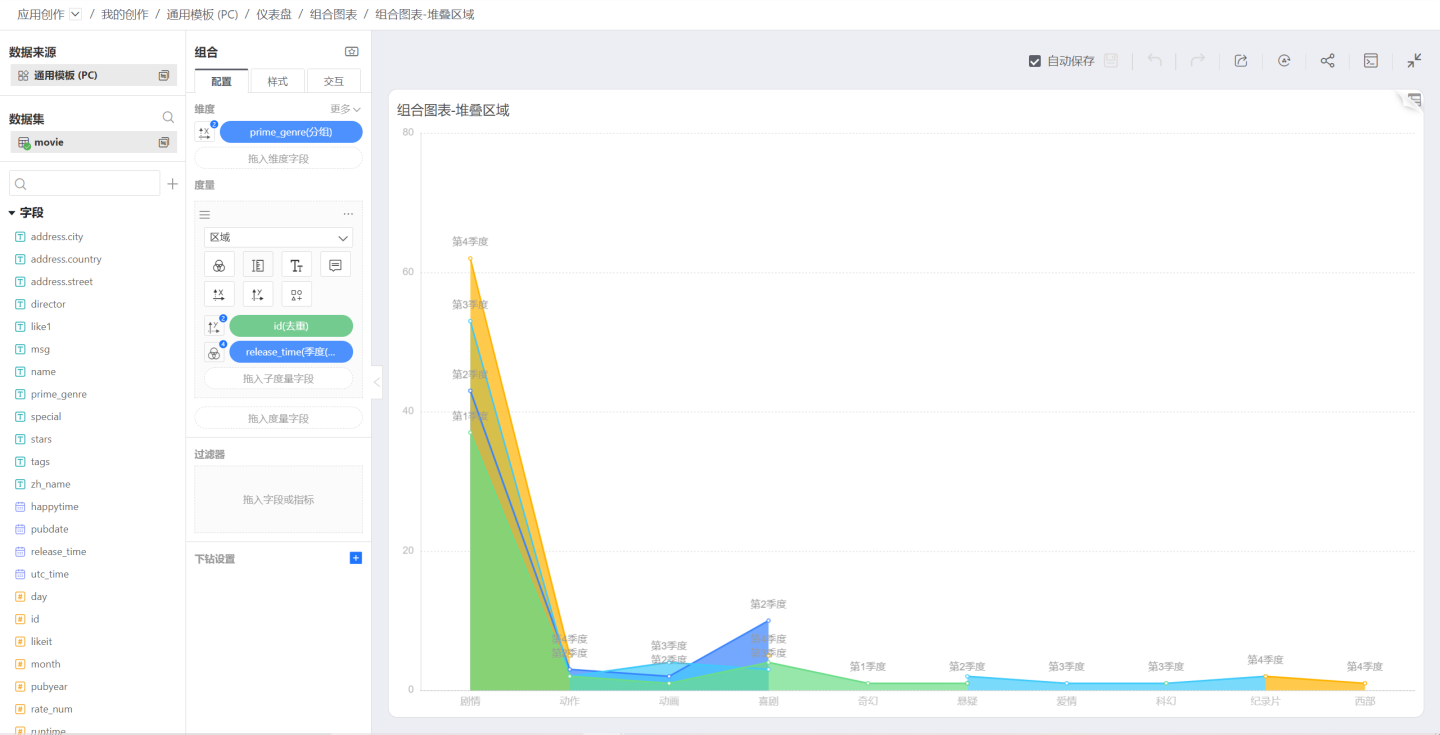
When the shape is selected as Area:
Drag a sub-dimension into the measure area, and the area chart becomes a stacked area chart. Then use the sub-dimension to control colors, labels, and tooltips:
Circle
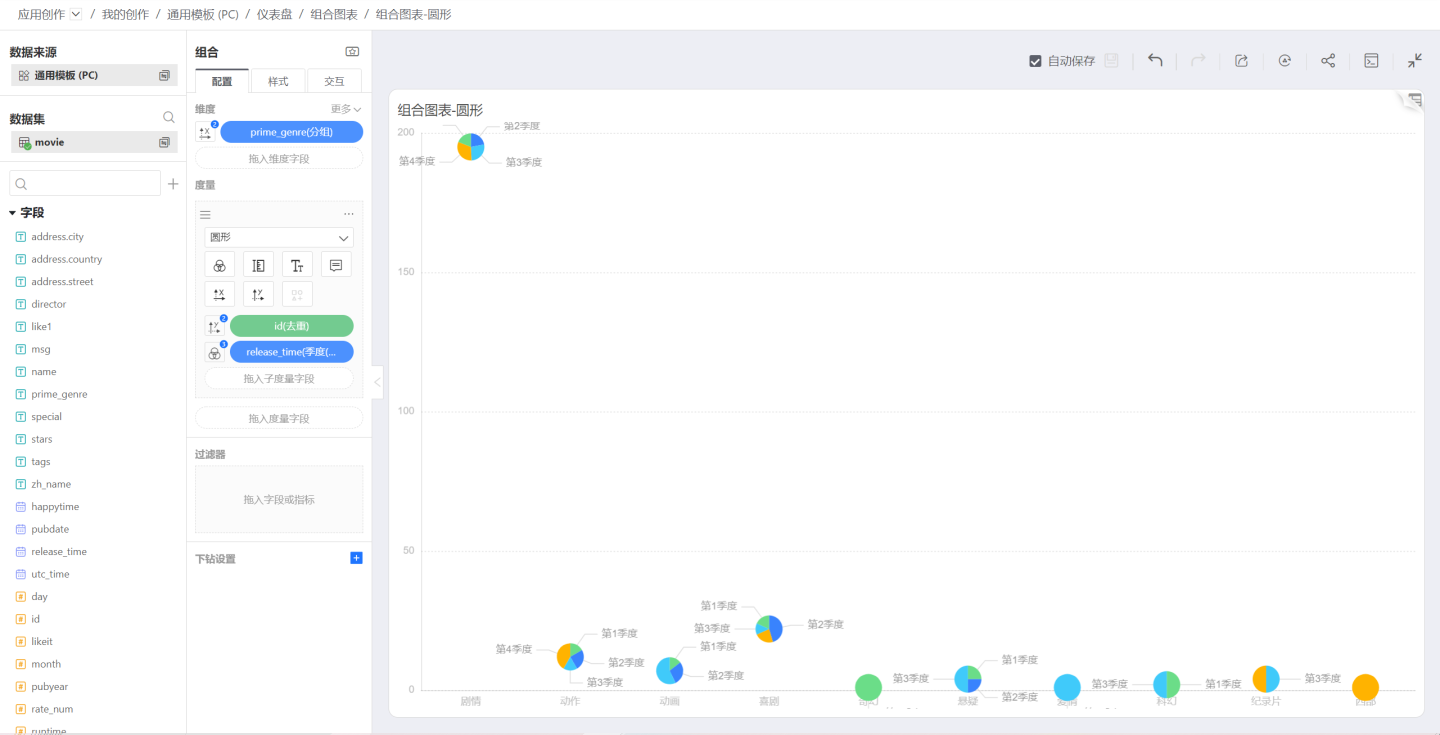
Based on the above, change the shape to Circle, and the chart will look like this. You can control the size of the circles using the Size icon:
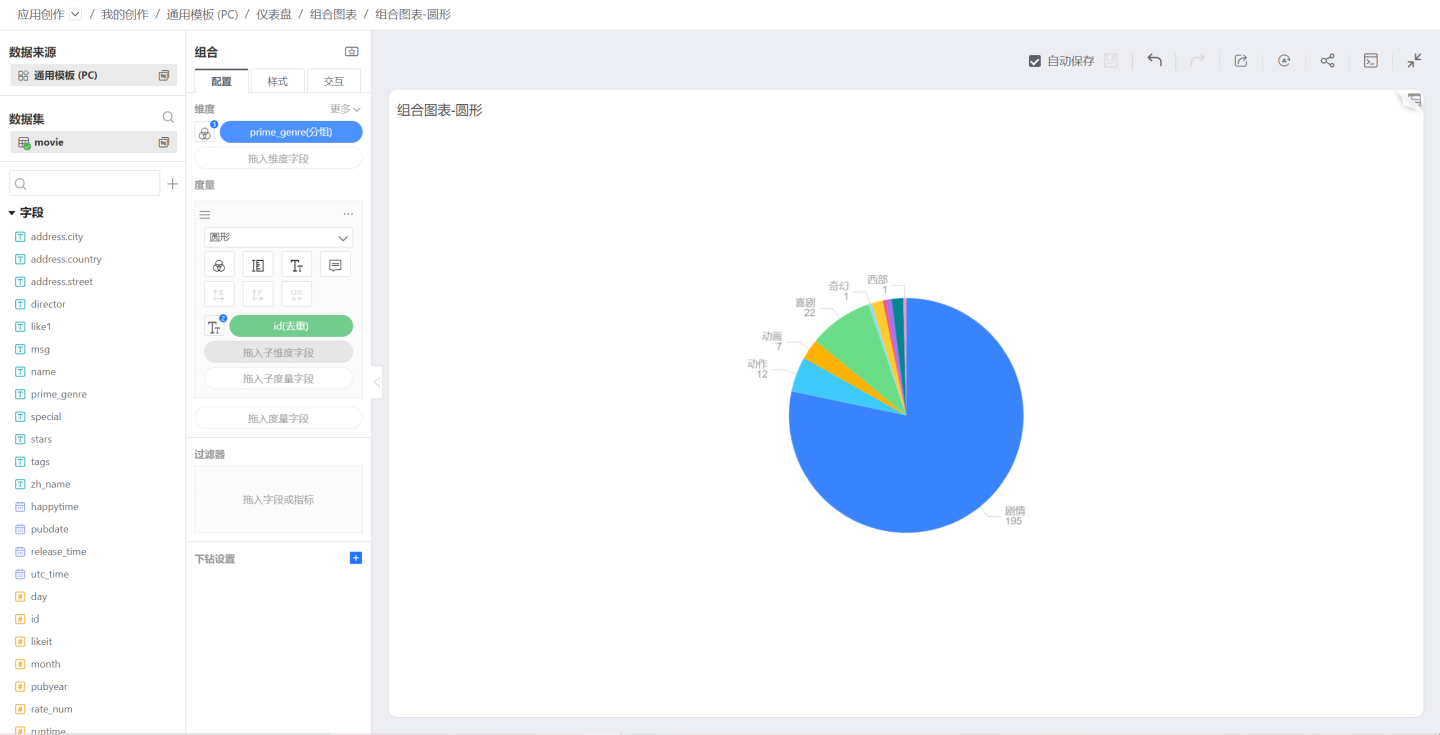
You can use Circle to draw a pie chart, with the condition that neither dimensions nor measures control the X and Y axes, dimensions control colors, labels, and tooltips, and measures control labels and tooltips:
Angle and Radius
When the shape is Circle, drag a sub-dimension, which can control the Angle and Radius of the circle.
Angle controls the sector angle corresponding to each sub-dimension value. If this option is not selected, each sector angle is the same.
Radius controls the sector radius size corresponding to each sub-dimension value. If this option is not selected, the chart is a pie chart; if selected, it becomes a Nightingale chart.

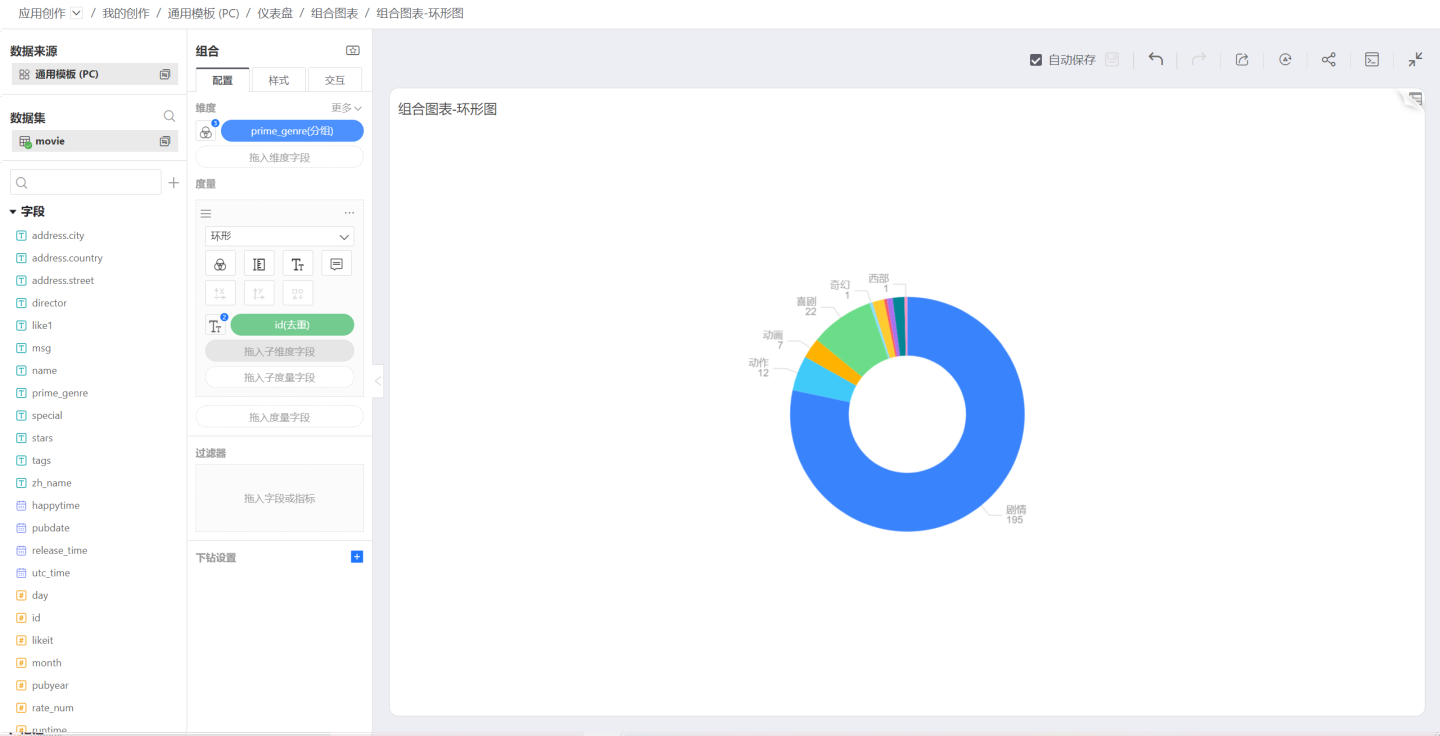
Ring
When the shape is selected as Ring, the chart becomes a ring chart.
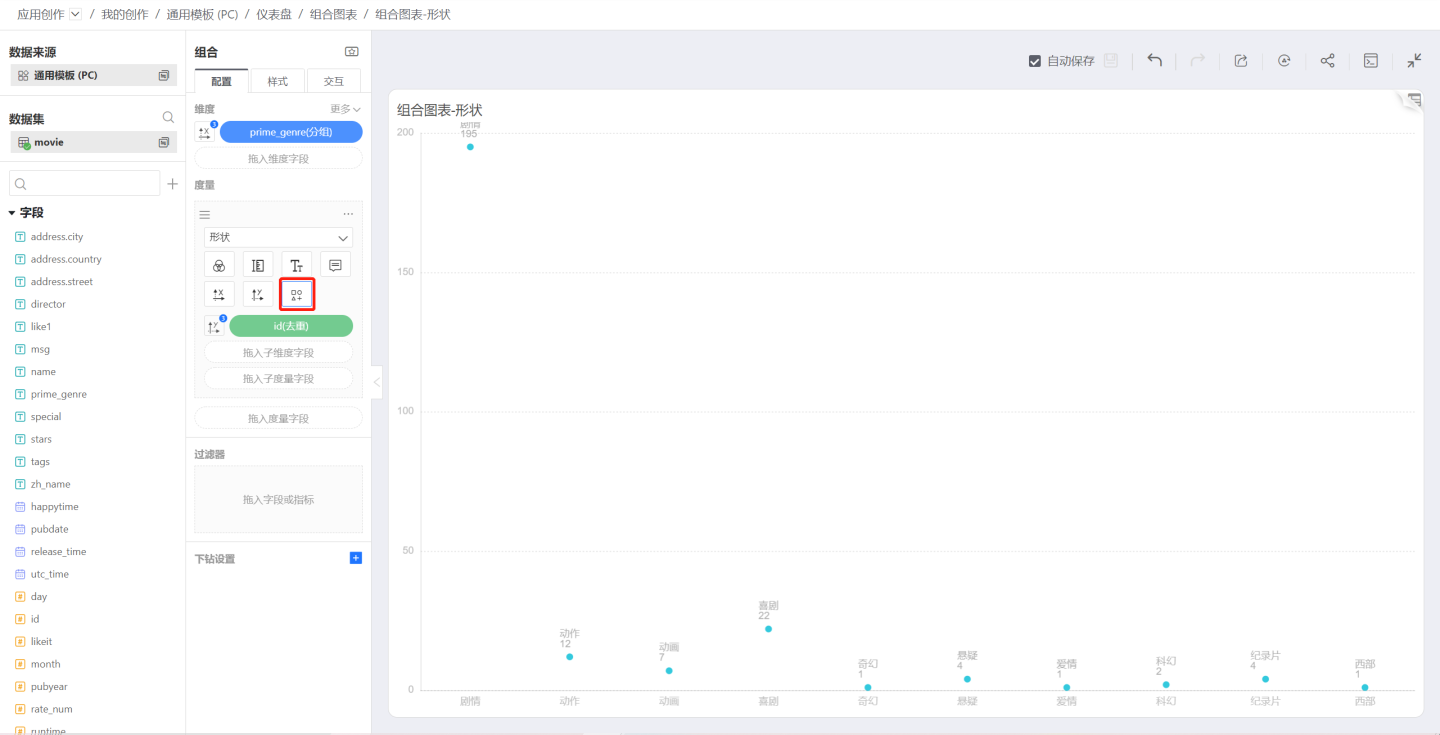
Shape
When the shape is selected as Shape, the numeric points display the selected symbol. You can choose the symbol to display through the symbol popup:
Color
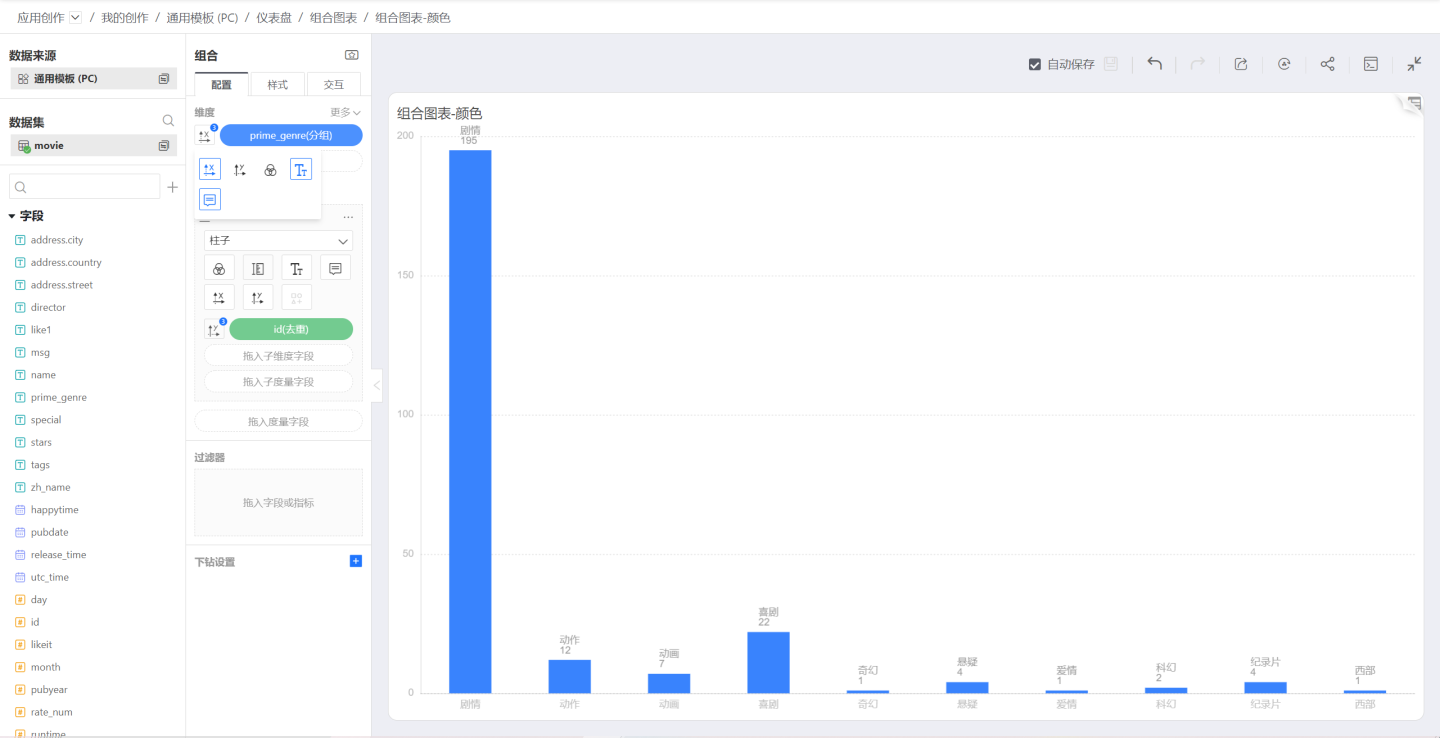
Single Color
When a chart is first created, there is no dimension/measure controlling the chart color, and the chart is single-colored, as follows:
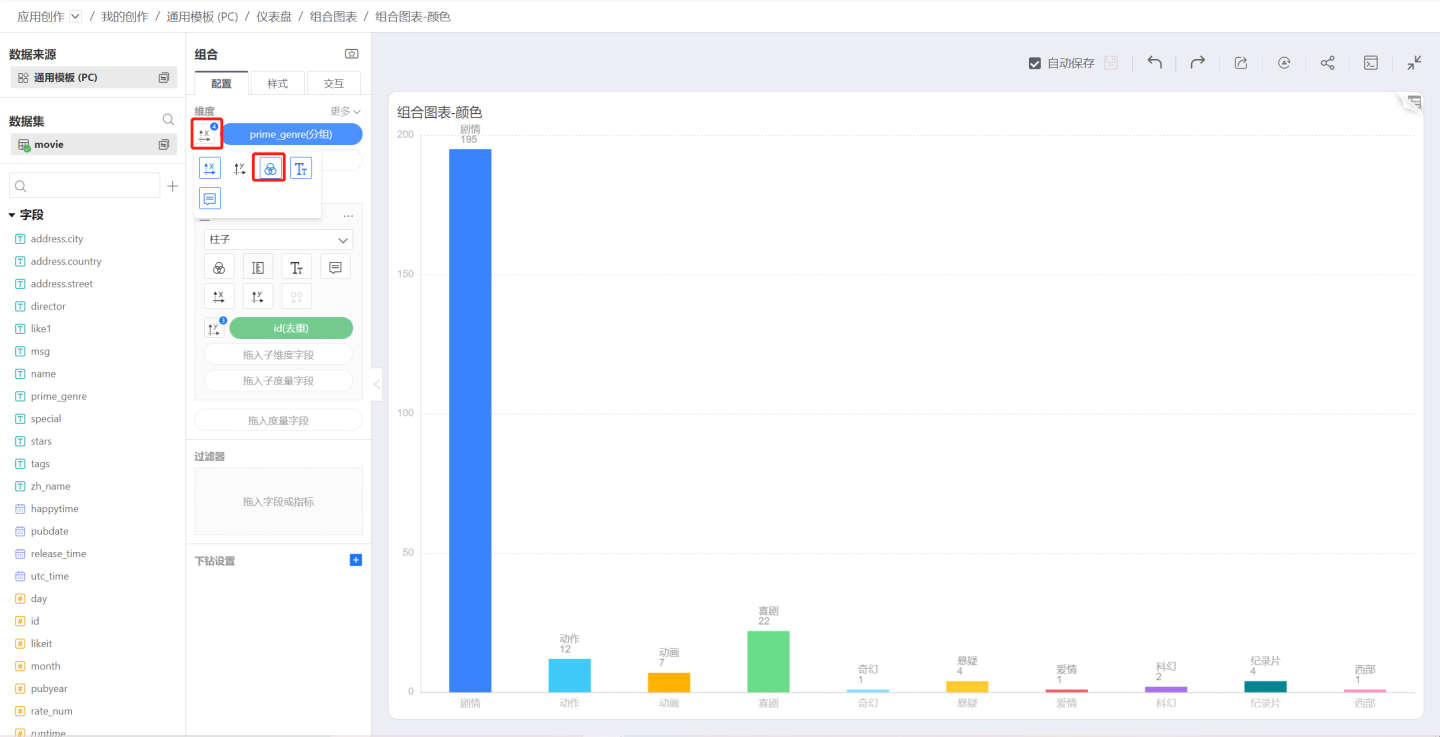
Discrete Color
To use a dimension to control the chart color, click the icon on the left side of the dimension to pop up the control menu, select the color icon, and the chart color will be discrete, i.e., each dimension value has a different color.
To change the color scheme, click the color icon below the graph to pop up the discrete color palette.
Also, if Show Gradient is selected in the palette, each column will display a gradient effect.

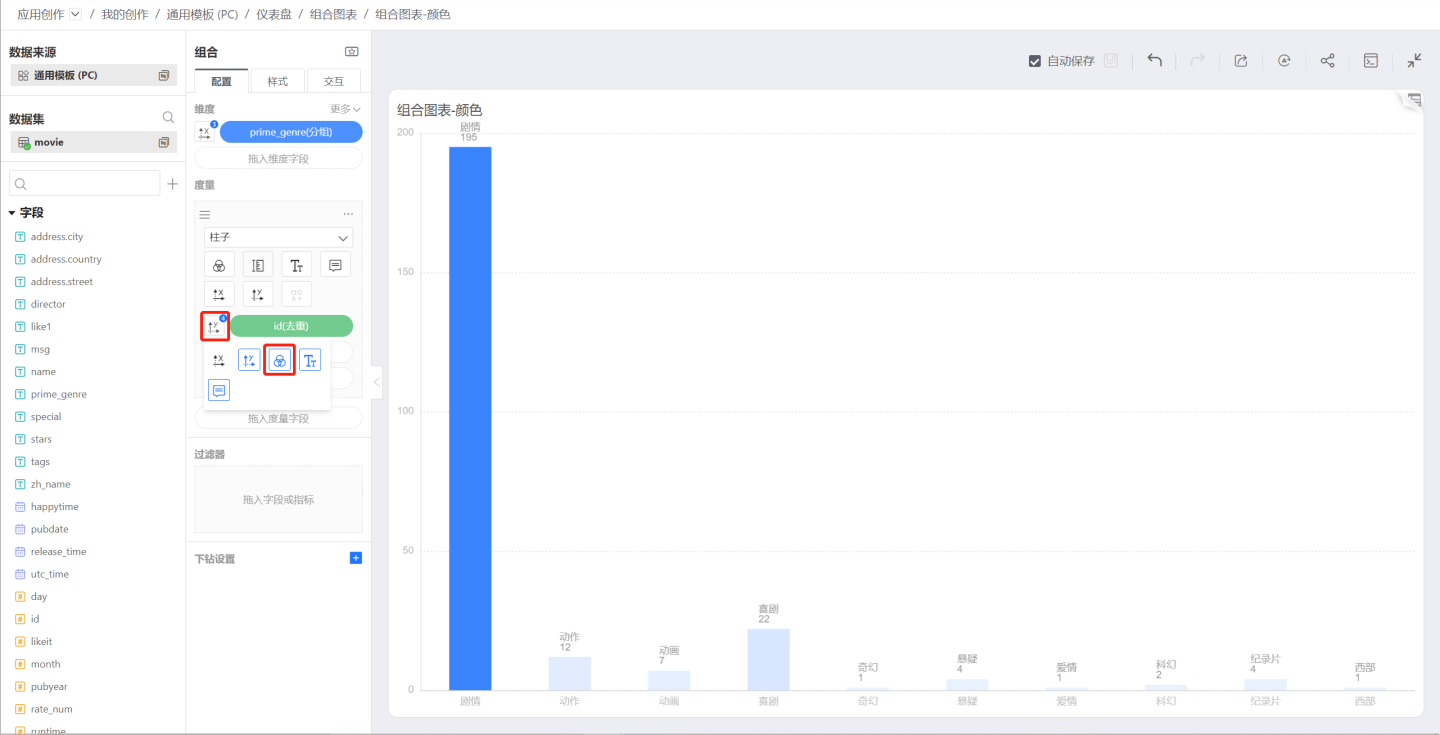
Continuous Color
To use a measure to control the chart color, click the icon on the left side of the measure to pop up the control menu, select the color icon, and the chart color will display a continuous gradient based on the measure value.
Size
The Size icon can control the size of various graphics, such as the thickness of columns, and the size of circles or rings.

Labels
Labels are used to set the display of labels. Additionally, various measures can be dragged in to control the label content.
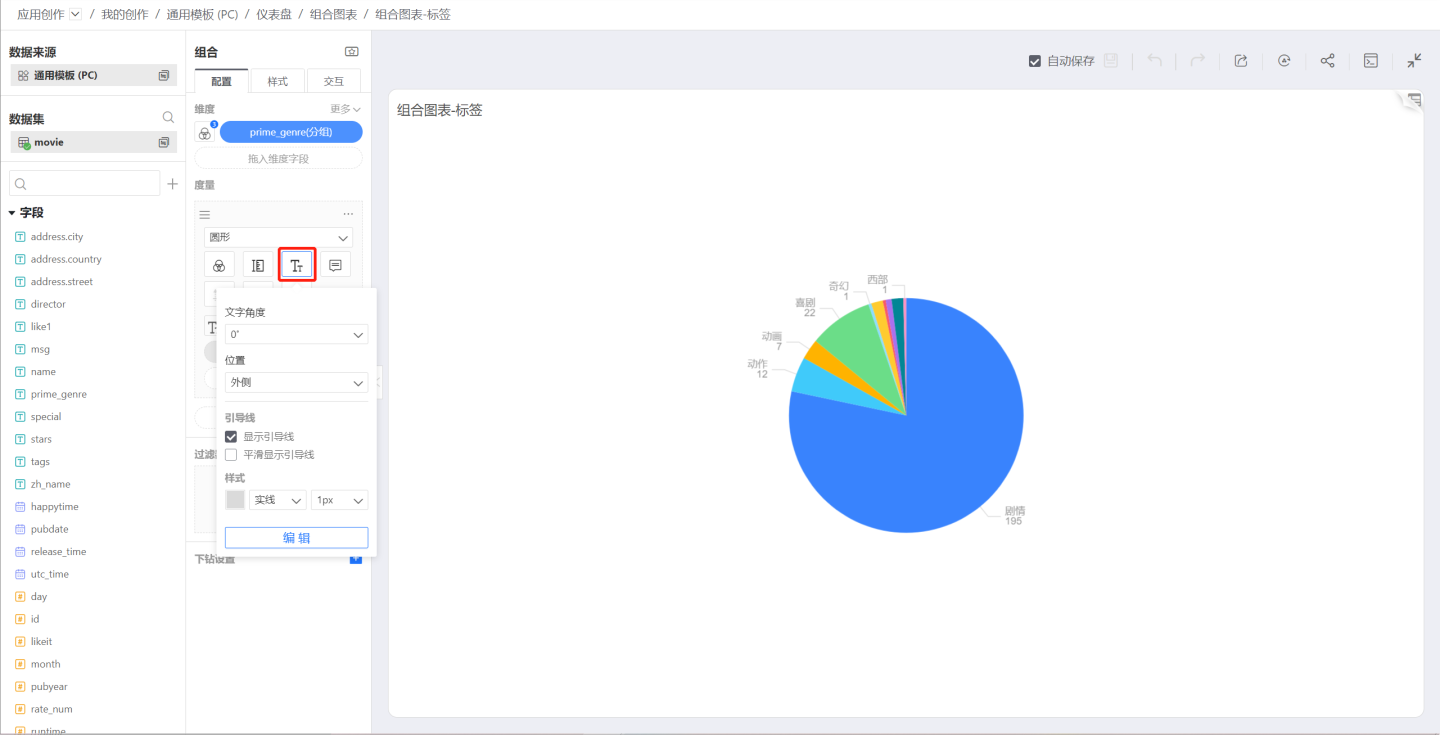
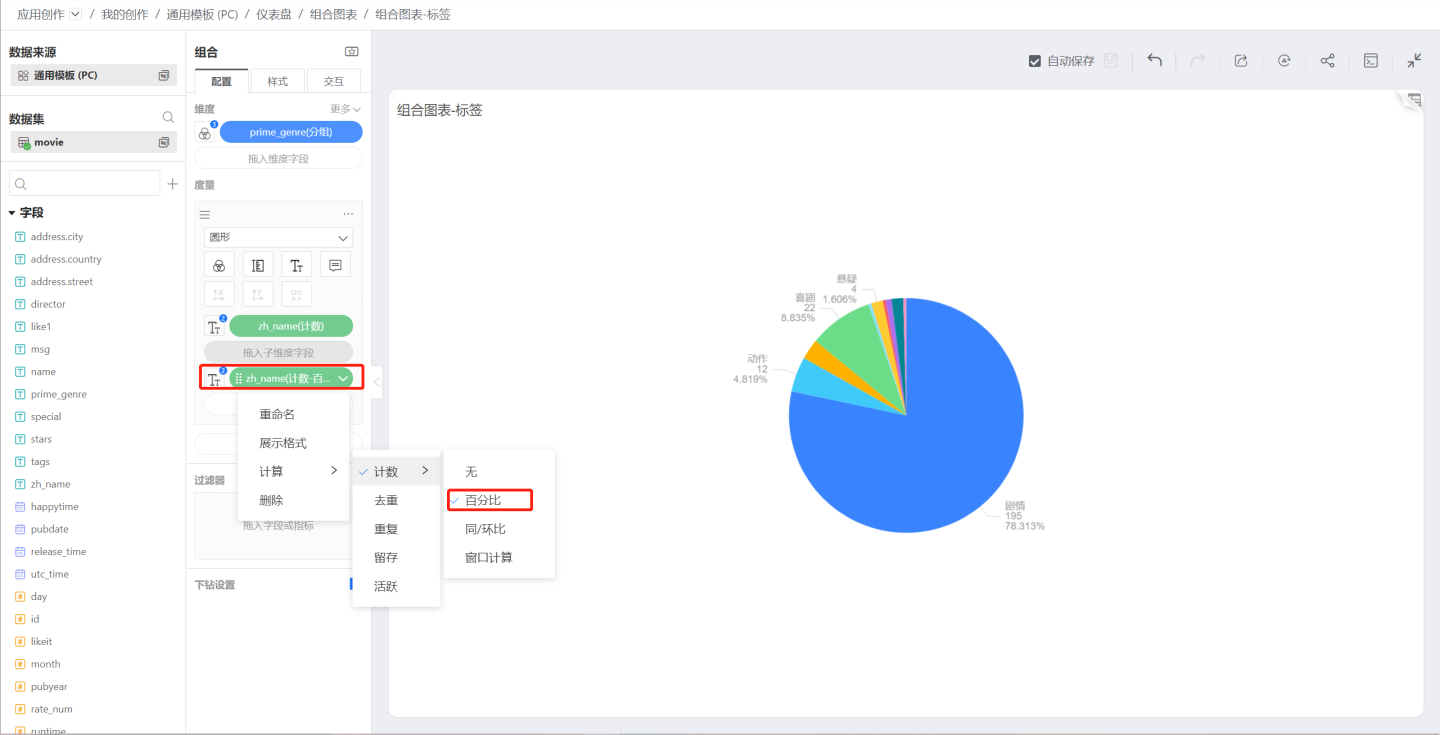
For example, in a pie chart, drag in a sub-measure, which is a count -> percentage, and the sub-measure does not control the element display but only Labels and Tooltips, so that both the measure and the measure percentage can be seen in the chart.
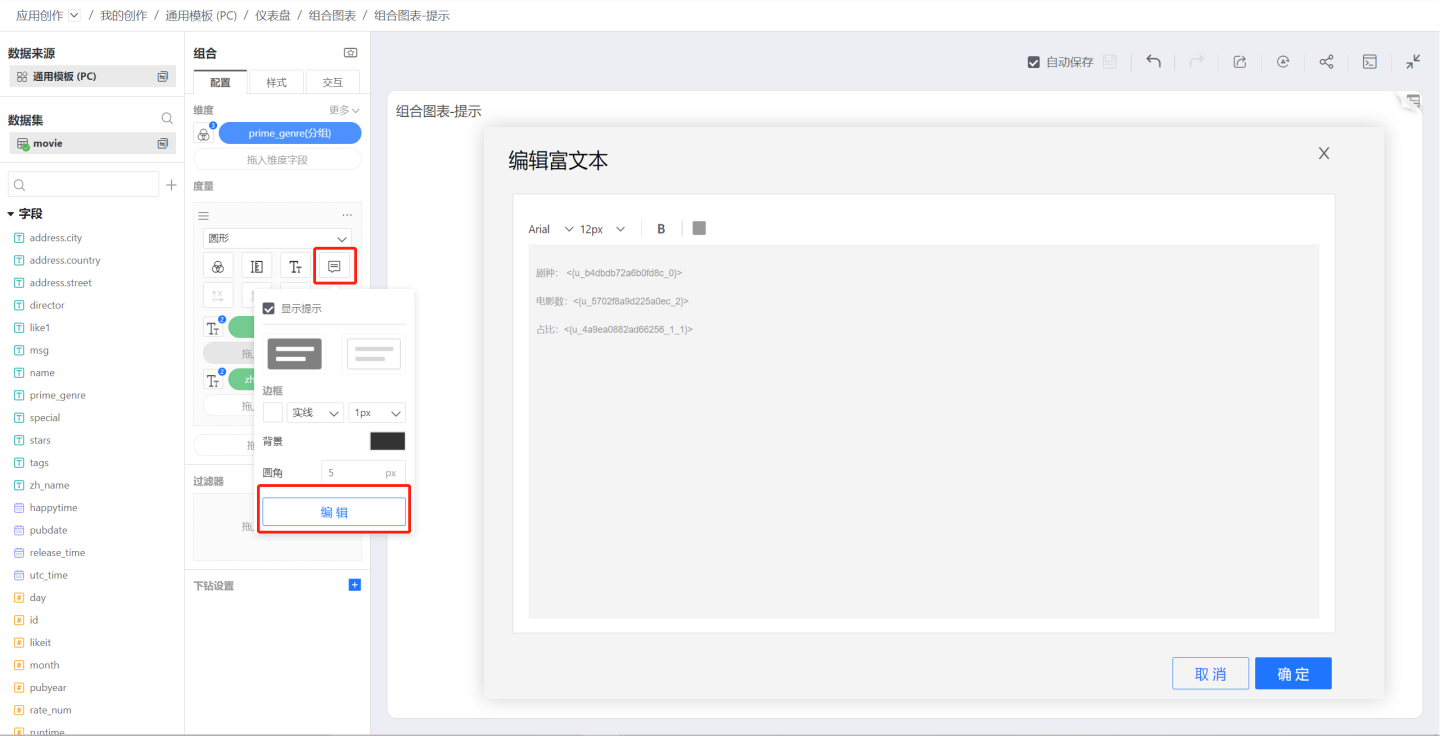
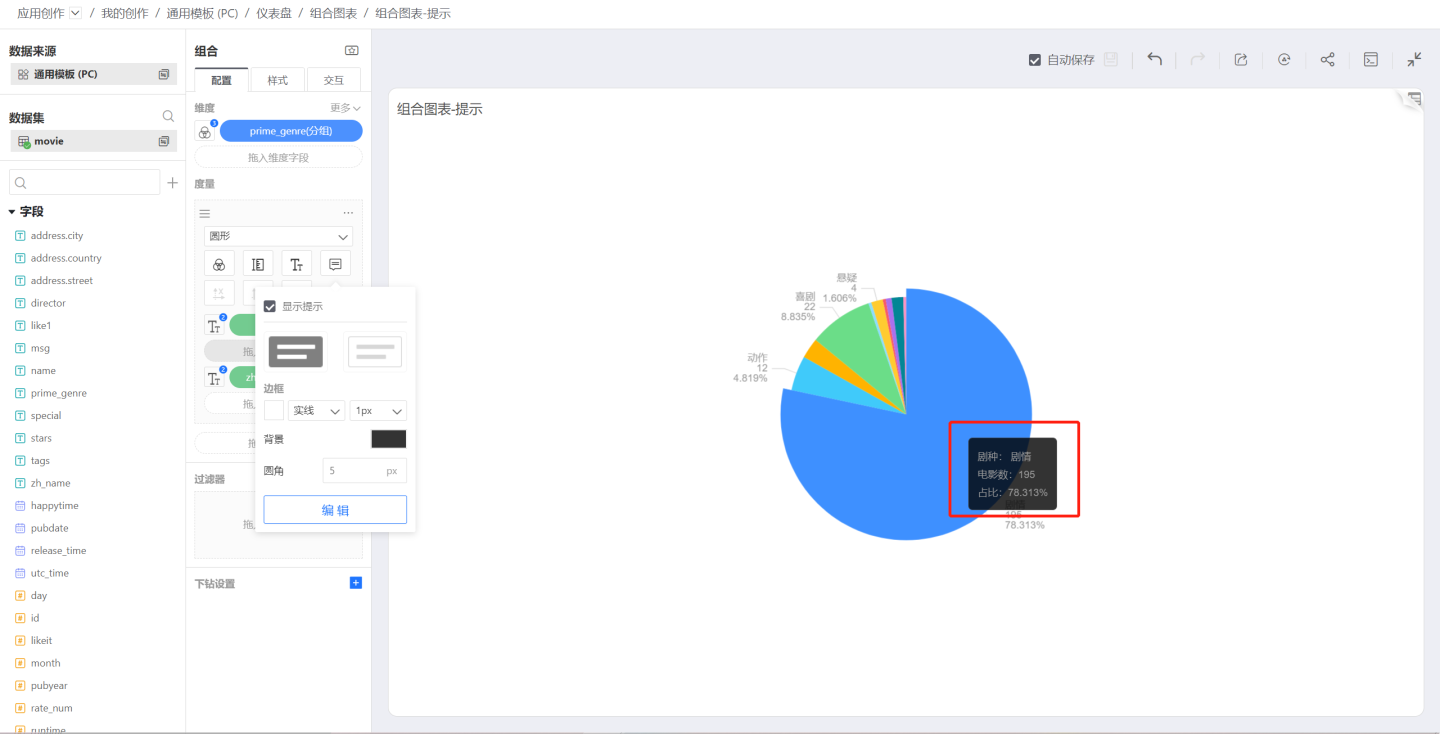
Tooltips
Tooltips are used to control the tooltip displayed when the mouse hovers over the chart. Like labels, sub-measures can be dragged in to add additional tooltips.
Symbols
When the graph is selected as a column, area, or shape, the Symbol icon will be enabled.
Symbols can control the shape of each data point. In the symbol list, custom symbols can be set.
The size of the symbols is controlled by the Size setting mentioned earlier.

Measure Operations
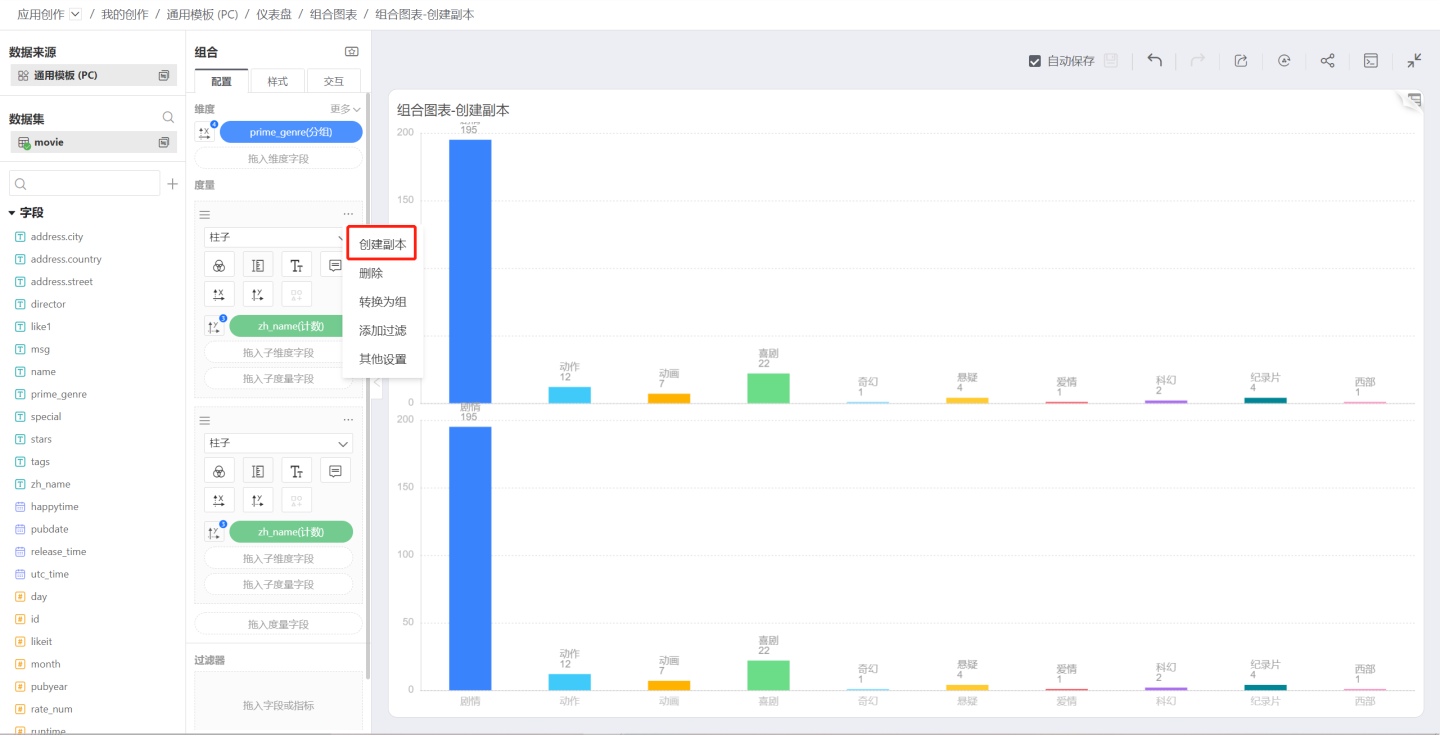
Click the three-dot menu in the upper right corner of the measure area to pop up the measure menu, including creating a copy, converting to a group, deleting, adding filters, etc.
Create Copy
Create Copy will create an identical measure that shares dimension settings with the original measure.
Convert to Group
Click Convert to Group in the measure menu to convert the measure into a group, with the default group name being Layer Group 0.
Join Group
After converting a measure to a group, click the menu of another measure, and Join Group will appear, allowing you to select the previously created group Layer Group 0. 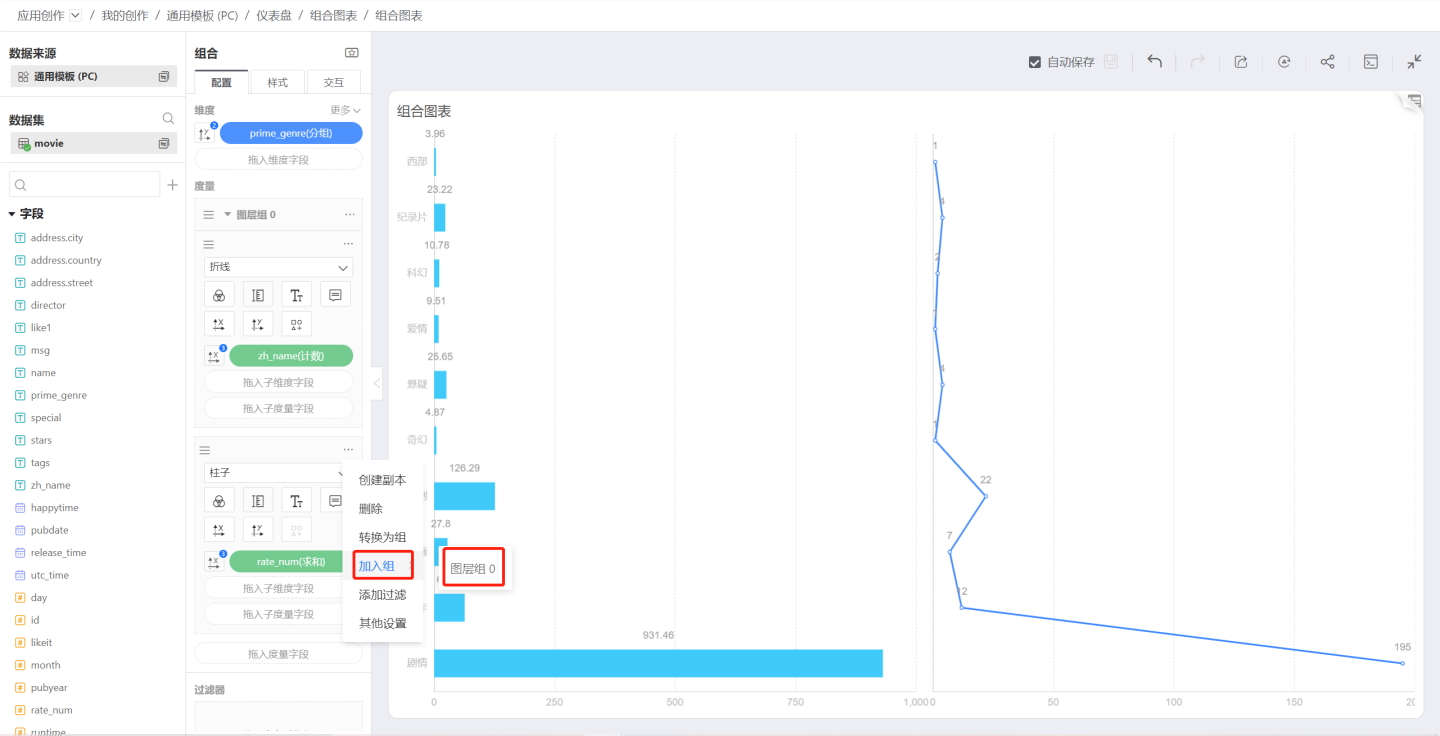
After joining the group.

Exit Group
In the layer group, click the three-dot menu in the joined measure and select Exit Group. After exiting the group, the measure becomes an independent measure and plots separately:
Add Filter
This function is the same as the measure filtering function in other charts, allowing individual measures to be filtered.
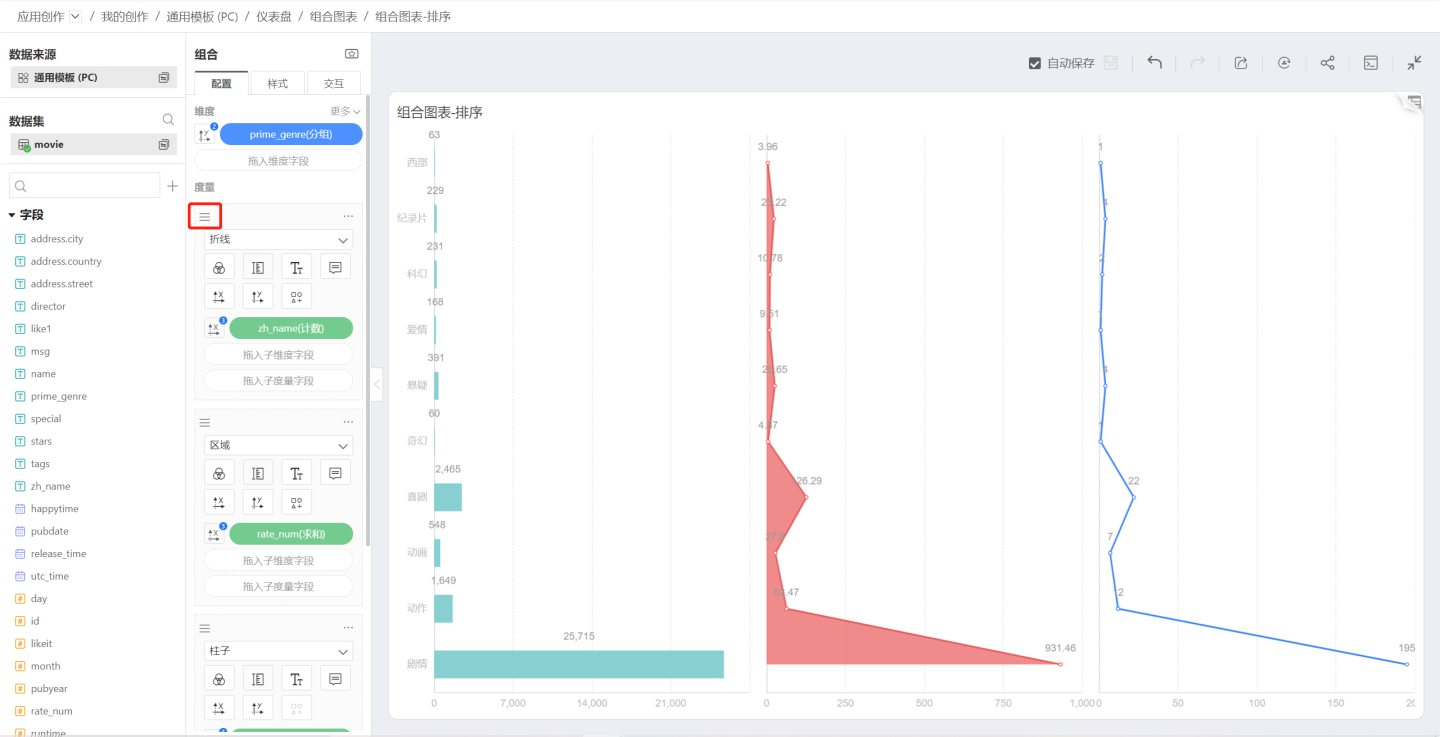
Measure Sorting
You can drag the sorting icon in the upper left corner of each measure to sort the measure graphics.
Sub-Dimension
Dragging a sub-dimension into the measure will divide the measure, generating stacked column charts, stacked area charts, etc., based on the graphic settings.
Sub-Measure
Dragging a sub-measure into the measure allows the sub-measure to control Colors, Labels, Tooltips, and can also control the X or Y axis. However, at this point, other measures within the measure cannot control the X or Y axis. In other words, whether it is a measure or a sub-measure, only one measure can control the plotting.
Layer Group Menu
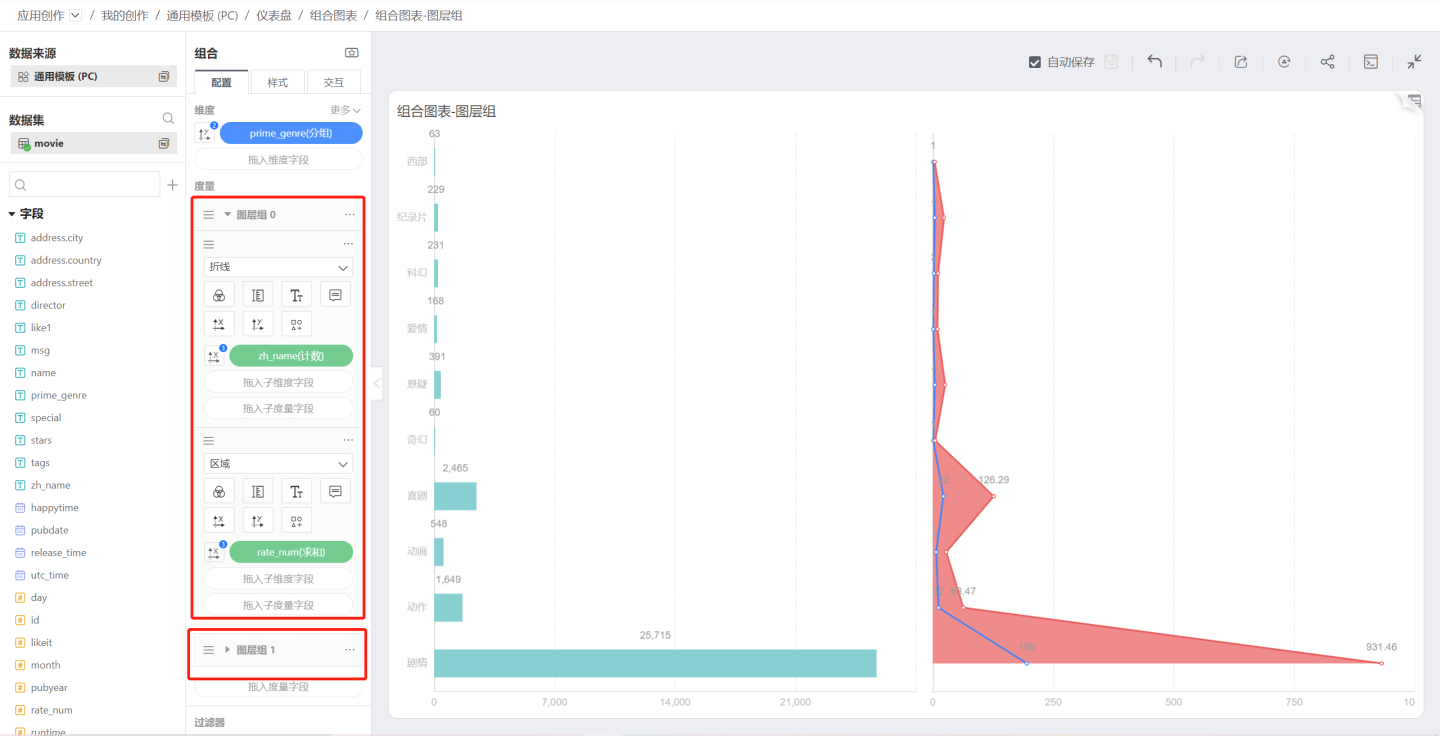
Modify Name
You can modify the layer group name to a more user-friendly name.
Create Copy
Create a layer group that is identical to the original layer group.
Merge Mode
Click the three-dot menu of the layer group to pop up the Merge Mode menu, which controls the merge mode between measure graphics within the group.
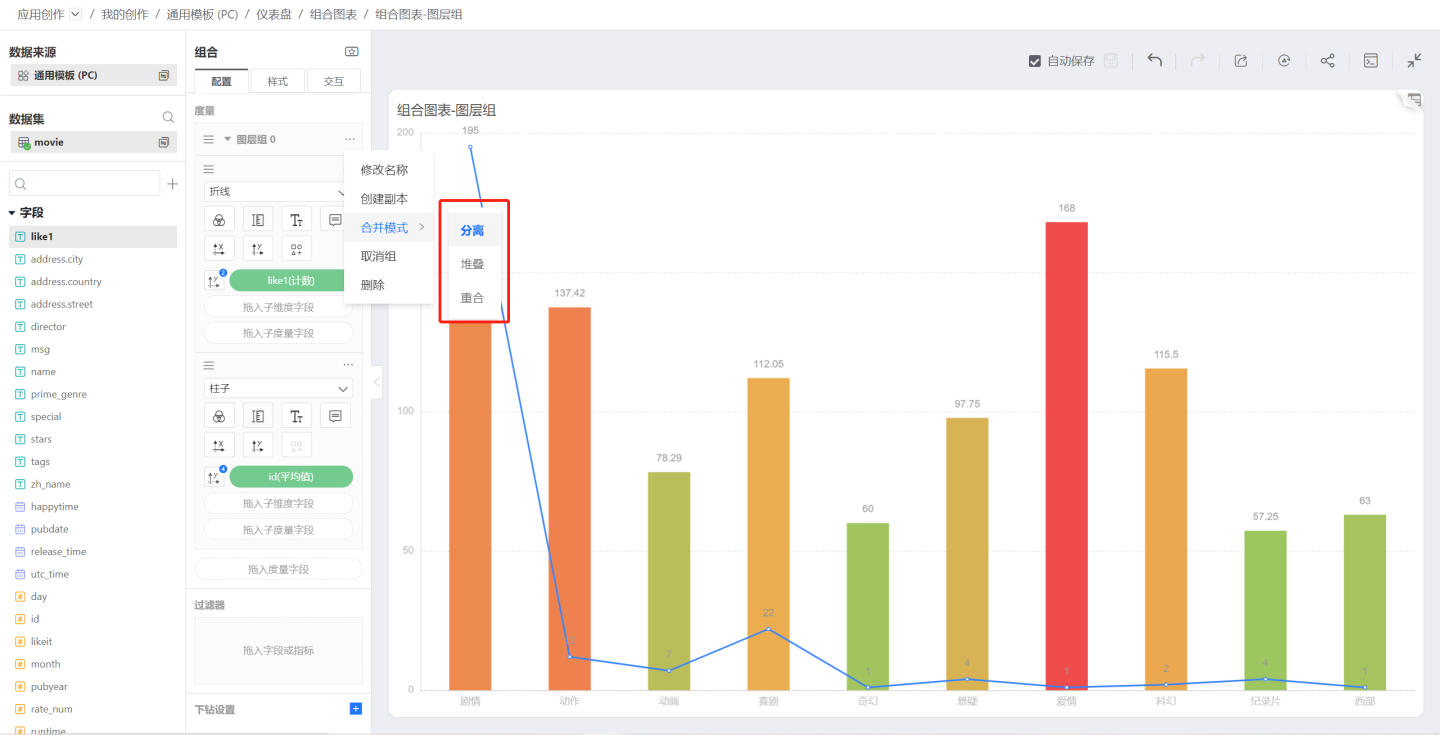
Separate
After joining the group, the default merge mode is Separate, and the two column charts merge to become clustered column charts: 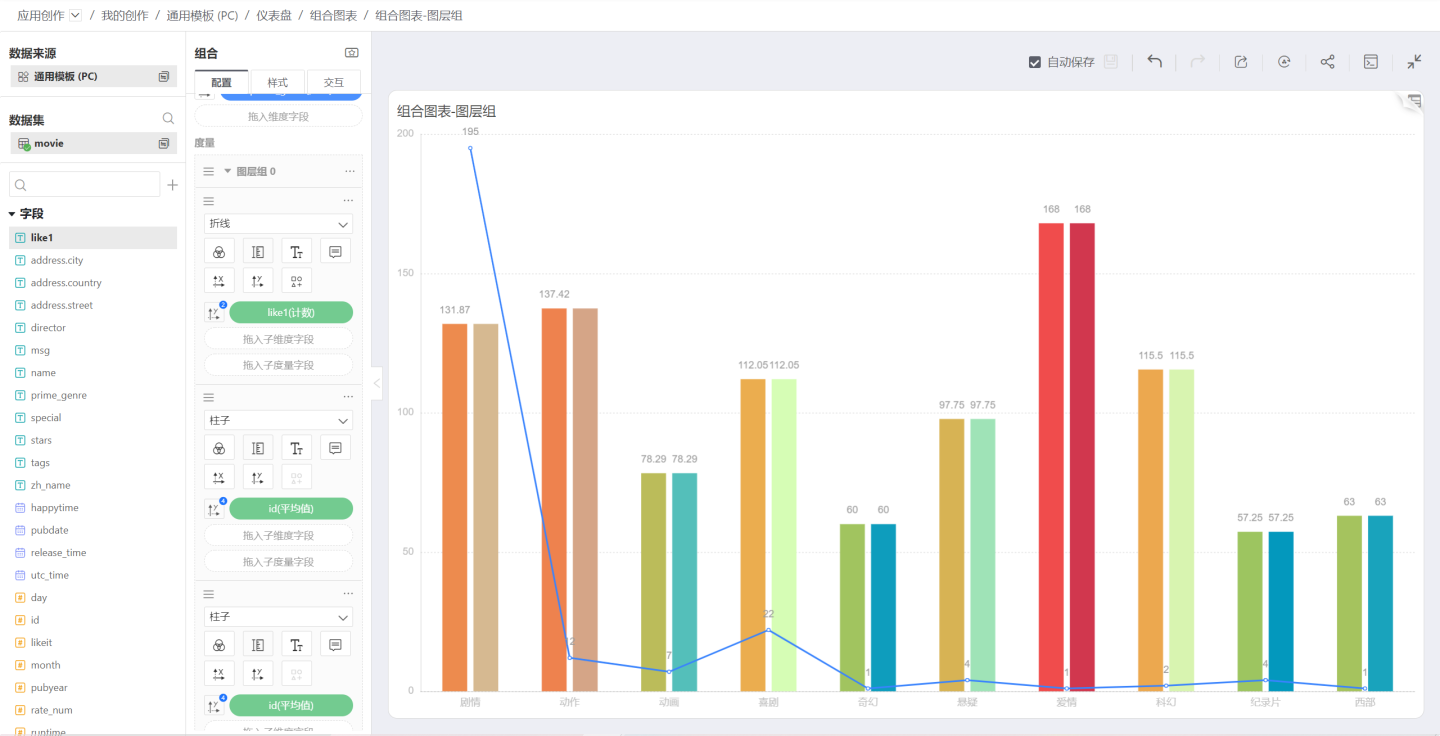
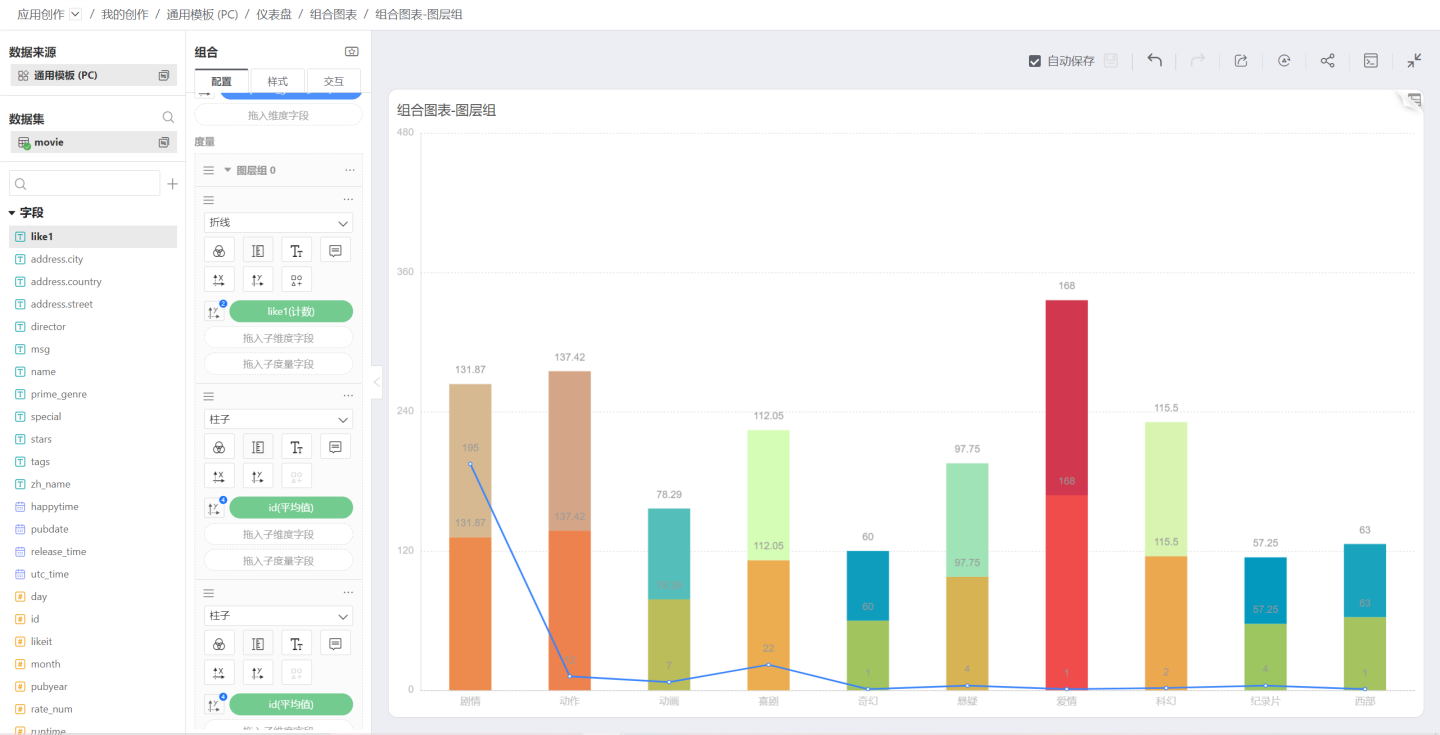
Stack
When the merge mode is selected as Stack, the two column charts merge to become stacked column charts. At this time, the dimension controlling the color needs to be canceled, and each measure controls its own color:
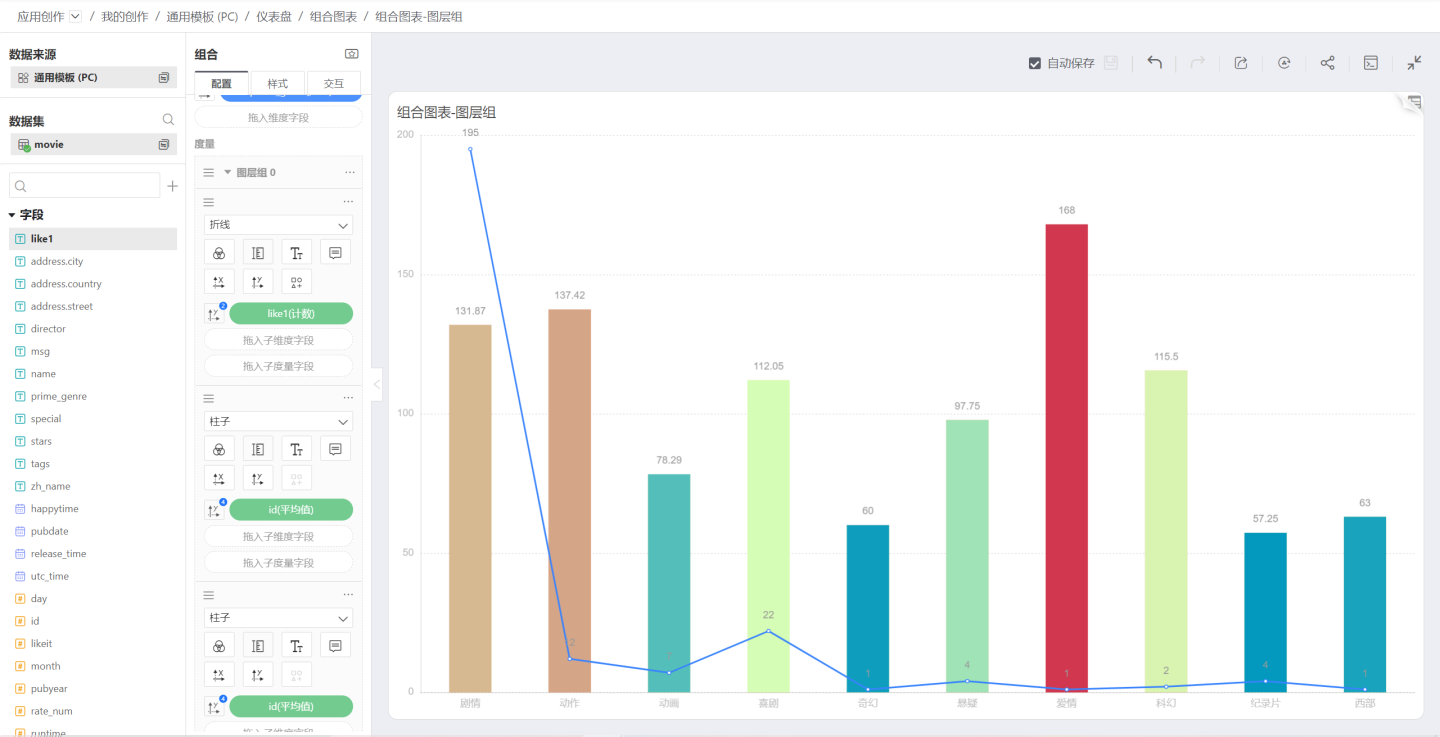
Overlap
When the merge mode is selected as Overlap, the measures will overlap each other. Below is the effect of two area charts overlapping:
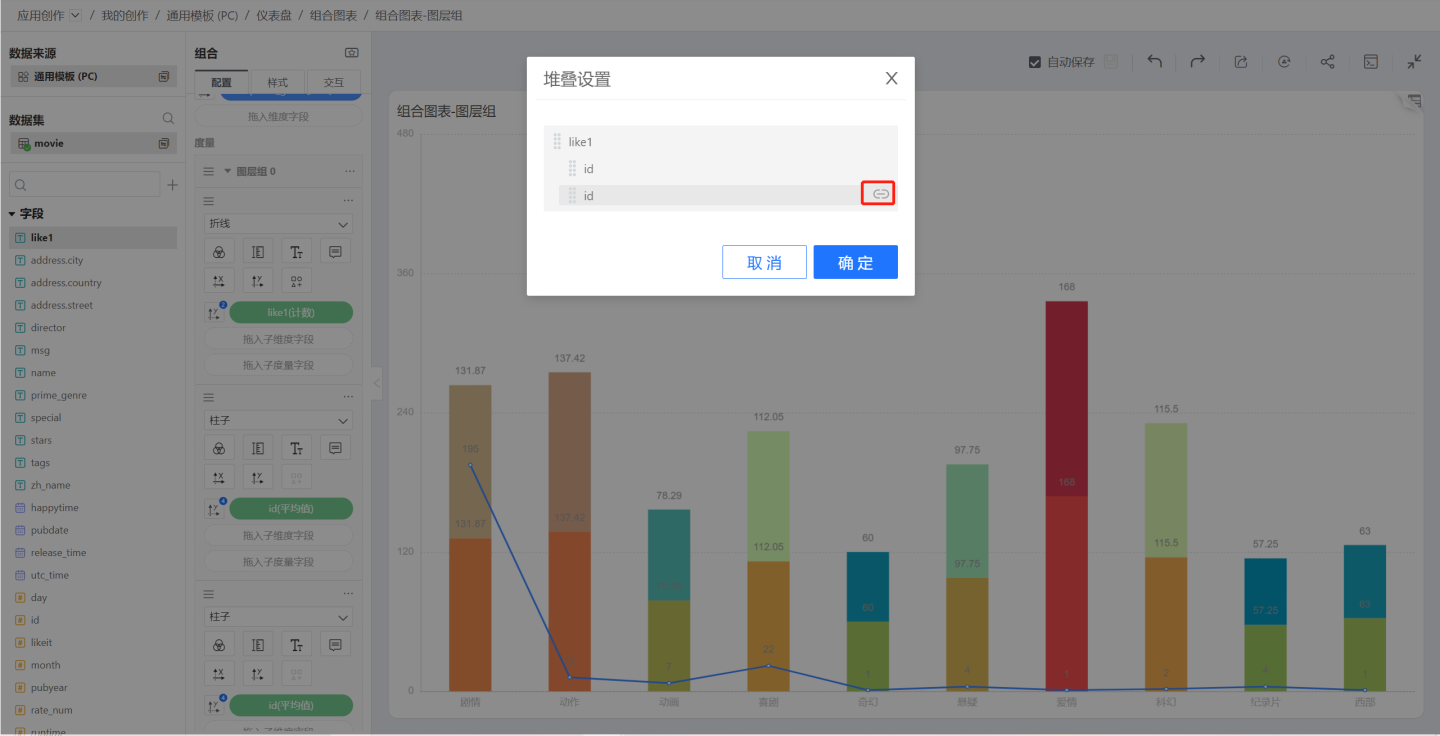
Stack Settings
When the merge mode between the measures in the layer group is Stack, the Stack Settings will appear in the layer group menu. Stack settings control the stacking relationship between the layers, such as having 5 columns, you can stack the first on the second, and the third and fourth on the fifth.
Click the Stack Settings menu of the layer group to pop up the Stack Settings window, and click the indent icon to control whether to stack.
In the figure below, the columns of two IDs are stacked.
Join Group
If there are multiple layer groups, Join Group will appear in the layer group menu, allowing you to select other listed groups and add the content of the current group to the selected layer group.
Ungroup
You can click the three-dot menu of the layer group and select Ungroup, and then the entire group will be scattered, all measures will revert to independent measures, and the Merge Mode will no longer take effect.
Delete
Delete all content of the selected group. If you want to restore after deletion, you can click the back button of the chart.
Layer Group Sorting
You can drag the sorting icon in the upper left corner of the layer group to sort between layer groups.