Data Agent Debugging
The Agent mode implements intelligent agent capabilities through the OpenAI Agents SDK. To create agents that meet user expectations and align with the company's actual scenarios, we have made the prompts for various stages of the agent available for customization. System administrators can adjust the fundamental behavior of the Data Agent. By modifying these instruction texts, the Agent can better understand business contexts, use terminology familiar to users, or change its response style.
Note
Instructions directly affect the agent's behavior, so proceed with caution.
Core Instructions for the Agent
These are the fundamental behavioral guidelines for the Agent, defining its role and response style. You can modify these to make the Agent more focused on specific business areas (such as sales analysis, financial reporting, etc.), adjust its tone (more professional/more friendly), or even add explanations for company-specific business terminology.
BI Engineer Instructions
This is the core instruction to make the Agent a professional BI Engineer, guiding it on how to create and edit visual dashboards. Here, you can define a complete methodology for dashboard design, such as: which chart types to choose for different business scenarios (bar charts for sales, line charts for trends), dashboard layout standards (key metrics at the top, detailed data at the bottom), color schemes, and visual styles. The visualization needs vary greatly across industries; the retail industry may focus on sales funnels and inventory boards, while the financial industry emphasizes risk indicators and compliance reports. By adjusting these instructions, the Agent can build dashboards according to the best practices of your industry.
Resource Search Instructions
Additional instructions used when the Agent searches for available datasets and fields. You can specify which datasets to prioritize, how to handle field aliases, or exclude certain less commonly used resources to help the Agent find data related to the user's query more efficiently.
Value Set Query Instructions
Additional instructions used when the Agent queries the optional values of a field (e.g., product categories, region lists, etc.). You can specify which values to prioritize, how to handle synonyms (e.g., 'Beijing' and 'Capital'), or set limits on the number of returned values to help the Agent better understand the user's filtering intent.
HQL Execution Instructions
Additional instructions for data queries executed by the Agent. Here, you can set default data limit counts, specify mandatory filter conditions (e.g., only query data from the past year), or define special data processing rules to ensure that the query results meet your analysis requirements.
Industry and Private Domain Instructions
Here, you can provide the Agent with industry background knowledge and company-specific information to help it better understand your business needs. You can add explanations of industry terminology, introductions to company culture, common business processes, and other content to enable the Agent to provide more practical advice and analysis by incorporating this background knowledge when answering questions.
Tip
This instruction is the same as the User System Prompt in Workflow.
Create Custom Tools
Data Agent extends its capabilities in a modular way through "Tools." As long as the target system provides accessible HTTP/HTTPS interfaces (REST, GraphQL, HTTP-based RPC, etc.), it can be integrated: internal knowledge bases, full-text/vector search, internal microservices, third-party SaaS/platform APIs, search engines, RPA services... This means that the Agent can not only understand and respond but also "invoke" your external/internal systems in real-time to retrieve or write data, forming a powerful capability boundary.
Tool Parameter Definition
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | Yes | Defaults to the function name (e.g., get_weather). |
| include | No | An array of regular expressions indicating that this tool is only available on pages matching the conditions. |
| exclude | No | An array of regular expressions indicating that this tool is not available on pages matching the conditions. |
| description | Yes | A clear, human-readable description provided to the LLM. |
| parameters | Yes | Can be a Zod schema or a raw JSON schema object. Using Zod parameters will automatically enable strict mode. |
| execute | Yes | (args, context) => string |
Example: Integrating Agent with Enterprise Knowledge Base, External APIs, etc.
Below is an example of integrating Tavily Web Search to demonstrate how to register a search-type Tool in "System Settings → Global JS":
// Ensure the Agent runtime environment has injected createTool
if (typeof window.heisenberg?.createTool === 'function') {
const apiKey = '<tavily_api_key>'; // It is recommended to use a proxy service for management instead of hardcoding
window.heisenberg.createTool({
// Tool Name: English + underscores for reliable LLM referencing
name: 'web_search',
// Tool Purpose: Helps the model determine when to call it
description: 'Use Tavily to search the latest internet information and return answers with sources',
// Parameters: Fully extensible as needed — any control items you want the LLM to generate/pass can be included
parameters: window.heisenberg.zod.object({
plan: window.heisenberg.zod.string().describe('The purpose and key information extraction for calling this tool'),
query: window.heisenberg.zod.string().describe('Search content/query keywords'),
max_results: window.heisenberg.zod.number().min(1).max(20).default(5).describe('Number of results needed'),
// Additional parameters like language, time_range, site, freshness, etc., can be added
}),
// Execution Logic: Integration is possible as long as HTTP requests can be made (fetch/axios/custom SDKs are all viable)
execute: async (args) => {
try {
const { query, max_results } = args;
const resp = await fetch('https://api.tavily.com/search', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${apiKey}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
max_results,
search_depth: 'basic',
include_answer: true,
include_raw_content: true,
include_images: false,
time_range: null,
}),
});
const data = await resp.json().catch(() => ({}));
if (!resp.ok) {
return `Search failed: ${data?.error || resp.status} ${resp.statusText}`;
}
return `Search Results:\n\n${data.answer || '(No direct answer)'}\n\nSources:\n${JSON.stringify(data.results || [], null, 2)}`;
} catch (err) {
return `Error occurred during search: ${err?.message || String(err)}`;
}
},
});
}After saving and refreshing, the Data Agent can search the internet using this Tool. Similarly, as long as the target capability can be accessed via HTTP requests, it can be encapsulated into a Tool and dynamically invoked by the Agent, enabling rapid expansion to enterprise internal systems or any third-party services.
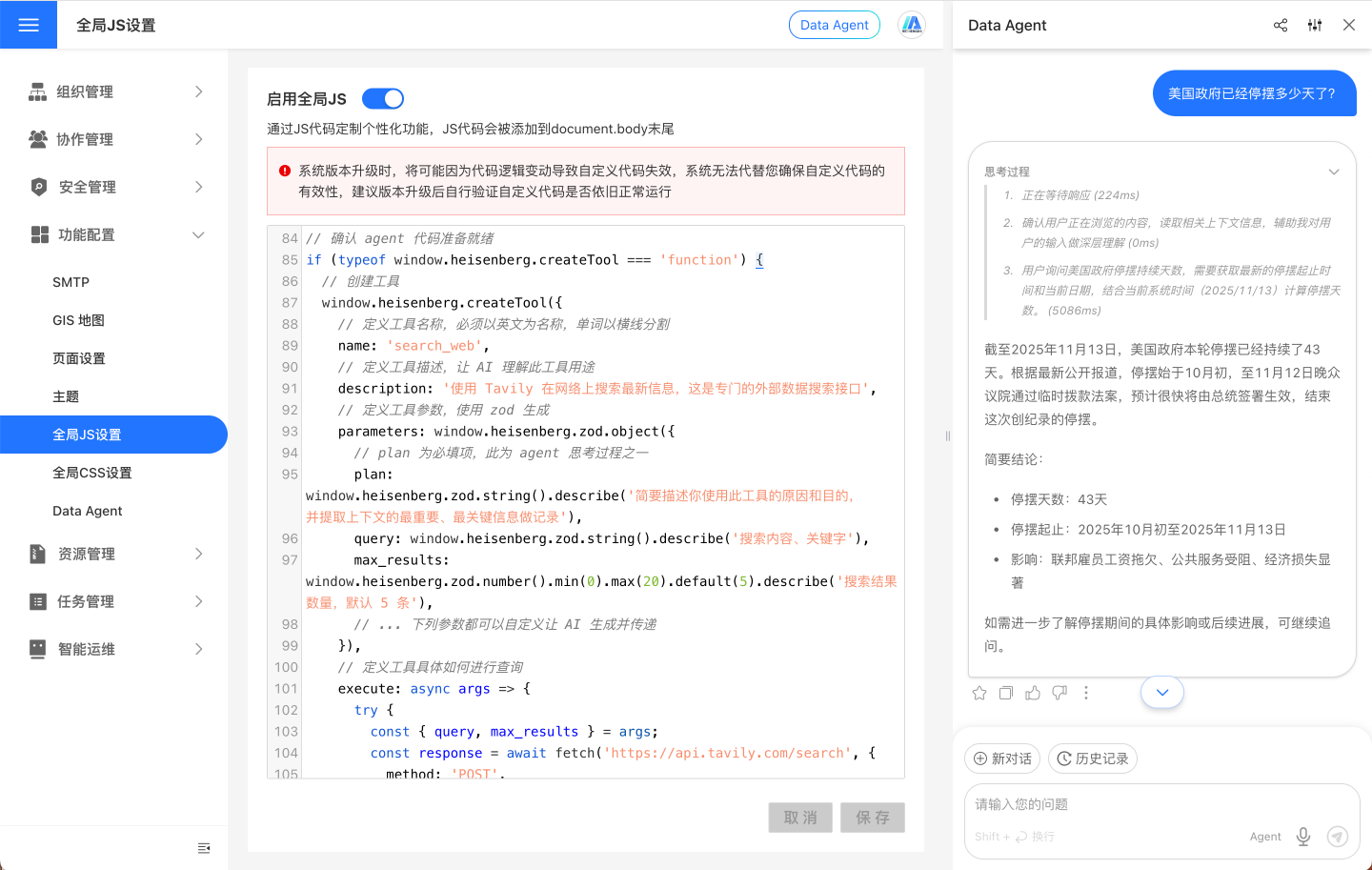
General Integration Recommendations:
- Identity and Security: Prefer using proxy service management to avoid exposing tokens in plain text in Global JS.
- Response Format: Extract the raw response into concise text or structured JSON, then concatenate it into a string to reduce irrelevant noise.
- Minimal Permissions: Implement authentication, IP/rate limiting, and access auditing on the server side to prevent abuse.
- Parameter Design: Expose only necessary and controllable parameters to the LLM to reduce unauthorized or invalid calls.
Tip
- You can register multiple Tools (search, knowledge base retrieval, report generation, process triggering, ticket creation, etc.), and the Agent will autonomously select and combine them in the reasoning chain, forming an evolving "capability surface."
- Tools extended via Global JS are currently only available on the web version and cannot be used in Agent API mode.
How to Use Agent Mode in AI API?
API calls use Workflow mode by default. If you need to use Agent mode, additional environment requirements and configurations are necessary.
Environment Requirements
- Node JS version 22 or above is required. You need to install the Node JS environment on the machine where the HENGSHI SENSE service is located to ensure the service can be invoked. Older systems, such as CentOS7, may not be supported.
Configuration Steps
- In
Settings - Security Management - API Authorization, add an authorization, fill in the name, check thesudofunction, and record theclientId. - In
Model General Configuration, enable theNODE_AGENT_ENABLEparameter. - In
Model General Configuration, set theNODE_AGENT_CLIENT_IDparameter to theclientIdcreated in the previous step.