API Data Source
When users use EXT API as data source, you can integrate the data into the HENGSHI SENSE system through the API data source. The API data source defines a unified data access specification, supporting a large number of API data sources without data computing capabilities. In addition to built-in multiple API data sources, it also supports user-defined development methods to add enterprise internal API data sources or other public API data sources, enabling quick access to API data sources. The API data source easily achieves rapid growth from 1 to N in accessing external API data, enhancing the data integration capabilities of HENGSHI SENSE.

Built-in API Data Sources
Mingdao Cloud Data Source
Users can connect application data on Mingdao Cloud to the HENGSHI SENSE system through simple configuration. The configuration steps are as follows:
Select API Data Source in the new data connection.

Enter the new connection name, and choose
mingdaoyunas API name.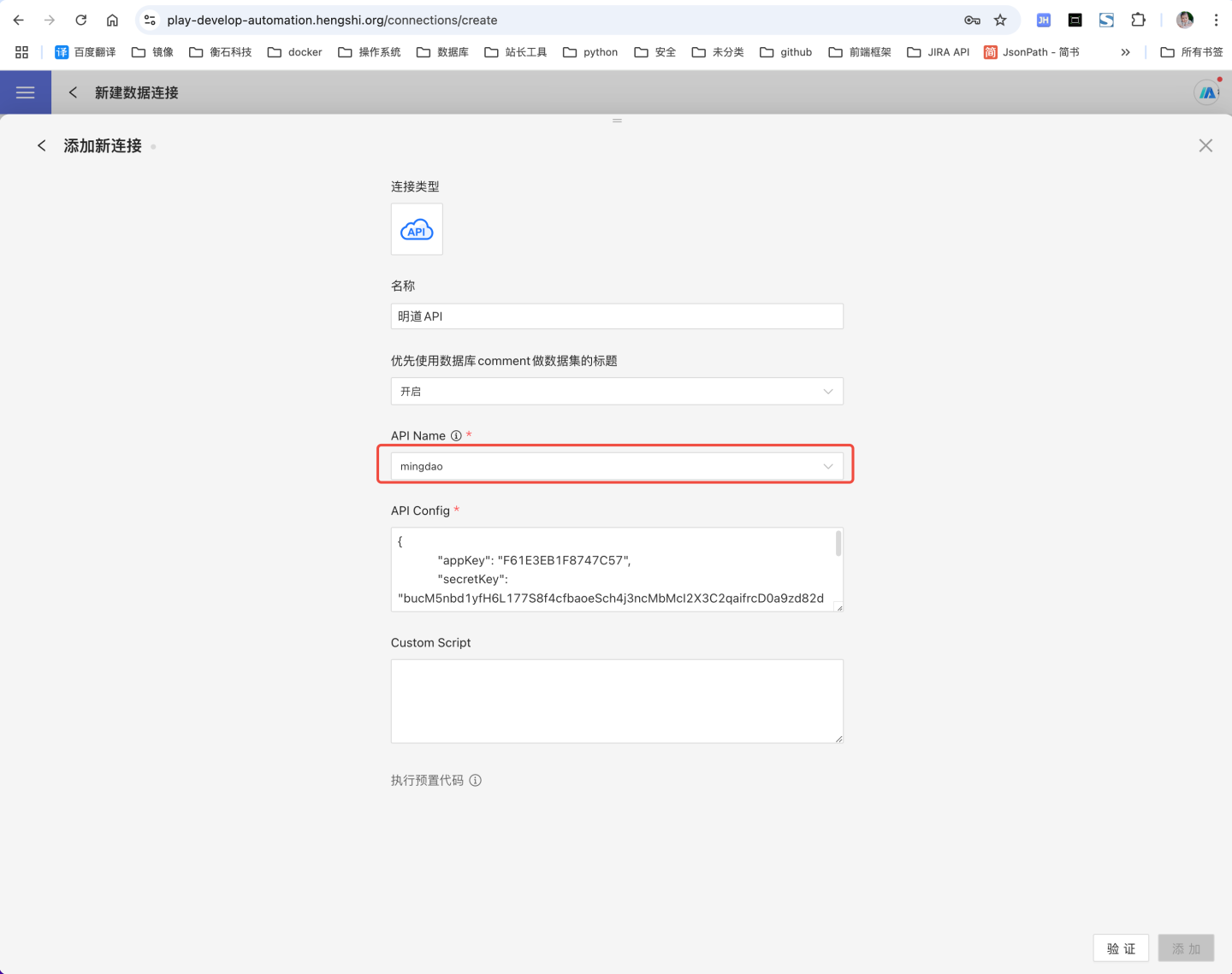
Fill in the Mingdao Cloud
API Config,such as:json{ "appKey":"ab1a55baxxxxxxxx", "secretKey":"68b7eqbp7r1p5ZeAbw60aXcG0h8G354qfB4xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "sign":"NWRiODkxZmQ0NzljNzcxZDhiMDZjMzE5ZDQzMDFlMWFiNDxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxQ==", "apiUrl": "https://api.mingdao.com/v2/open" }API Configof Mingdao Cloudfield Required Description appKey Y The appKey of an app in Mingdao Cloud. secretKey Y The secretKey of an app in Mingdao Cloud. sign Y The sign of an app in Mingdao Cloud. apiUrl N For private deployment, fill in the private deployment address for apiUrl; for public deployment, apiUrl can be left empty or filled with the default address. After successful verification, click save, and the data connection is created. You can view and use the data in Mingdao Cloud in the system.
FTP Data Source
The system supports FTP data sources, allowing simple configuration in HENGSHI SENSE to read files from a specified path on ftp. The configuration steps are as follows.
Select API Data Source in the new data connection.

Enter the new connection name, choose
ftpas API name, such as: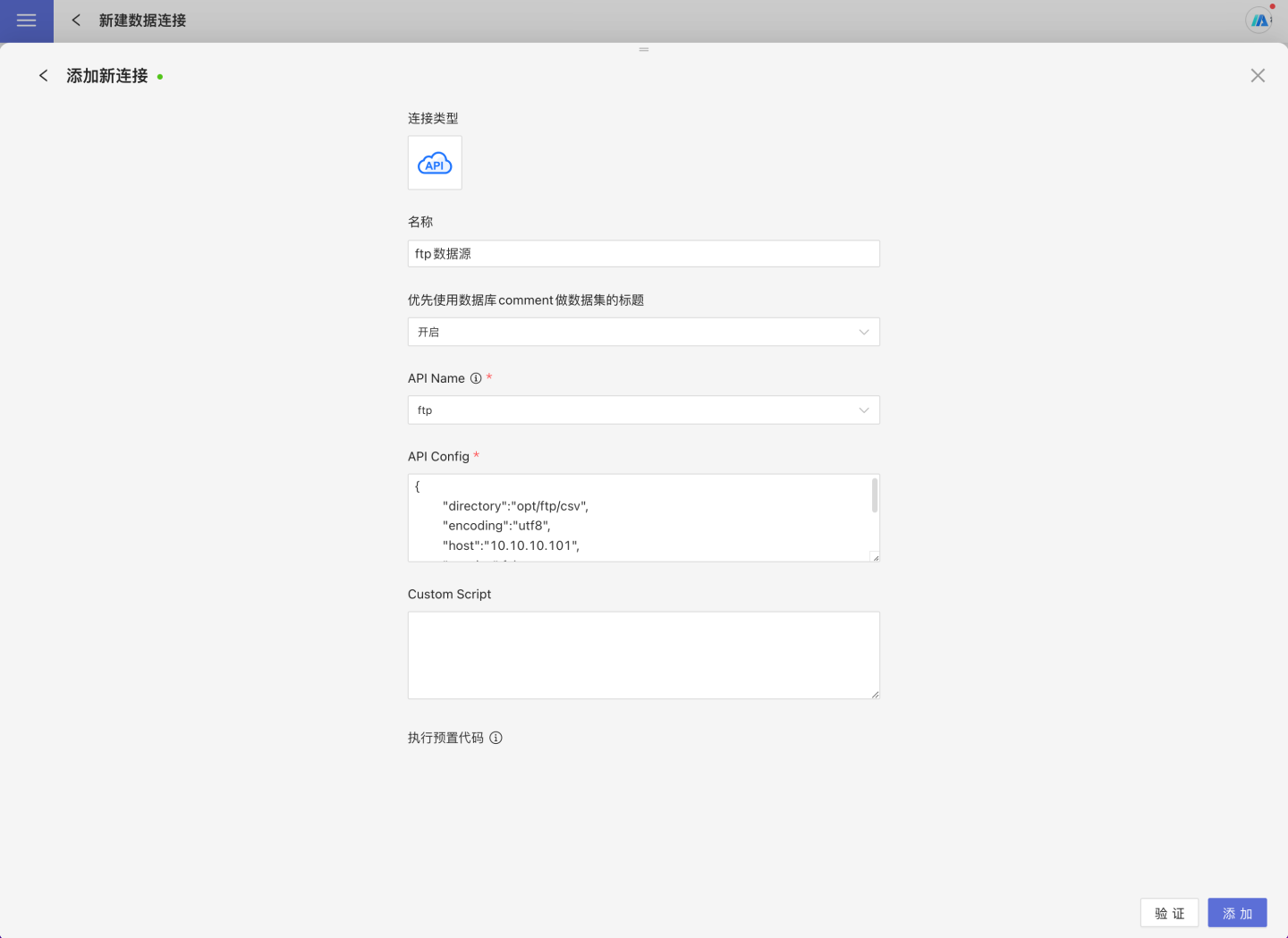
Fill in the FTP configuration information in
API Config,such as:json{ "host":"10.10.x.y", "username":"anonymous", "password":"anonymous", "directory":"/", "encoding":"utf8", "passive":true, }
API Config of FTP
| field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| host | Y | The host of ftp server |
| username | Y | username of ftp |
| password | Y | password of ftp |
| directory | Y | The directory of ftp server which you want to scan. |
| encoding | N | The encoding when connected to ftp |
| passive | N |
- After successful verification, click save, and the data connection is created. You can view and use the connected data in the system.
Tip
The FTP data source can only parse csv and excel files into table format; other types of files are not supported.
Other Built-in API Data Sources
In addition to FTP and Mingdao Cloud, the system also supports S3, 旺店通, 企业微信, 石墨文档,聚水潭, 易仓科技, Wai Qin, and other API data sources. After configuring the API config, users can integrate the data into the HENGSHI SENSE system.
API Config examples
Here are API Config examples for supported API data sources.
Example of API Config for S3
{
"access_key_id": "AKIAWBC5HCDHELXXXXXXXX",
"secret_key_id": "67U4ZvclZxkqiM9oxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"region": "cn-north-x",
"useVirtualFolderDelimiter": false,
"bucket": "",
"path": ""
}Example of API Config for 旺店通
{
"appsecret": "3a5737fcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"sid": "xxxxxxxx",
"appkey": "xxxxxxxx-ot",
"env": "production",
"customizedStartTime": "2022-01-01 00:00:00",
"addHSTimeColumn": true,
"tableConfig": {
"/stockin_order_query.php": {
"timeWindow": 60,
"timeWindowLimit": 50
}
}
}Example of API Config for 企业微信
{
"corpid": "wwcXXXXXXXXXX",
"corpsecret": "XGGBxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"customizedStartTime": "2022-09-01 00:00:00",
"addHSTimeColumn": false,
"templates": [
"ZLyhvnbAYmJnwLXyyxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx1",
"ZLyhvnbAYmJnwLXyyxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2"
]
}Example of API Config for 石墨文档
{
"sid": "s%3A7db3e9d7bab34969a6d592xxxxxxxxxxxx.hnmK3aq2yOYYJB9exxxxxxx",
"addHSTimeColumn": true,
"customCacheMaxLifetime": 5
}Example of API Config for 聚水潭
{
"app_key": "b0b7d1db226d4216xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"app_secret": "99c4cef262f34ca88xxxxxxxxxxxx",
"access_token": "b7e3b1e24e174593xxxxxxxxxxx",
"env": "test",
"customizedStartTime": "2022-11-15 00:00:00",
"addHSTimeColumn": true,
"tableConfig": {
"/open/orders/single/query": {
"timeWindow": 30,
"timeWindowLimit": 3
}
}
}Example of API Config for 易仓科技
{
"app_key": "e4bd91dcxxxxxxxx",
"service_id": "xxxxxxxx",
"secret_key": "bab4d5xxxxxxxx"
}Example of API Config for Wai Qin
{
"openId": "76776371xxxxxxxx",
"appKey": "u7To2bdLxxxxxxxx",
"customFormList": [
"74842108646xxxxxxxx1",
"74842108646xxxxxxxx2"
],
"aiProductIdentificationResultQueryStartTime": "2025-01-01 00:00:00"
}Custom API Data Source
In addition to built-in API data sources, the system supports user-defined API data sources by following steps:
Select API Data Source in the new data connection.

Enter the new connection name, choose
customas API name, such as: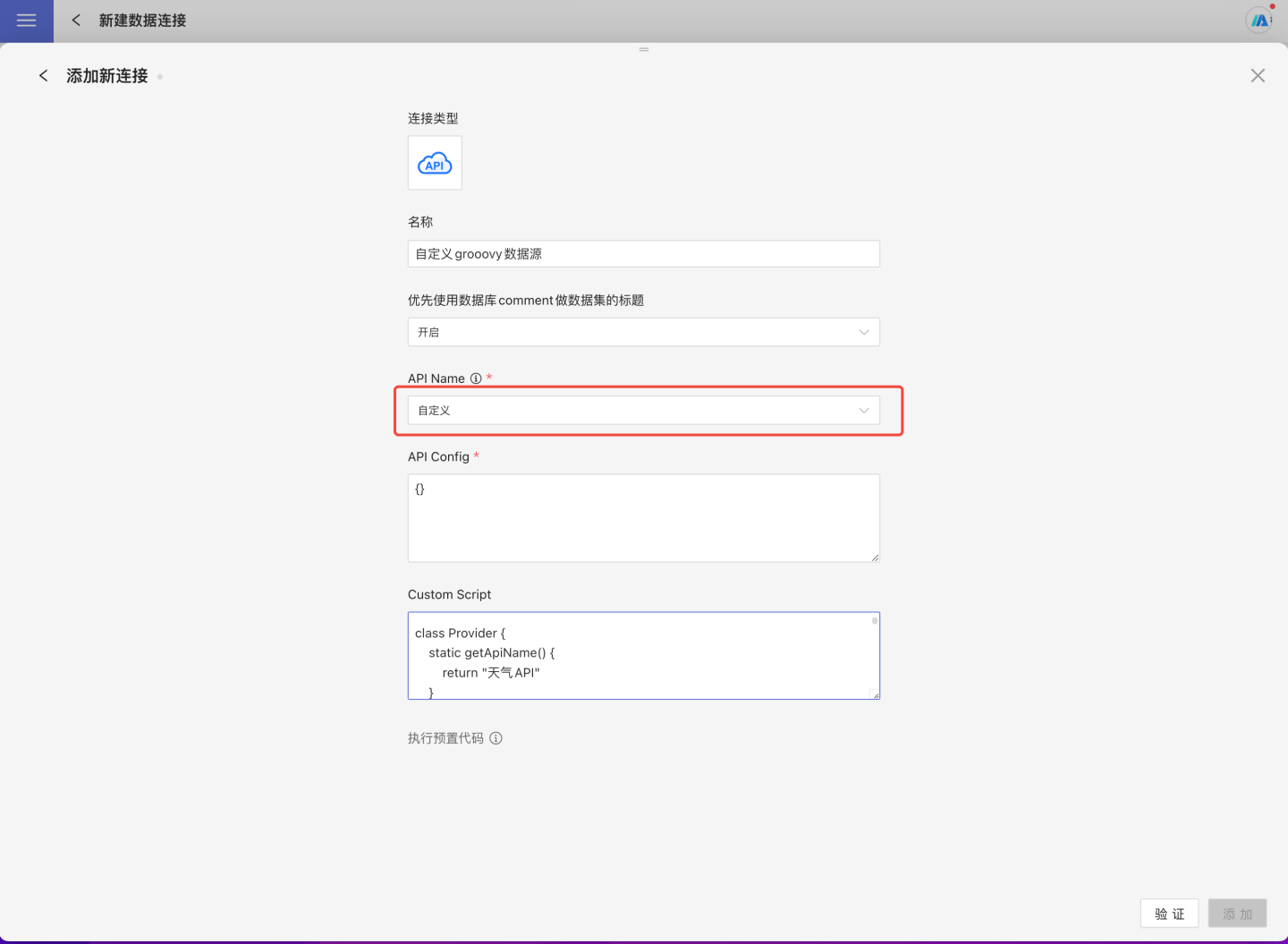
Fill in the
API Config, null as{}Fill groovy code in
Custom Script, such as: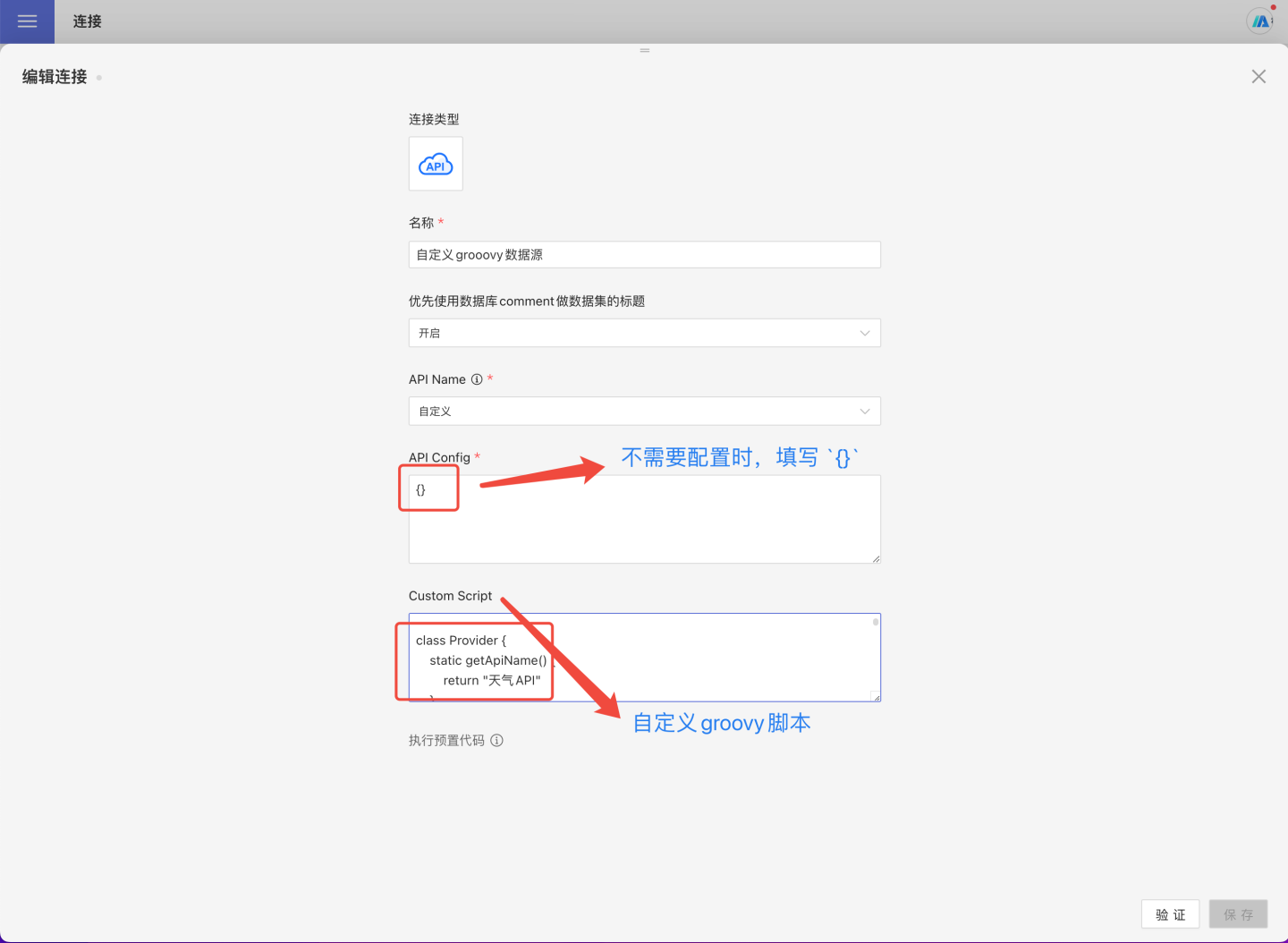
API Data Source Specification
When accessing custom data sources, the following four interfaces need to be implemented in the Groovy script.
- getAPIName: Used to get the API name.
- setOptions: Used to process authentication and authorization-related configuration information.
- fetchPathTables: Used to get the data source directory structure.
- fetchTableData: Used to get the data of the table node.
getAPIName
The function getAPIName outputs the API name. This name will appear in the API Name dropdown selection box on the page. Each API data source name must be unique; otherwise, conflicts will occur. This function is a static class function, and the return value is a string of type string.
static getApiName() {
return "TrivalApiDemo"
}setOptions
The function setOptions is used to save and process authentication and authorization-related configuration information. If it does not involve external network requests, it can be left blank. This function is an object function, and the parameter is a JSON string, which is the information filled in by the user when adding a data connection.
def setOptions(String options) {
if (!options?.trim()) {
return
}
def json = jsonSlurper.parseText(options)
if (json.cityCodeURL?.trim()) {
config.cityCodeURL = JSON.cityCodeURL
}
if (json.weatherURL?.trim()) {
config.weatherURL = JSON.weatherURL
}
}getPathTables
The function getPathTables returns the directory tree, returning the structure of all catalog/schema/table of the data source. The code example is as follows.
def getPathTables() {
def tableTree = [
[pathType: "table", name: "table1", tableType: "table"],
[pathType: "path", name: "schema2", children: [
[pathType: "table", name: "table3", tableType: "view"],
[pathType: "table", name: "table4", tableType: "table", remarks: "Table Alias 4"]
]]
]
return new JsonBuilder(tableTree).toString()
}Structure definition description:
- pathType has two types: table (representing the leaf node table) and path (representing the schema or catalog in the database)
- name is the table name or schema/catalog name
- tableType is only meaningful for table, and its type is generally written as table (the other option is view, which is not commonly used)
- when pathType is path, it means this node is not a table but an intermediate directory structure such as schema or catalog, and it can have a children array node
- remarks is an explanation of the current node, which can be provided when needed and is optional.
Through the above function definition of schema, you can view the following tables in the data connection.
fetchTableData
The function fetchTableData is used to get the data of a leaf node, i.e., the table node. The code example is as follows.
def fetchTableData(List<String> tablePath) {
def tableName = tablePath.last()
def schemaData = [
schema: [
[fieldName: "field1", label: "Field Alias 1", type: "string"],
[fieldName: "field2", label: null, type: "string"],
[fieldName: "field3", type: "number"],
[fieldName: "field4", type: "date"],
[fieldName: "field5", type: "time"]],
data: [
["a", "b", 10, "2022-01-01", "2022-01-01 23:59:59"],
["c", "d", 20.20, "2019-12-39", "2019-12-39 23:59:59"]
]
]
return new JsonBuilder(schemaData).toString()
}Schema structure definition:
- fieldName: Field name, which must be unique within the table to distinguish different fields.
- type: Field type, common types include: string, number, date, time, json, bool.
- label: Field alias.
Data structure definition:
- Each element in data is an array, and the number of elements in the array must be the same as the schema, with data types matching one by one.
Custom API Data Source Groovy Code Example
Here is a weather API custom data source constructed using Groovy. The content of the weather.groovy file is defined as follows.
//Weather.groovy
import com.hengshi.nangaparbat.dto.DatasetResultDto
import com.hengshi.nangaparbat.model.PathTableNode
import static com.hengshi.nangaparbat.model.Dataset.Field
import static com.hengshi.nangaparbat.model.Type.TypeName
import groovy.json.JsonSlurper
class Provider {
static getApiName() {
return "Weather API"
}
def setOptions(String options) {
if (!options?.trim()) {
return
}
def json = jsonSlurper.parseText(options)
if (json.cityCodeURL?.trim()) {
config.cityCodeURL = json.cityCodeURL
}
if (json.weatherURL?.trim()) {
config.weatherURL = json.weatherURL
}
}
def getPathTables() {
def txt = config.cityCodeURL.toURL().text
def arr = jsonSlurper.parseText(txt)
return arr.collect{ obj ->
def node = PathTableNode.createTableNode(obj.city_code)
node.setRemarks(obj.city_name)
return node
}
}
def fetchTableData(List<String> tablePath) {
def url = config.weatherURL + tablePath.last()
def txt = url.toURL().text;
def result = new DatasetResultDto()
def schema = []
def data = []
def row = []
def arr = jsonSlurper.parseText(txt)
arr.data.each{ k, v ->
def field = new Field();
field.setFieldName(k)
field.setType(TypeName.string)
if (k.startsWith("pm")) {
field.setType(TypeName.integer)
}
schema.add(field)
row.add(v);
}
result.setSchema(schema)
data.add(row)
result.setData(data)
return result
}
def jsonSlurper = new JsonSlurper()
def config = [
cityCodeURL: "https://github.com/baichengzhou/weather.api/raw/master/src/main/resources/citycode-2019-08-23.json",
weatherURL: "http://t.weather.itboy.net/api/weather/city/"
]
}Code explanation:
- DatasetResultDto defines the return result of fetchTableData, which consists of schema and data, written through setData and setSchema.
- PathTableNode defines the return of getPathTables, which consists of pathType, name, children, and tableType, also written through respective setters.
- The schema consists of multiple Fields, each Field consisting of fieldName, type, and label.
- The type is an enumeration type defined by TypeName.
- The directory structure is defined in CityCode.
- The Weather Website is the source of weather data, recording weather data for various cities.
Using the above sample code to define the weather API data source, after importing weather.groovy into the system, API data can be obtained.