SQL Query Dataset
SQL Query Dataset refers to a type of dataset that retrieves data by defining dataset conditions through custom SQL statements.
Create Dataset
Follow the steps below to create an SQL query dataset.
In the dataset interface, click "New Dataset" and select "SQL Query Dataset."
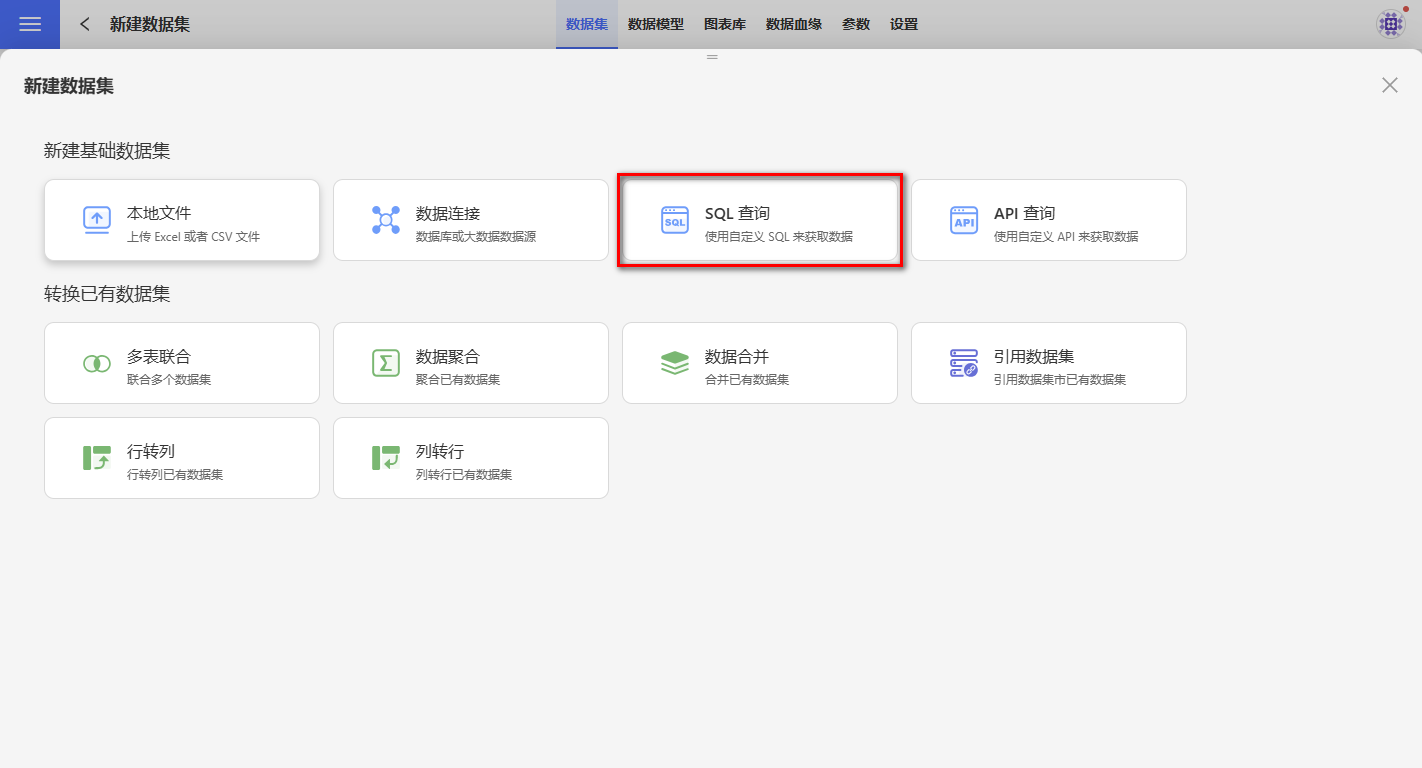
Select the data connection to be used for creating the dataset.
Tip
If the desired data connection is not found, contact the data administrator to authorize the required
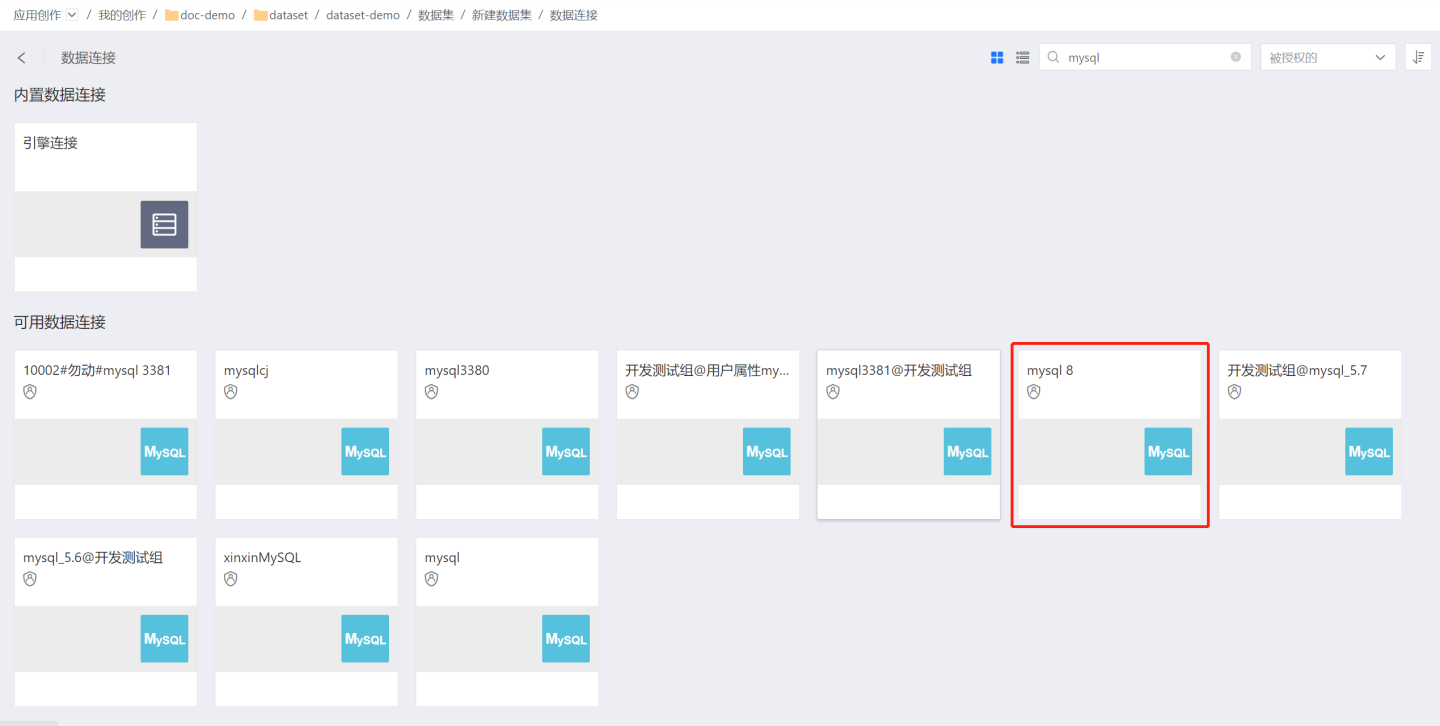
Data Connectionfor use.Write SQL code in the editor to define dataset conditions. Click "Execute" to view the results, and after confirming there are no issues, click "Next."
Tip
Each time the SQL statement is modified, you need to click "Execute." Only after successful execution can you proceed to the next step.
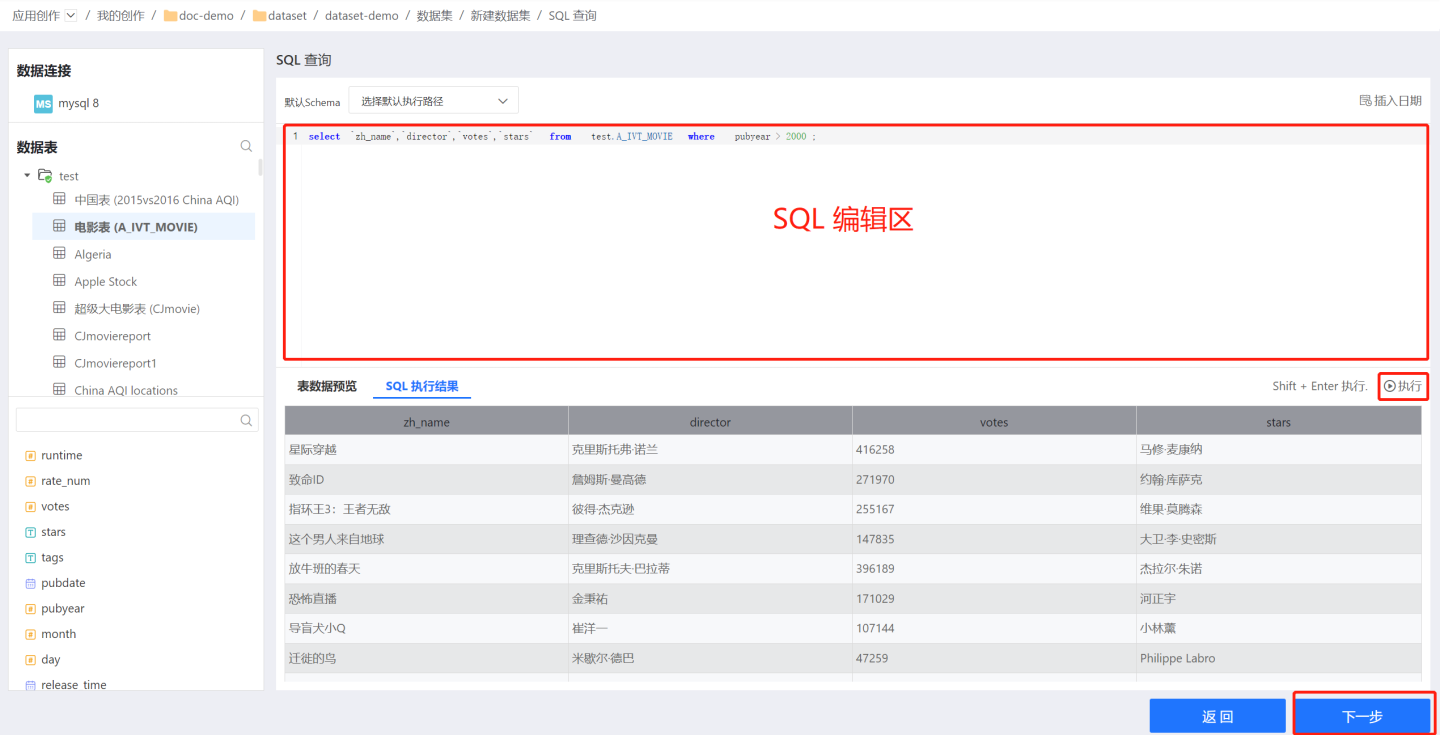
Enter the data structure page, where you can set field aliases and types.
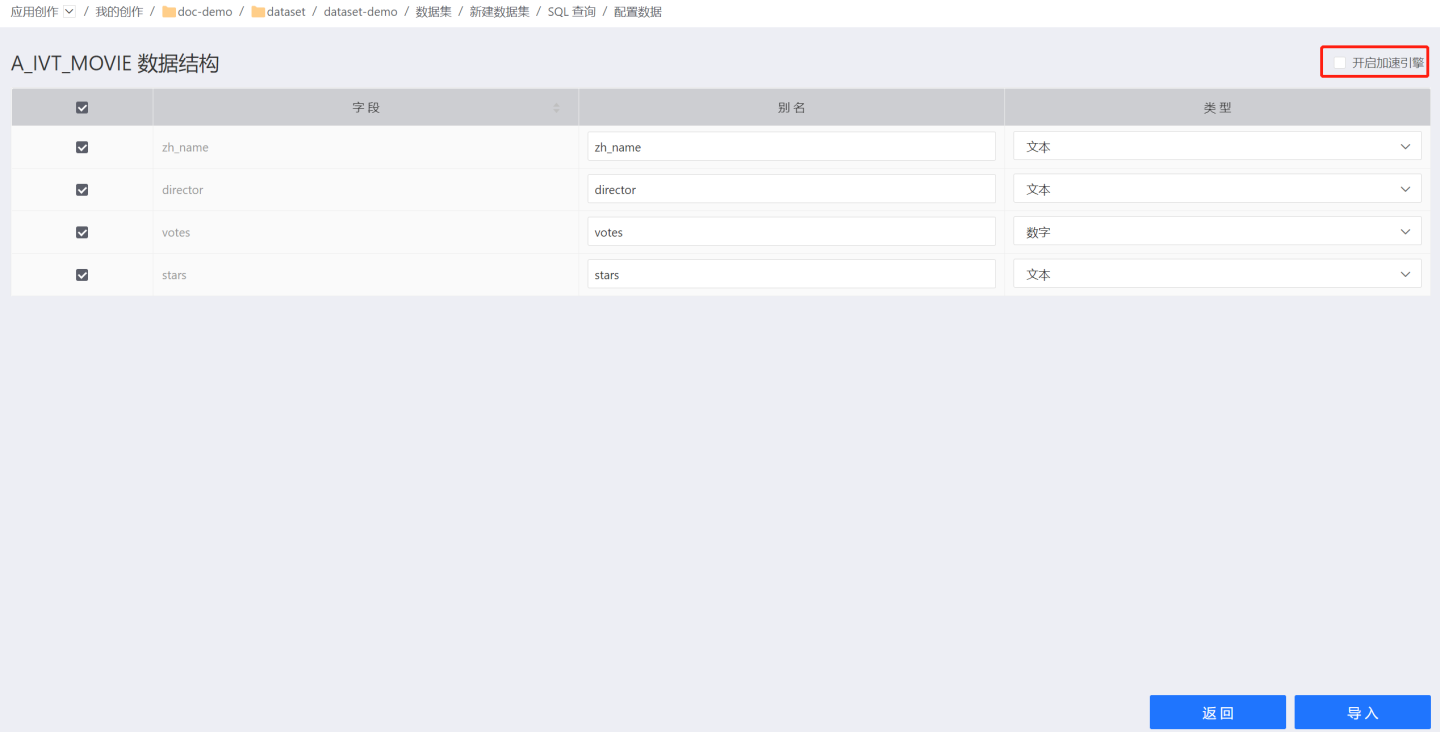
You can enable the acceleration engine, which imports the dataset into the acceleration engine upon activation.
After clicking "Import," set the dataset name to complete the dataset creation.
Dynamic Macros
SQL query datasets support dynamic macros, allowing the creation conditions of datasets to be defined dynamically. The content of the dataset changes along with the dynamic macros.
Dynamic Macro Definition Method
Dynamic macros start with {{!! and end with }}. The code in between is of SQL type, as shown in the figure.
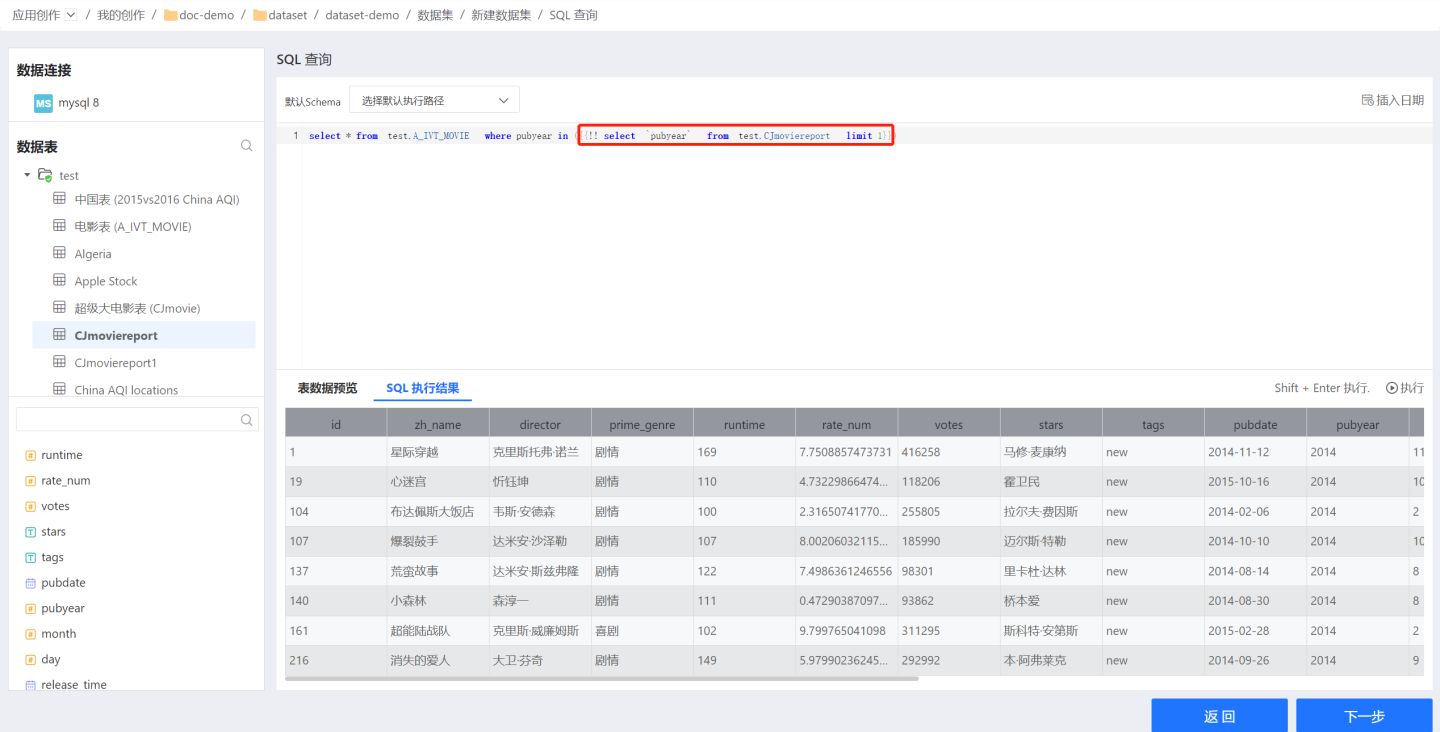
Tip
- The code within dynamic macros must return a value of type String or number, and it can only contain one field and one value; otherwise, an exception will be thrown.
- The processing order for SQL datasets is to first perform parameter and user attribute replacement, followed by the parsing and execution of dynamic macros.
Dynamic Macro Usage Example
Dynamic macros treat the incoming macro value as an expression for calculation, and then use the calculated value as the macro value for input. This approach can be applied in SQL functions where expression calculations are not possible.
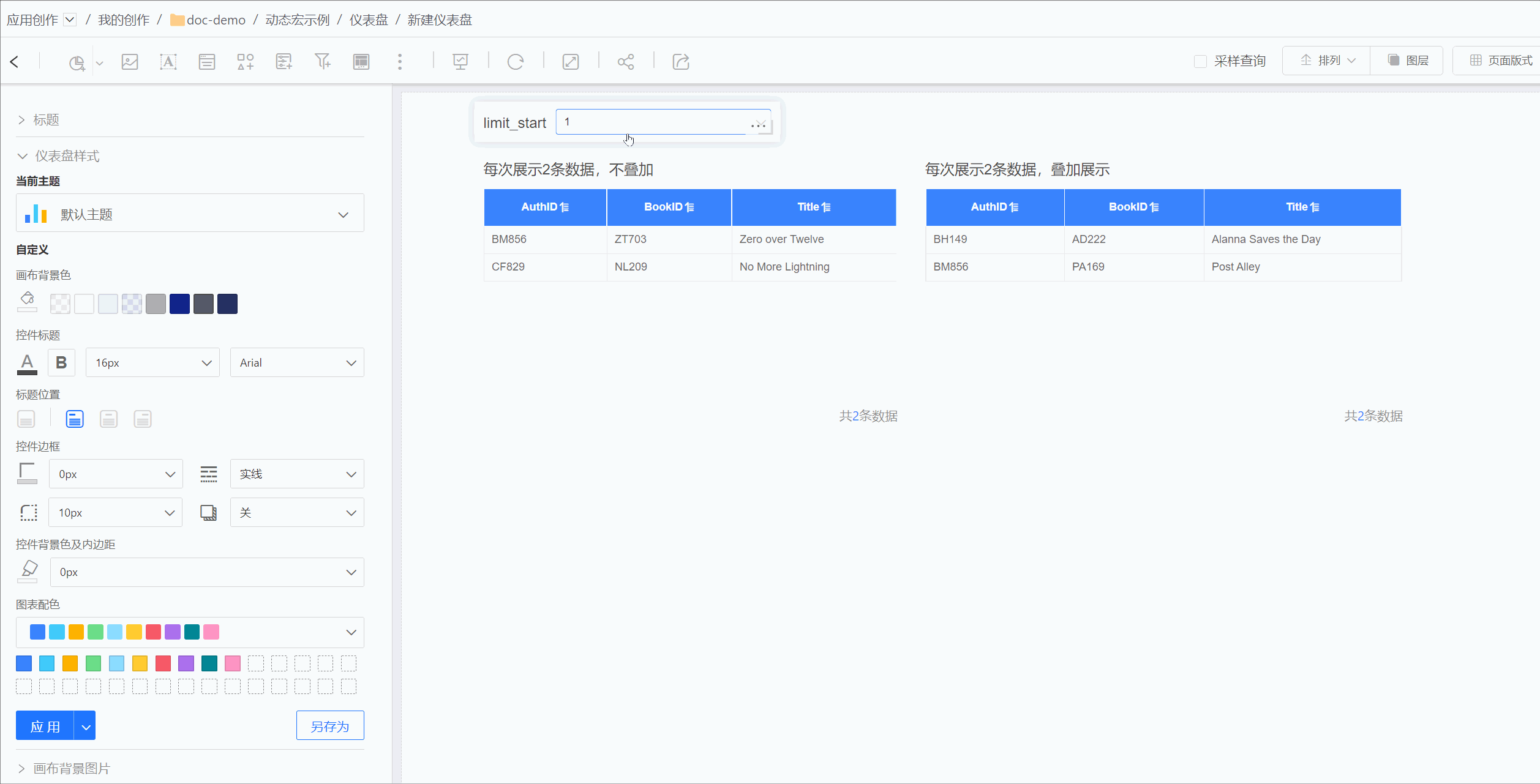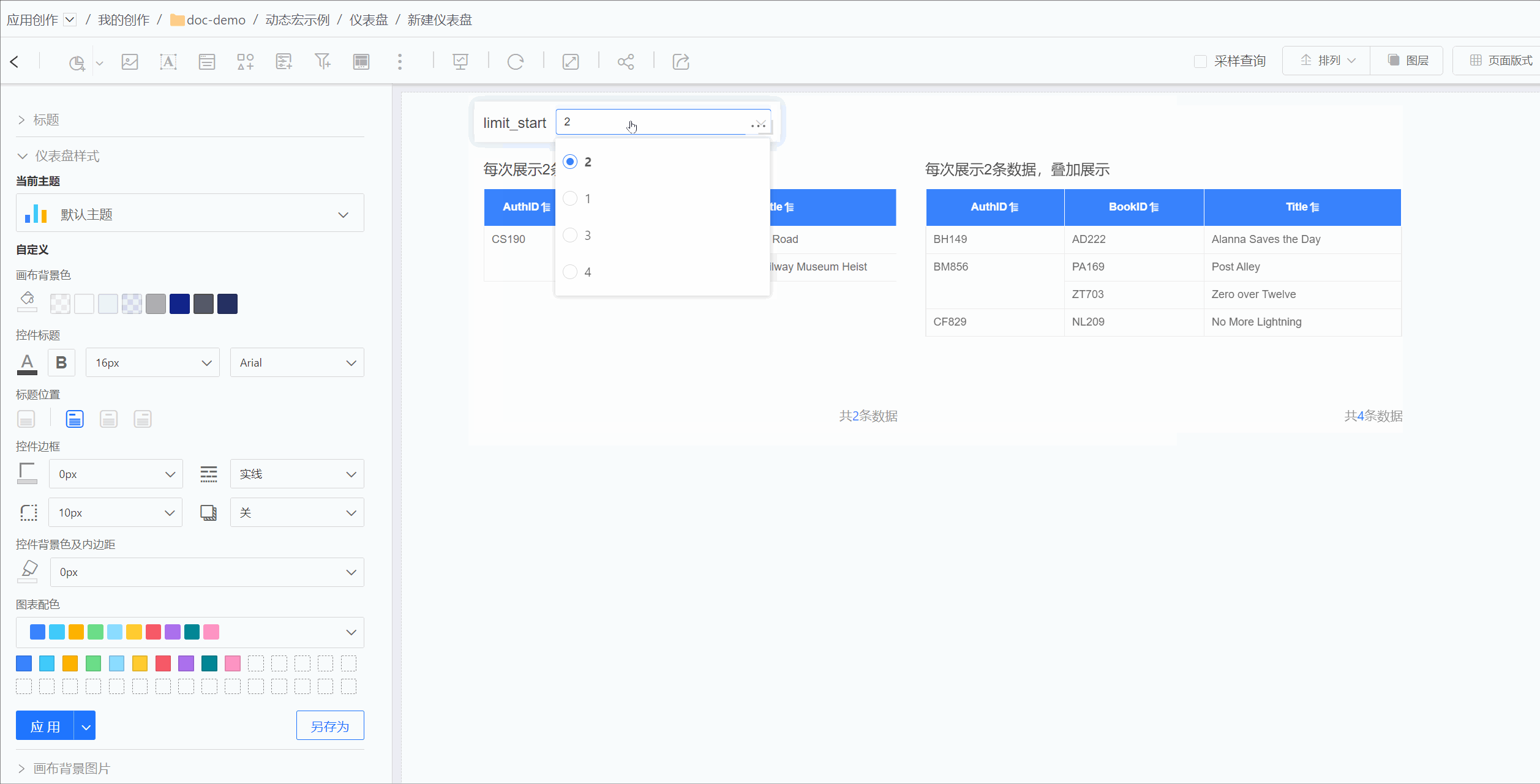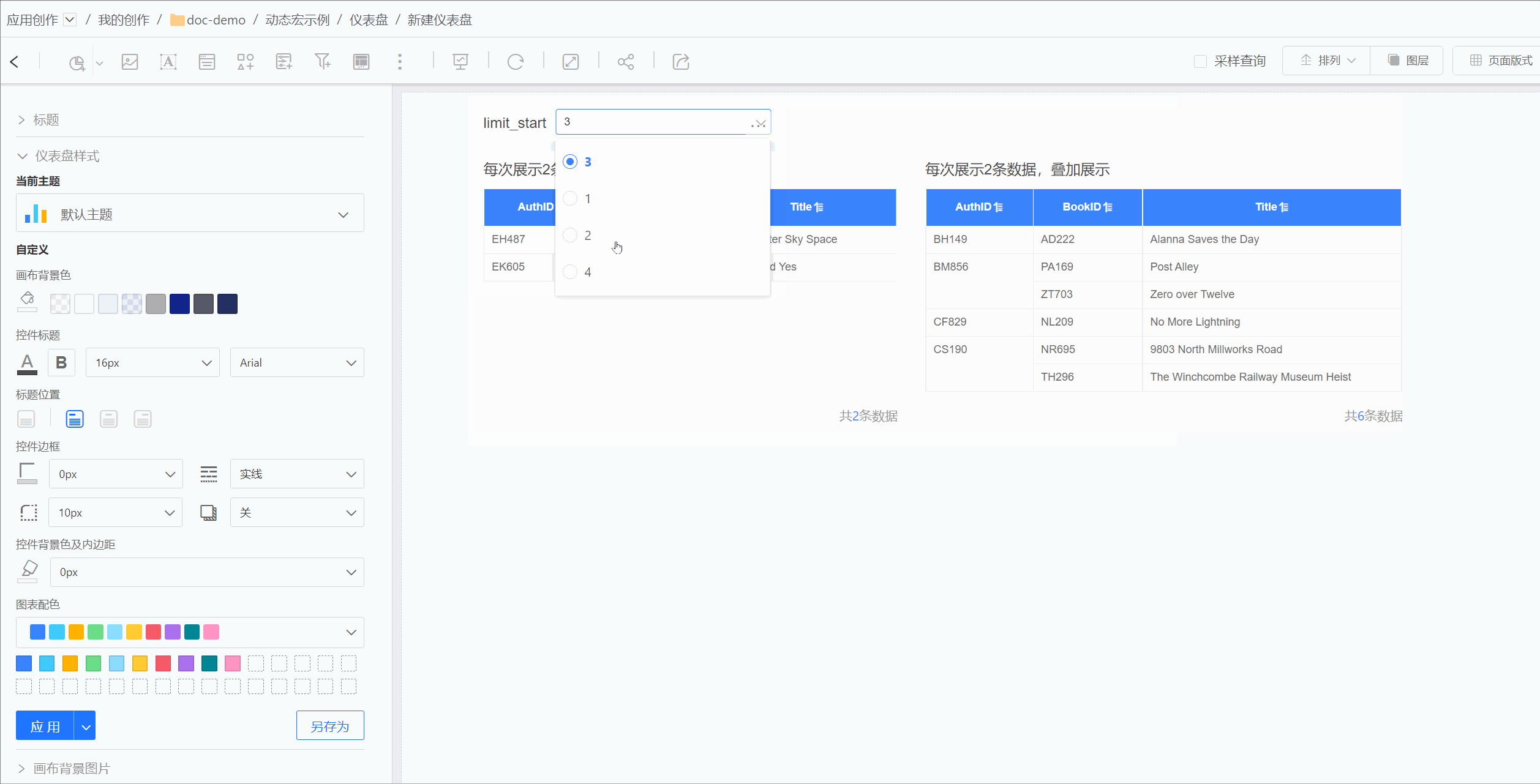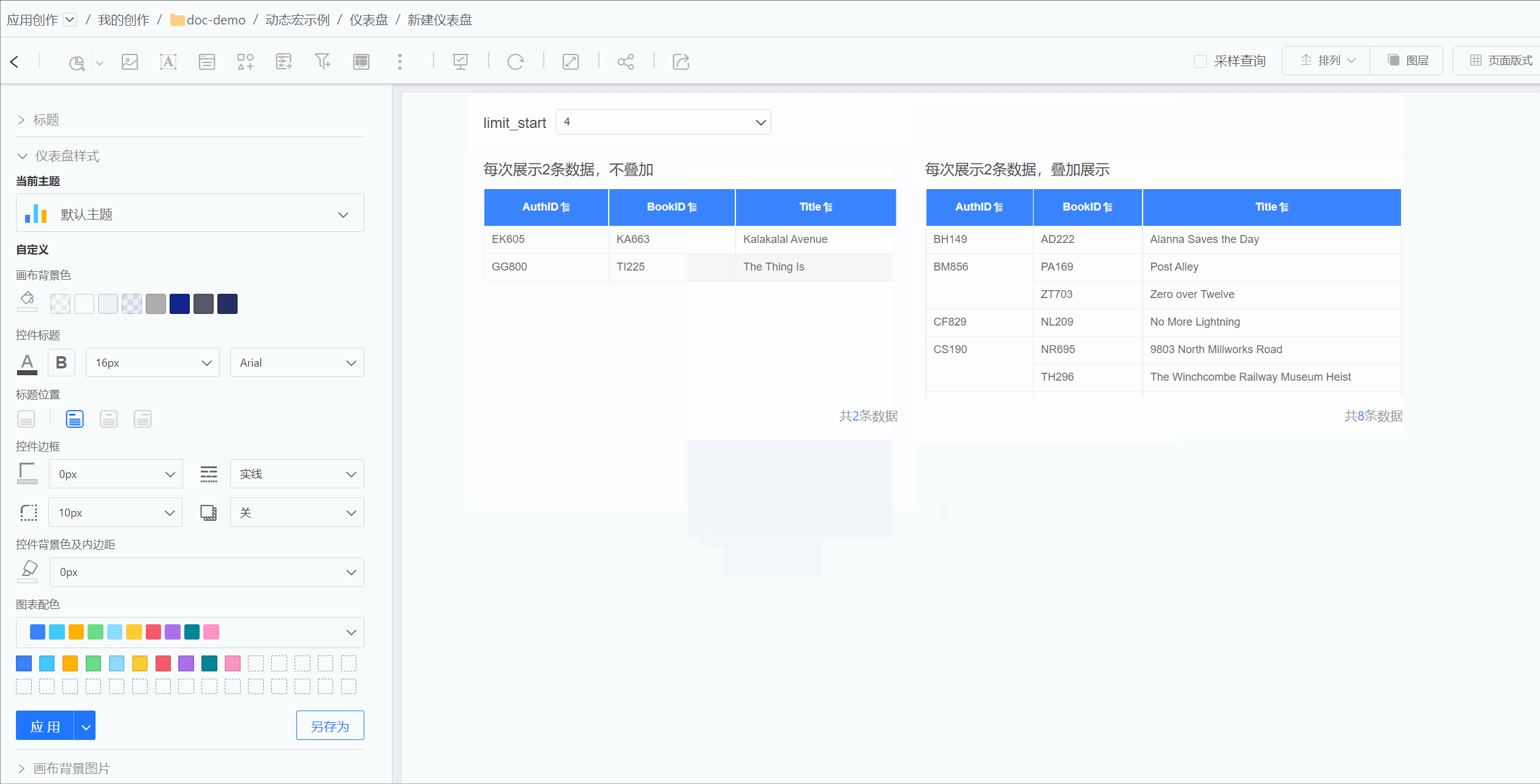
For example, in MySQL data sources, the limit function cannot perform expression calculations. For the requirement to retrieve two rows of data each time with select * from table1 limit n*2,2, the limit function cannot achieve this directly. In such cases, dynamic macros can be used to implement this functionality.
When creating a dataset, the starting position for retrieval can be dynamically changed through parameter expressions, retrieving two rows of data each time. 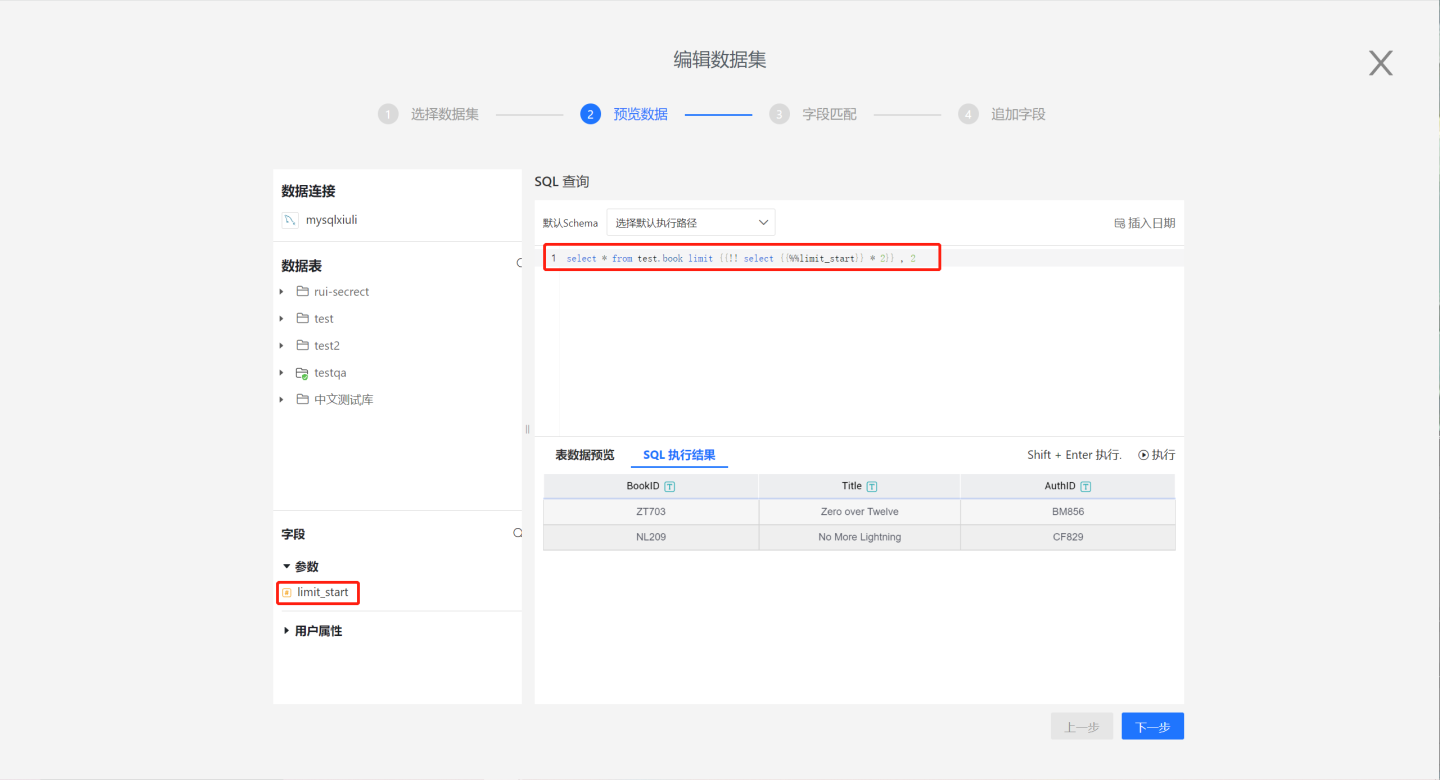
The effect is shown in the figure below. The table on the left uses dynamic macros to implement limit n*2,2, retrieving two rows of data each time. The table on the right uses dynamic macros to implement limit 0,2*n, retrieving two rows of data each time and displaying them cumulatively. Both tables dynamically control the retrieval content through the same parameter.