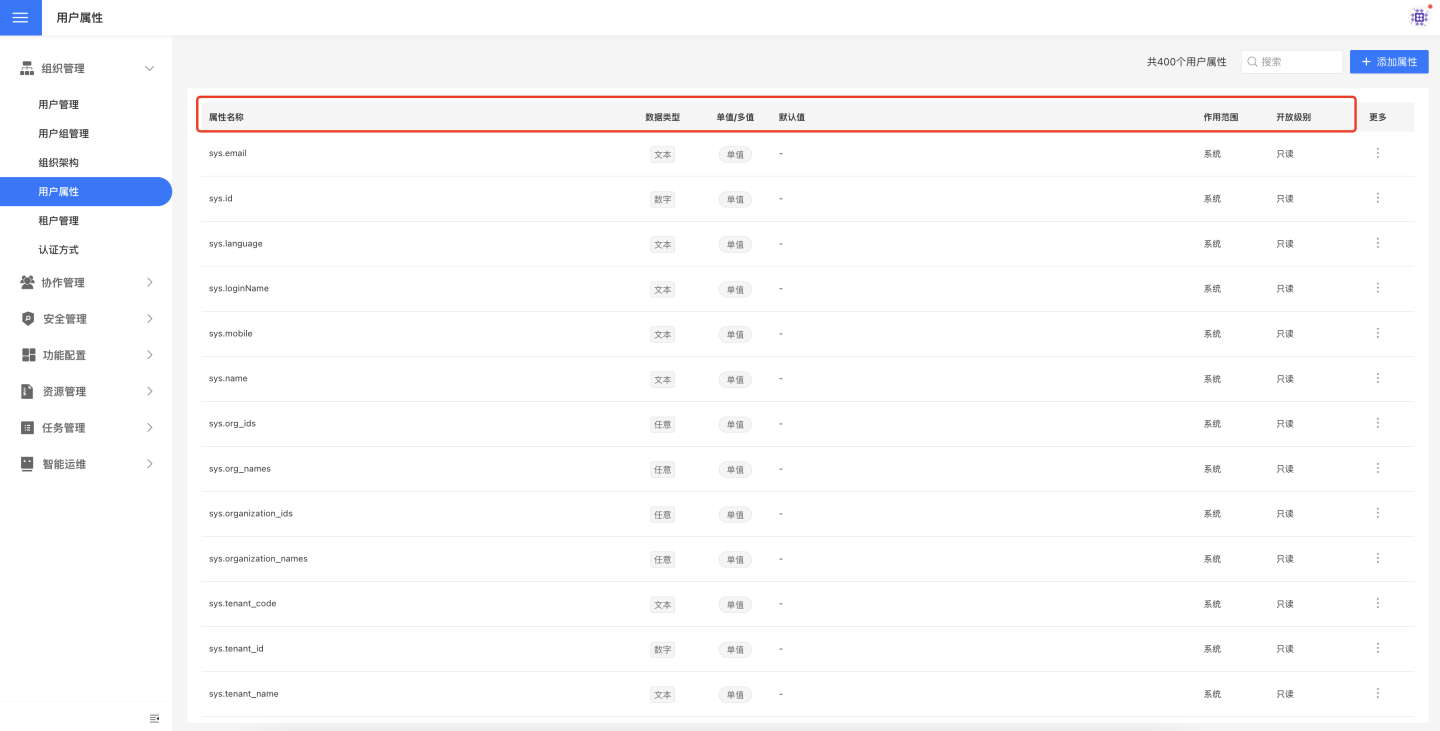
User Attributes
User attributes are the characteristics possessed by each user, and the attribute values may vary among different users. On the user attributes page, you can view the list of all attributes associated with a user.
First, let's introduce the basic concepts related to user attributes, including attribute categories, data types, scope of application, and access levels.
User Attribute Categories
User attributes include system attributes and custom attributes.
System Attributes
System attributes are prefixed with sys., and are provided by the system. These attributes cannot be added, edited, or deleted.
Custom Attributes
Custom attributes are attributes added by users themselves. They support CRUD operations, meaning they can be added, viewed, edited, and deleted.
User Attribute Types
The data types of user attributes include the following:
- Text: Replace user attribute operations with text strings.
- Number: Replace user attribute operations with numeric strings.
- Date: Replace user attribute operations with date strings.
- Any Type: Can be converted to any type, such as entering
[1,2,3]in the user attribute value to use as an array.
User Attribute Scope
In a multi-tenant scenario, sometimes the platform needs to manage tenant attributes uniformly. This can be achieved by setting the scope of user attributes. The scope options are as follows:
- Internal: User attributes with an internal scope can only be used within the tenant or by the platform itself internally. They cannot be used across tenants, and tenants are isolated from each other.
- Global: User attributes with a global scope can be used internally by the platform. More importantly, the platform can set their values for different tenants, and tenants can access these values within their own environment.
After the platform administrator creates an attribute with a global scope, they can set the attribute value for individual tenants on the tenant editing page. Once this is done, all users under that tenant will have this attribute value.
User Attribute Access Levels
In multi-tenant or multi-organization scenarios, data may be stored in different database instances, different databases, different schemas, or different tables. In such cases, user attributes can typically be used to dynamically connect to these different databases.
However, for certain information like passwords, we do not want regular users to view attribute values. This is where the access levels of attributes can be used for control.
- Read-Only: User attributes with a read-only access level have their values accessible to each user. Each user can view their own attribute values and use them in most analysis scenarios.
- Hidden: User attributes with a hidden access level have their values inaccessible to regular users. Regular users cannot see the specific values. Typically, such hidden attributes can only be used in data connections. They cannot be used in datasets, charts, or dashboards.
User Attribute Related Operations
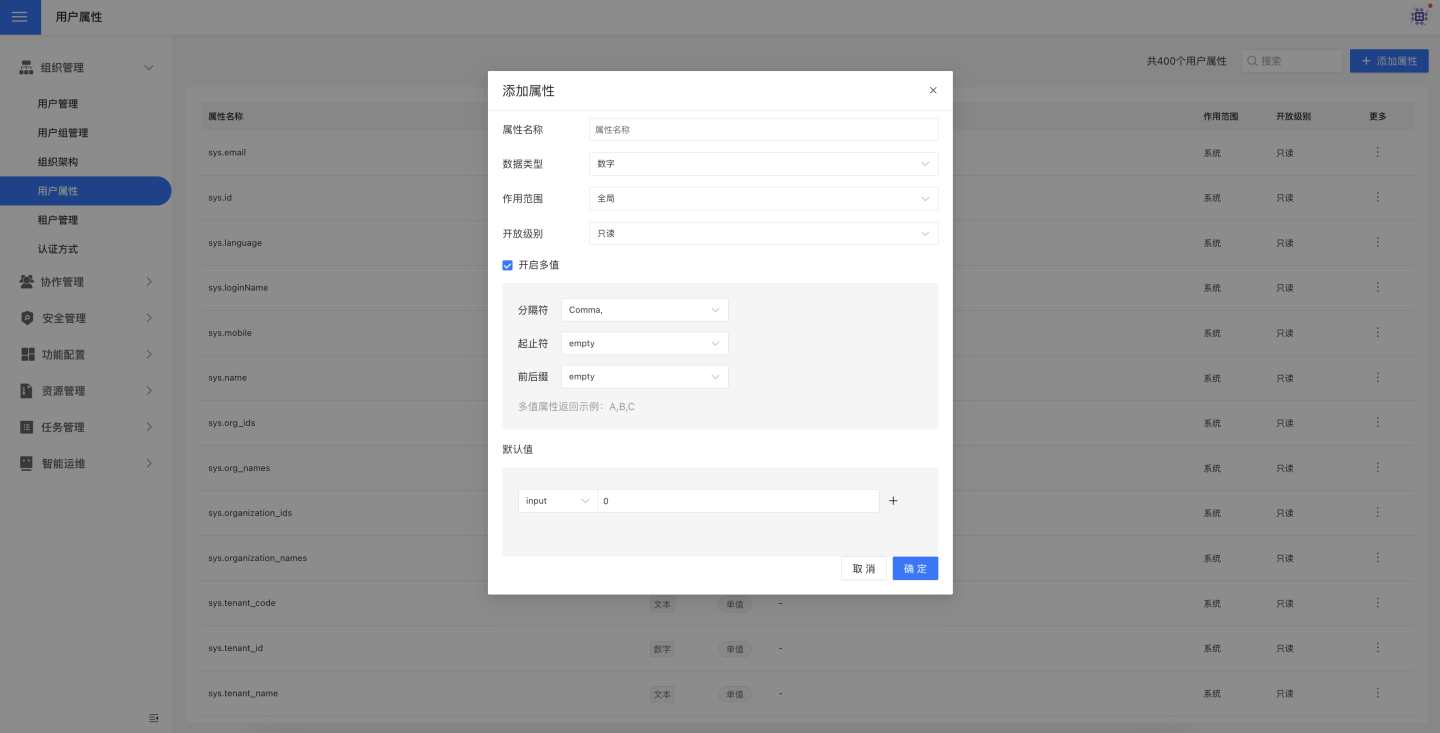
Add User Attributes
Click "Add Attribute," then enter the attribute name, type, scope, access level, and manually input the default value for the attribute in the popup window. It supports setting empty values and NULL values. User attributes allow multi-value settings.
Note
- In tenant management, both platform administrators and tenant administrators can define user attributes. The definition of user attributes is not isolated, and once defined, all administrators can view them.
- Once the multi-value feature is enabled, it cannot be modified again. For example, if multi-value is enabled when adding a user attribute, it cannot be disabled later. Similarly, if it is not enabled initially, it cannot be enabled later.
View User Attributes
You can view detailed information about custom attributes, and it also supports viewing the values of custom attribute settings for each user.
Edit User Attributes
User attributes can be edited and modified. Click the edit page on the right side of each attribute to edit custom attributes. Custom attributes only support modifications to scope, access level, and default value.
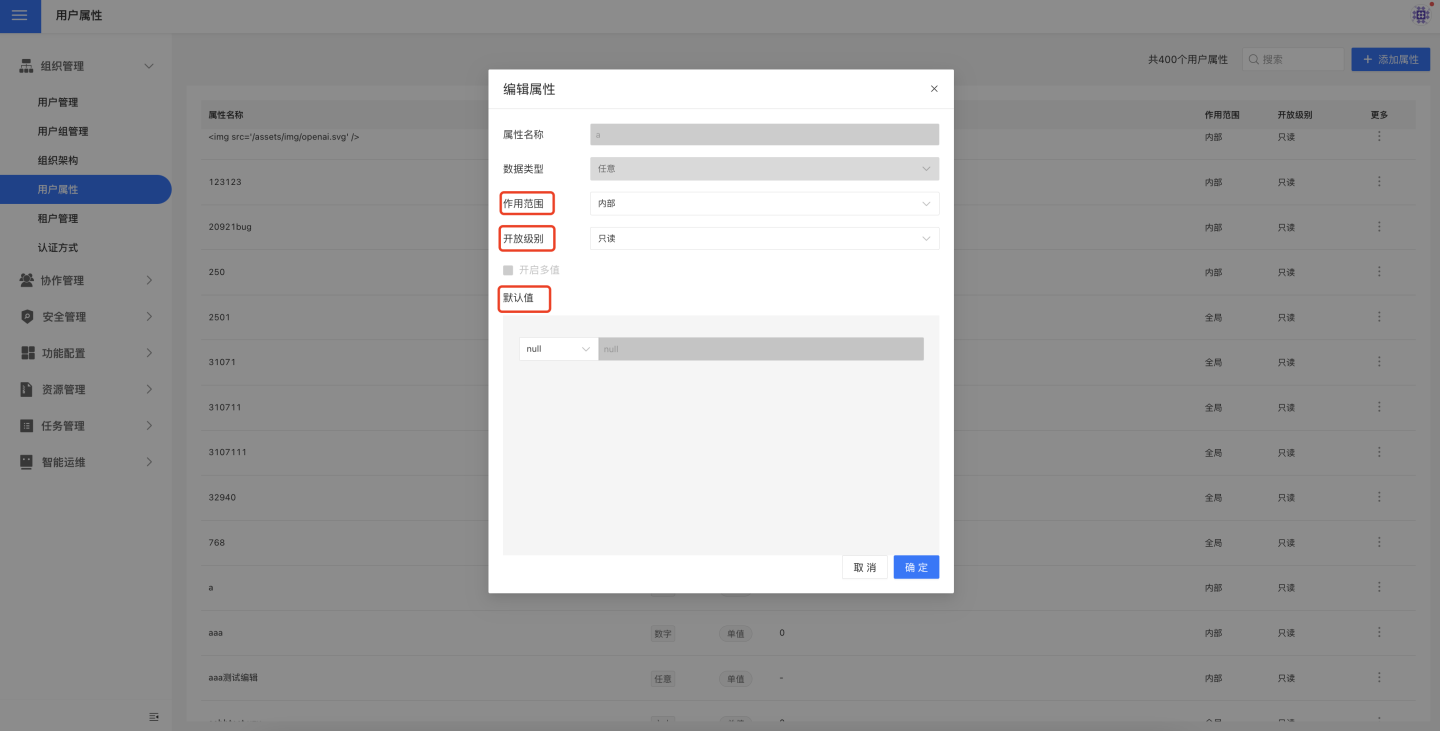
The specific values of each user's own attributes can also be modified. When viewing a user and locating the specific attribute value, simply click to modify it.
Delete User Attributes
Click the delete button on the right side of the user-defined attribute to remove the user-defined attribute. The user attributes within the user will also be eliminated simultaneously.
User Attribute Usage Scenarios
Users can utilize user attributes in the following scenarios:
- Creating data connections
- Selecting tables for direct connection datasets
- Creating SQL query data
- Setting filter conditions for datasets
- Defining expressions for new fields and new metrics
- Using filters in charts and dashboards
- Configuring reference lines
- Managing access control
User attributes have a wide range of applications. Below are some typical usage scenarios.
Usage of User Attributes
| Purpose | HE | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| User Attribute | {“kind”: “attr”, “op”:”User Attribute Name”} | {{$User Attribute Name}} |
| User Attribute Value | {{$$User Attribute Name}} |
Tip
User attributes use a single dollar symbol, while user attribute values use a double dollar symbol. When using {{$User Attribute Name}}, the backend will convert it into an HE expression, and quotes are not required during usage. When using {{$$User Attribute Name}}, the backend will directly query the value of the user attribute and perform text replacement. Quotes can be added as needed. In HENGSHI's advanced expressions, such as expressions for adding fields/metrics, chart filter expressions, and new dataset filter expressions, you must use {{$User Attribute Name}}. When creating data connections or SQL query datasets, you must use user attribute values: {{$$User Attribute Name}}.
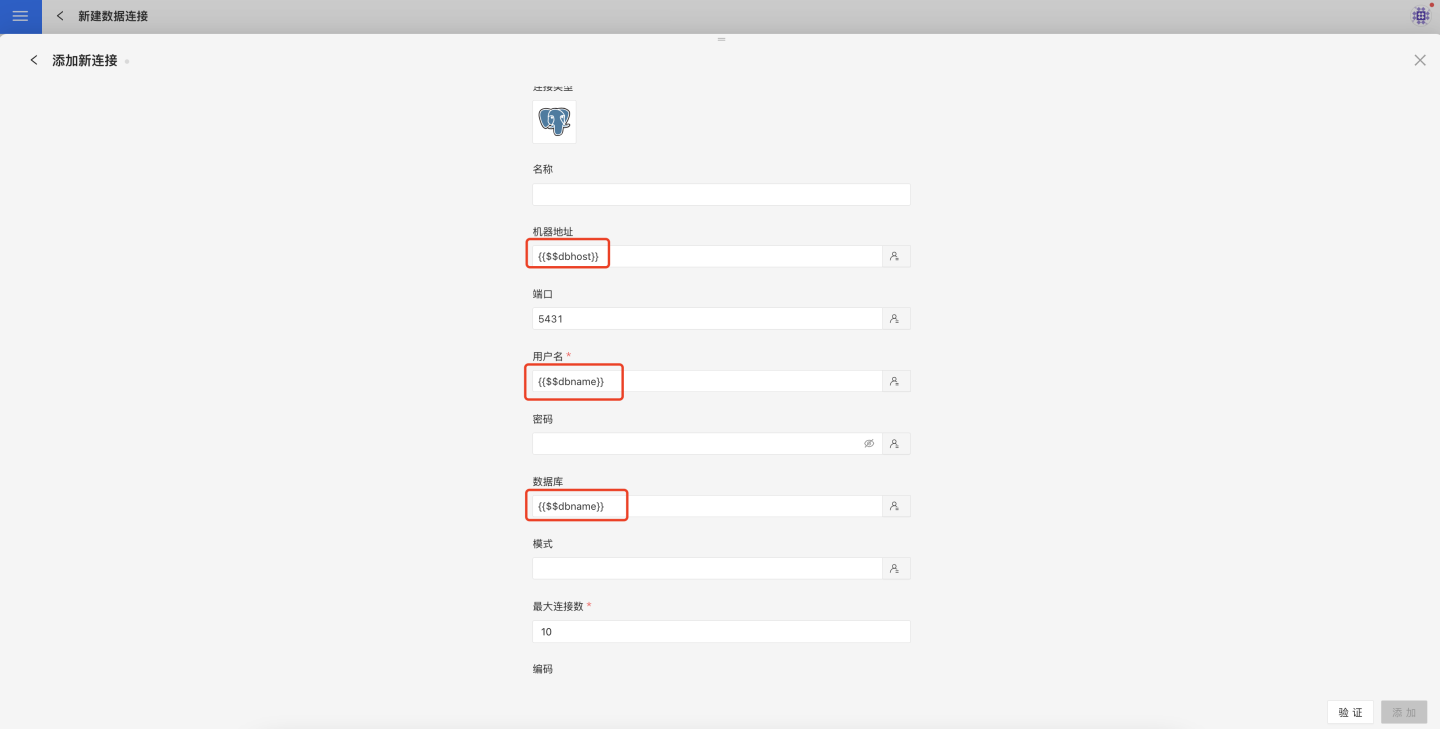
Using User Attributes When Creating Data Connections
User attributes can be used when creating data connections, but parameters cannot, as parameters belong to the app, while user attributes belong to the system.
When creating a connection, you must use the format User Attribute Value {{$$UserAttributeName}}.
When creating a connection, only the user password cannot use user attributes; all other fields can use user attributes. The user password is taken as entered, without conversion or calculation.
In the diagram, both dbhost and dbname are user attributes.
Use User Attributes in the Filter Conditions of a New Dataset
Simple filtering using user attributes:
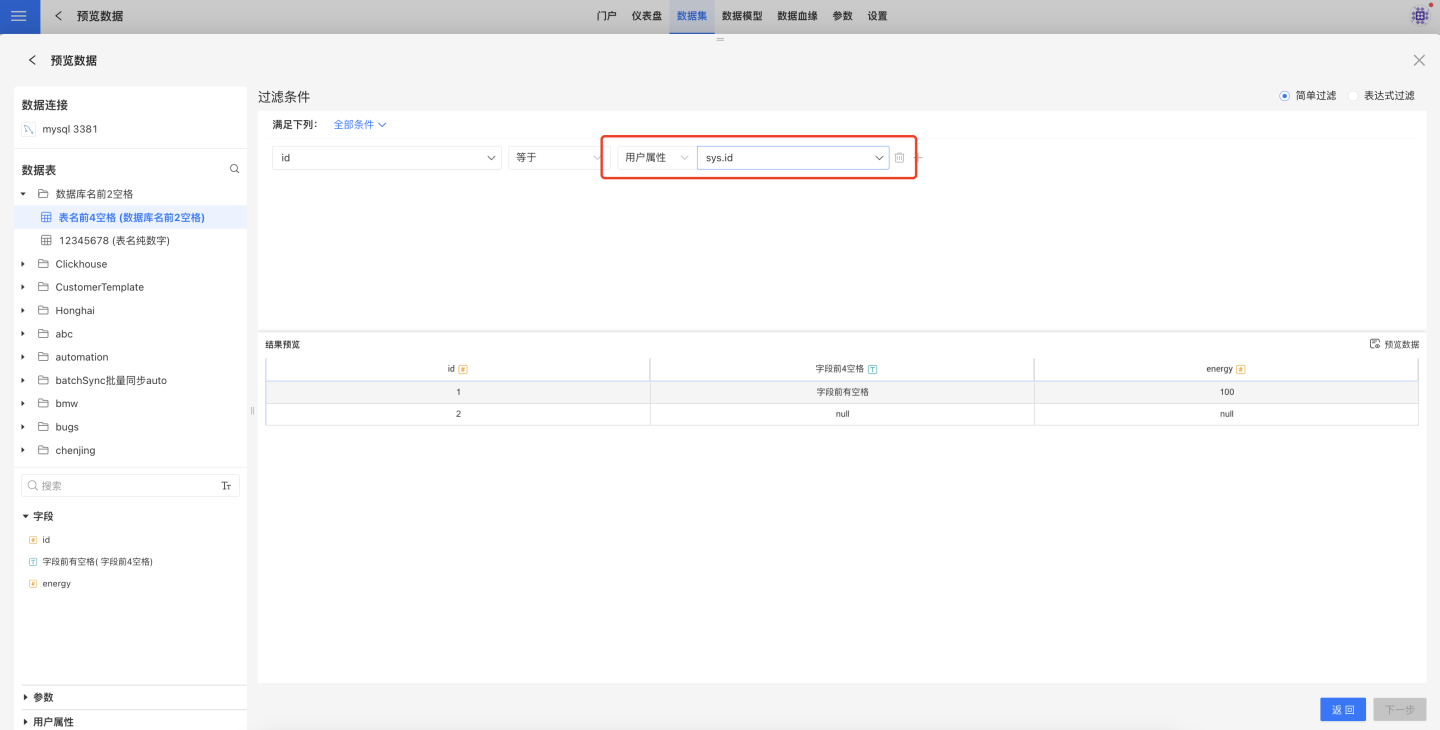
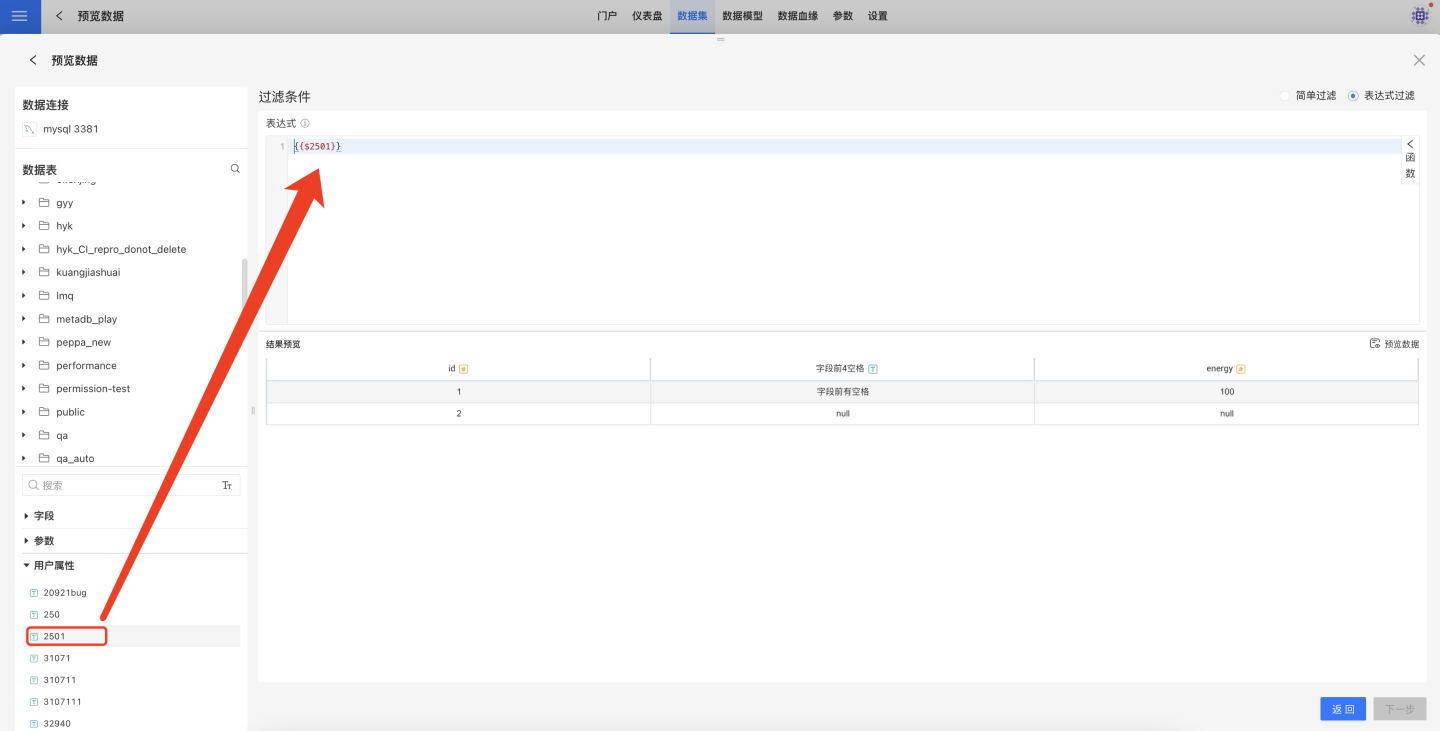
Expression filtering using user attributes must be in the form of {{$UserAttributeName}}:
Using User Attributes When Creating SQL Query Datasets
When creating SQL queries, you must use the User Attribute Value in the form of {{$$User Attribute Name}}:
select * from movie where id > {{$User Attribute Name}}
select * from {{$User Attribute Name}}Use User Attributes When Creating Fields/Measures
When creating fields or measures, you must use the User Attributes format {{$UserAttributeName}}:
{price} + {{$UserAttributeName}}Using User Attributes in Filter Expressions
In chart filter expressions, you must use the User Attributes in the form of {{$UserAttributeName}}:
{region} = {{$UserAttributeName}}