Acceleration Engine
The system is equipped with a high-speed MPP engine, enabling ad-hoc analysis of data at the billion-row scale. It also allows for the unified storage and modeling of heterogeneous data, followed by associative computations.
When the acceleration engine is enabled for a dataset, the dataset's data will be imported into the engine. Queries on the dataset will then directly access the engine table.
Tip
Currently, it is not recommended to import large-scale data into the engine for big data sources such as Hive, Spark, Impala, Presto, and Max Compute. The import process for large datasets does not support streaming replication, which can consume a significant amount of memory and potentially cause system crashes. While these data sources are allowed to enable the engine for the convenience of importing small tables, this does not imply that we recommend large-scale imports into the engine, as this is not considered best practice. It is advised to use datasets from these data sources via direct connection. Our support for direct connections is now almost on par with the engine.
Enable Acceleration Engine
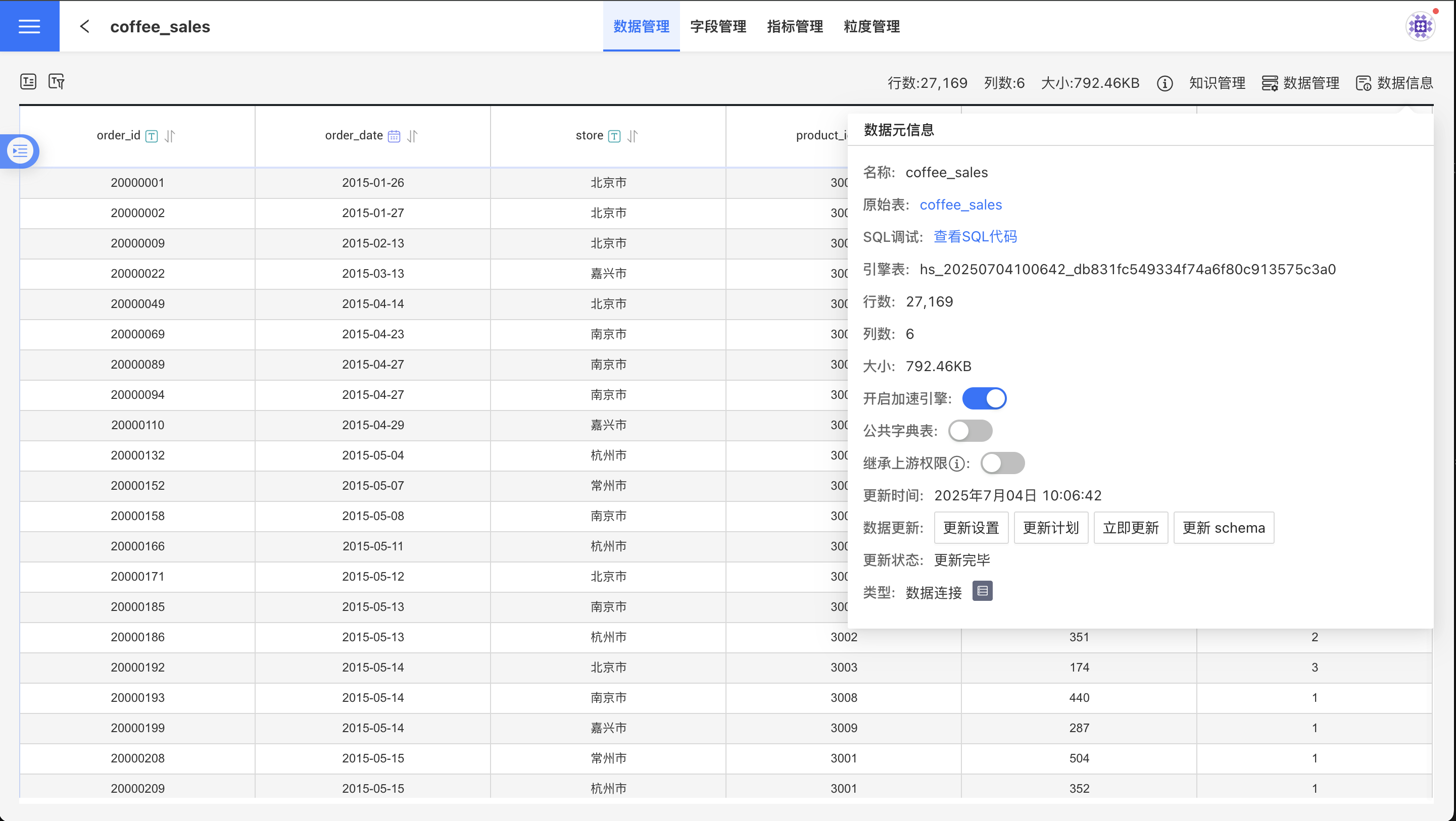
Click the Data Source Information menu to open the Data Element Information window. Enable the Acceleration Engine, and the system will prompt "Please wait, data extraction in progress...". At this point, the system will extract the dataset into the engine.
Once completed, the engine table name will be displayed in the metadata, as shown in the figure:
Note
The acceleration engine cannot be enabled if the dataset size exceeds the system's configured Dataset Cache Size.
Turn Off Acceleration Engine
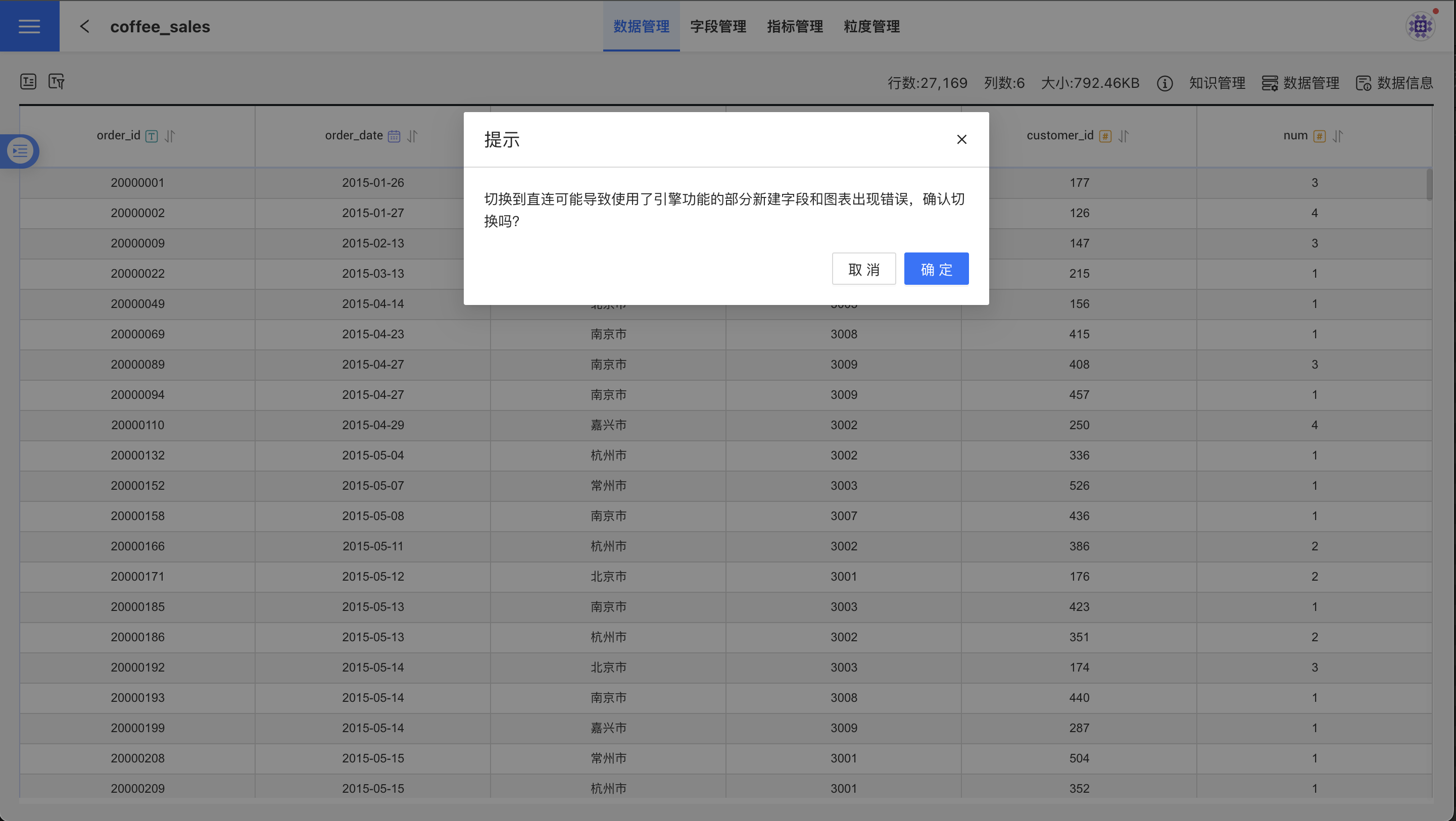
In the Data Metadata window, turn off Enable Acceleration Engine. After turning off the acceleration engine, the dataset will revert to direct connection mode with the original table. At this point, if new fields use functions supported by the engine but not supported by the original database, the dataset will fail to load. If new metrics use functions supported by the engine but not supported by the original data, the chart using these metrics will encounter errors. Therefore, the system will display a confirmation window as shown below. Click confirm to turn off the acceleration engine:
Update Plan
In the Update Plan, you can set the synchronization frequency between the engine table and the original dataset table.
For more details, see Update Plan.
Features Supported Only After Enabling the Acceleration Engine
- Non-homogeneous Dataset Multi-table Union
- Functions Not Supported by Certain Direct Connection Datasets: All functions listed in the engine support documentation are supported. Functions not supported by other data sources require importing into the engine for support.
Acceleration Engine Types and Related Data Sources
The system supports the use of built-in engines and external engines.
- The built-in engine refers to the acceleration engine provided by the system, including three types: Greenplum, StarRocks, and Apache Doris, with Greenplum as the default. Users can change the type of built-in engine during system installation.
- The external engine refers to users using their own data sources as acceleration engines. Currently, the data sources that support enabling acceleration engines include: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Greenplum, Oracle, SQL Server, Spark SQL, TiDB, Amazon Redshift, MaxCompute PostgreSQL, DB2, Hive, Cloudera Impala, Presto, MongoDB, HBase, ClickHouse.
ClickHouse Materialized View
When the system's acceleration engine is ClickHouse, the Multi-Table Joined Dataset can use ClickHouse Materialized Views when imported into the engine. These materialized views enable real-time updates to the dataset without the need to set update schedules, thereby improving the query performance of associated data.
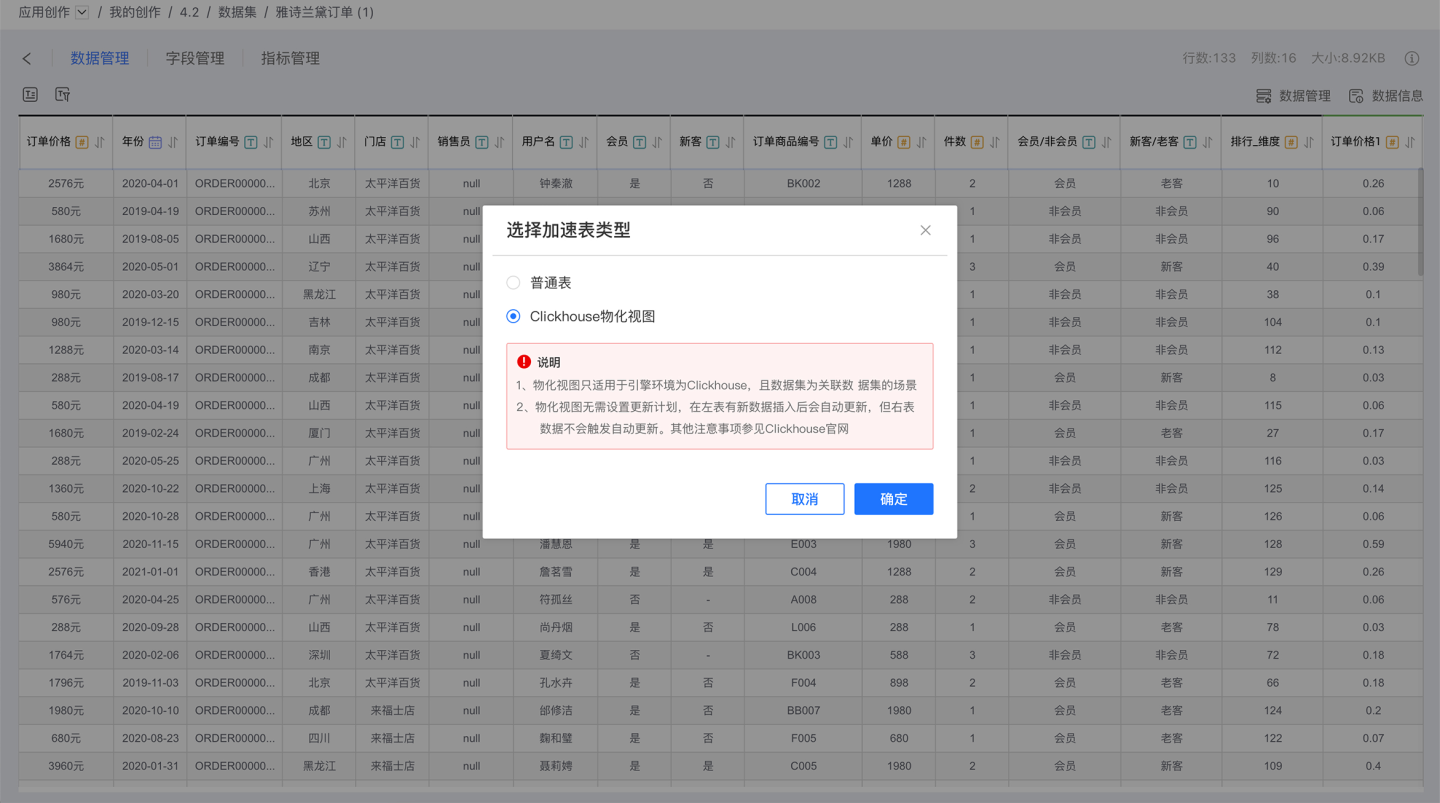
Using ClickHouse Materialized Views requires that the data source of the multi-table joined dataset must be ClickHouse and must be in the same cluster as the engine. Due to the implementation mechanism of ClickHouse, only updates to the left table will trigger the view for data updates. For more details, please refer to the ClickHouse Official Documentation.